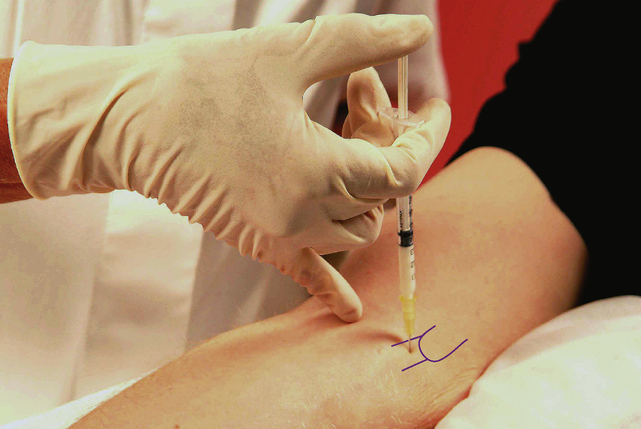
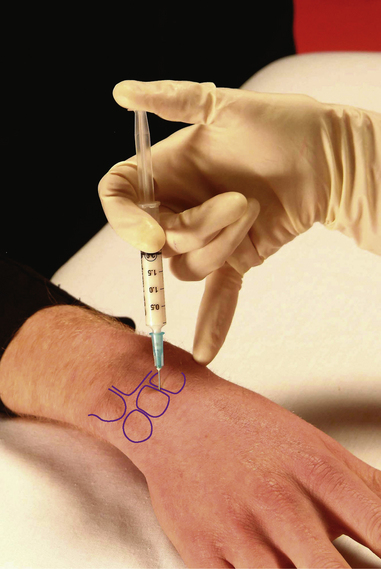
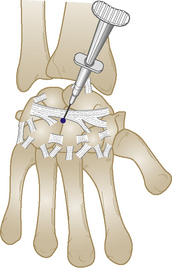
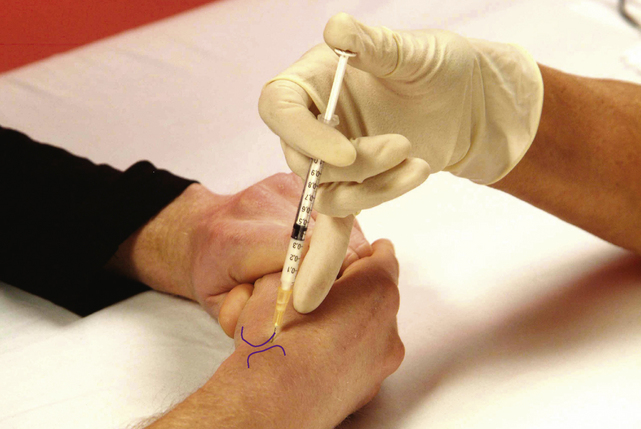
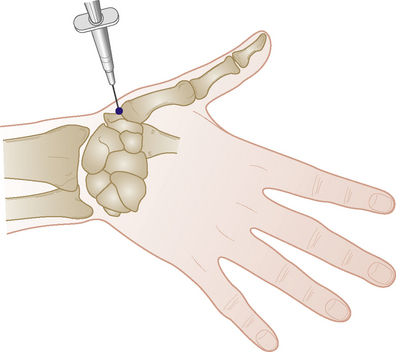
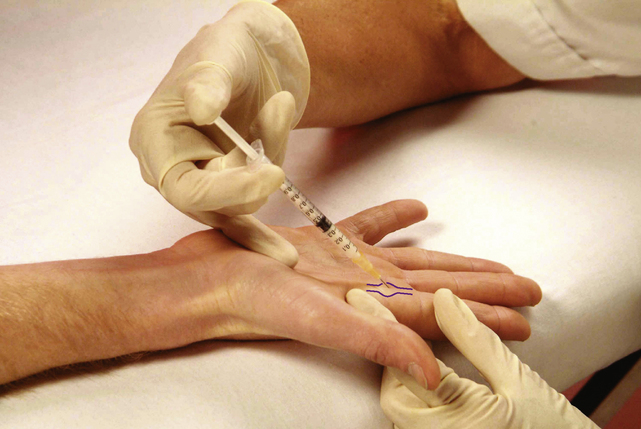
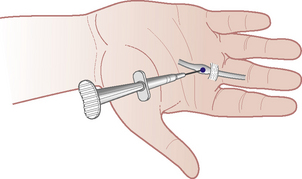
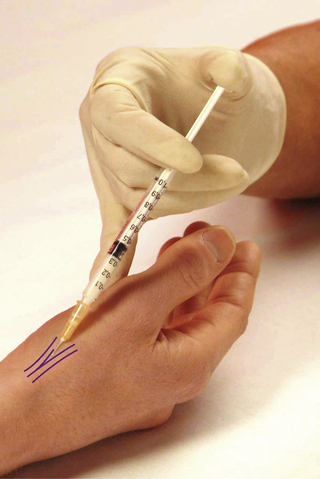
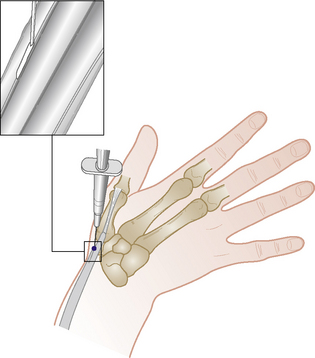
Section 3 Upper Limb Injections
Examination of the upper limb
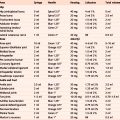
| Shoulder tests | |
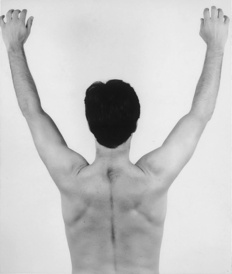
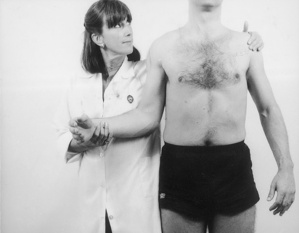
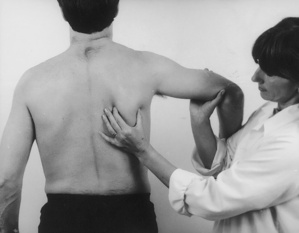
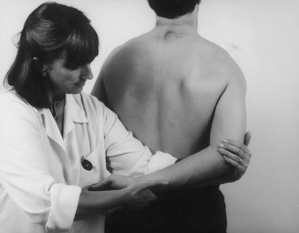
| Active flexion above head | Resisted abduction |
| Passive flexion with overpressure | Resisted lateral rotation |
| Active abduction to ear for painful arc | Resisted medial rotation |
| Passive lateral rotation | Resisted elbow flexion |
| Passive abduction | Resisted elbow extension |
