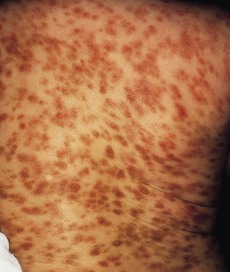
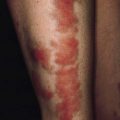
199 Urticaria pigmentosa
Advanced-level questions
What do you know about systemic mastocytosis?
What diagnostic tests would you order?
• Urinary histamine is elevated in most cases (an elevated urinary histamine level is not a required finding for a diagnosis of mastocytosis; there is poor correlation between the urinary histamine content and the severity of symptoms in mastocytosis).
• Serum tryptase is elevated in most cases (the tryptase level is elevated in >83% of patients and is highly specific for this disease).
• Coagulation defects may occur as a result of the release of mast-cell heparin.
• Bone marrow biopsy is often diagnostic (revealing the focal infiltration of mast cells).
• Immunohistochemical analysis with monoclonal antibodies against the mast-cell markers tryptase and CD117 is used to confirm the diagnosis.
How would you manage such patients?
• H1 blocker: for flushing and itch (e.g. chlormethiazole)
• H2 blocker: for gastric and duodenal manifestations (e.g. ranitidine, cimetidine)
• Oral sodium cromoglycate for diarrhoea and abdominal pain
• NSAID for flushing not responsive to antihistamines
• Interferon-alfa has been used for patients with aggressive disease
• Imatinib, an inhibitor of c-Kit tyrosine kinase, also shows promise