Uveitis
OCT Features:
The presence of optic disc edema, CME, subretinal fluid, and vitritis are clinical features of uveitis that can be well visualized with OCT. Active sarcoid posterior uveitis can lead to optic disc edema, CME, and subretinal fluid (Fig. 11.3.1). OCT is useful in this setting to monitor for treatment response (Fig. 11.3.2). Sarcoid anterior uveitis can also result in isolated CME, which can sometimes be more readily detected on an OCT thickness map rather than a line scan (Fig. 11.3.3). Pars planitis often leads to associated CME (Fig. 11.3.4), which can respond well to treatment with periocular steroids (Fig. 11.3.5).
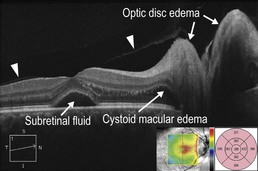
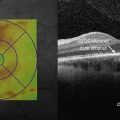
Figure 11.3.1 OCT in a case of sarcoid posterior uveitis. Optic disc edema, cystoid macular edema, and subretinal fluid are present. The posterior hyaloid can be seen (arrowheads). The associated thickness map (inset) artifactually picks up the subretinal fluid as retinal thickness due to an error in the segmentation algorithm, which measures from the retinal pigment epithelium layer instead of the most posterior retina structure.
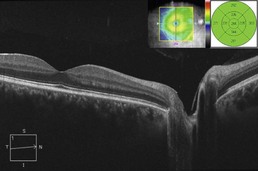
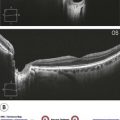
Figure 11.3.2 OCT three months following treatment with oral steroids (corresponding to Figure 11.3.1) shows resolution of the optic disc edema, cystoid macular edema, and subretinal fluid. Due to the segmentation error, the associated thickness map (inset) is useful to monitor improvement over time.
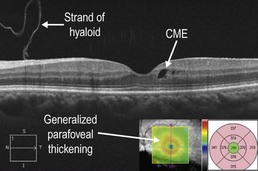
Figure 11.3.3 OCT in a case of sarcoid anterior uveitis shows subtle cystoid macular edema (CME), which was clinically symptomatic. The associated thickness map (inset) shows generalized parafoveal thickening, which gives a better overall sense of the CME than the isolated line scan. There is a strand of hyaloid that is visible, which is not of any clinical significance.
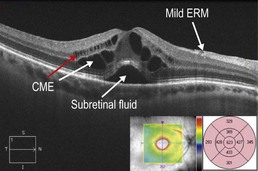
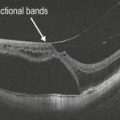
Figure 11.3.4 OCT in a case of pars planitis shows severe CME with associated subretinal fluid. The CME is located within the inner nuclear layer (red arrow) and Henle fiber layer (or axonal outer plexiform layer; white arrow). There is also a mild associated ERM.
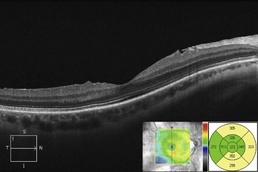
Figure 11.3.5 OCT one month following treatment with sub-Tenons triamcinolone (corresponding to Figure 11.3.4) shows complete resolution of cystoid macular edema and subretinal fluid. The associated thickness map (inset) highlights these changes.