| Passive medial rotation | Resisted adduction |
| Impingement/lag/stability/proprioception tests | |
| Shoulder capsular pattern: most loss of lateral rotation, less of abduction, least of medial rotation | |
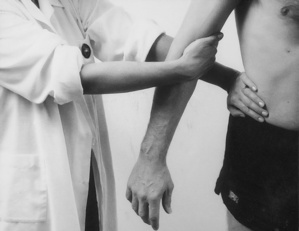
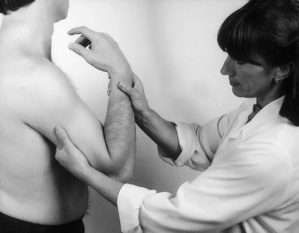
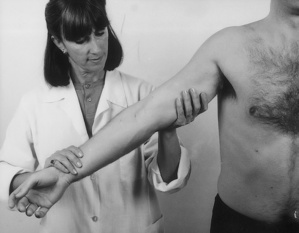
| Elbow tests | |
| Passive flexion | Resisted flexion |
| Passive extension | Resisted extension |
| Passive pronation | Resisted pronation |
| Passive supination | Resisted supination |
| Resisted wrist flexion | |
| Resisted wrist extension | |
| Elbow capsular pattern: more loss of flexion than extension | |
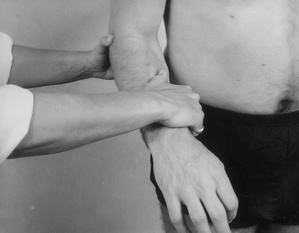
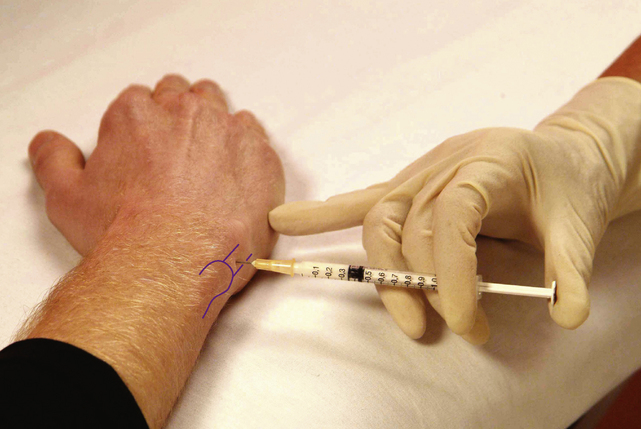
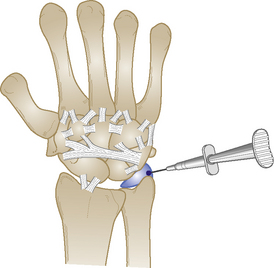
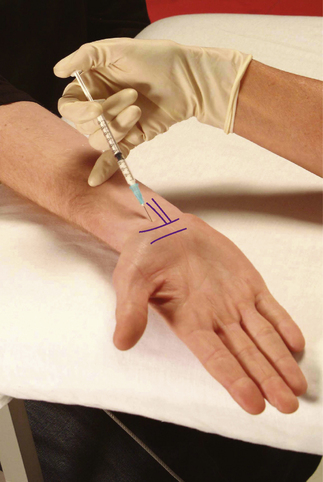
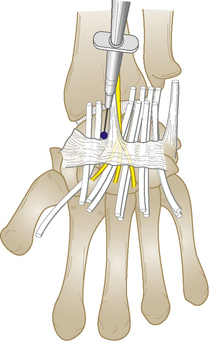
| Wrist tests | |
| Passive pronation | Resisted extension |
| Passive supination | Resisted flexion |
| Passive extension | Resisted radial deviation |
| Passive flexion | Resisted ulnar deviation |
| Passive radial deviation | |
| Passive ulnar deviation | |
| Wrist capsular pattern: equal loss of flexion and extension | |
| Finger tests | |
| Passive thumb extension | Passive finger extension |
| Resisted thumb abduction | Passive finger flexion |
| Resisted thumb adduction | Resisted finger abduction |
| Resisted thumb extension | Resisted finger adduction |
| Resisted thumb flexion | |
| Finger capsular patterns: Loss of: | |
| Thumb: extension & abduction | |
| Metacarpophalangeal joints: extension and radial deviation | |
| Interphalangeal joints: flexion | |
| Distal phalangeal joints: extension | |
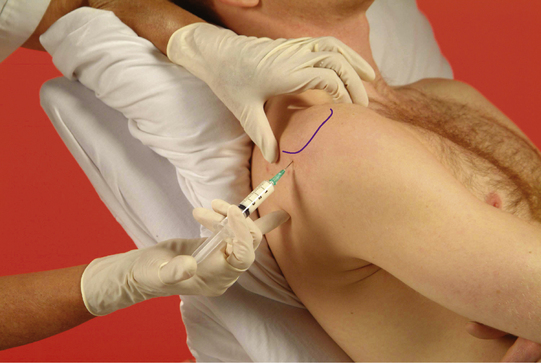
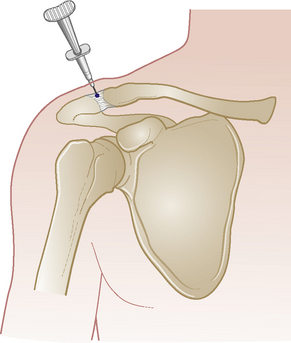
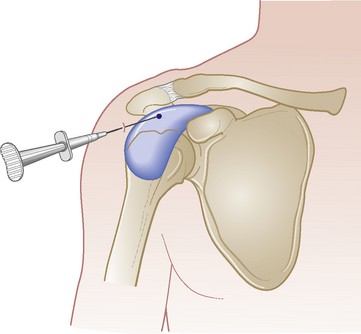
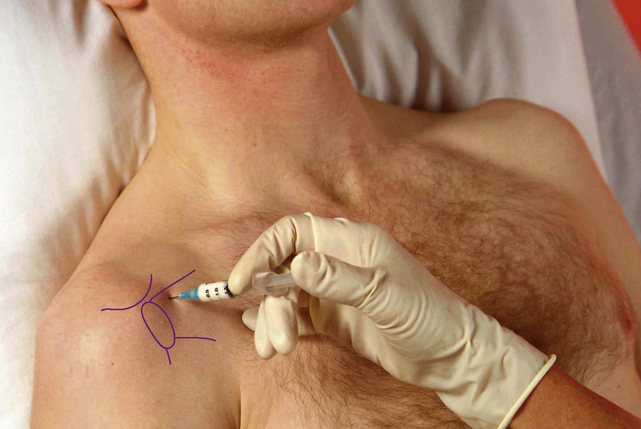
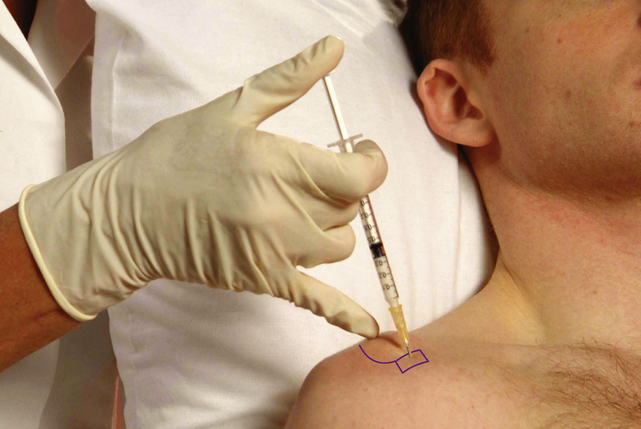
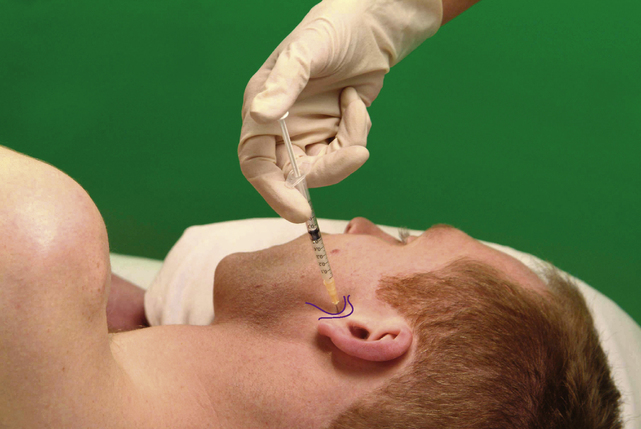
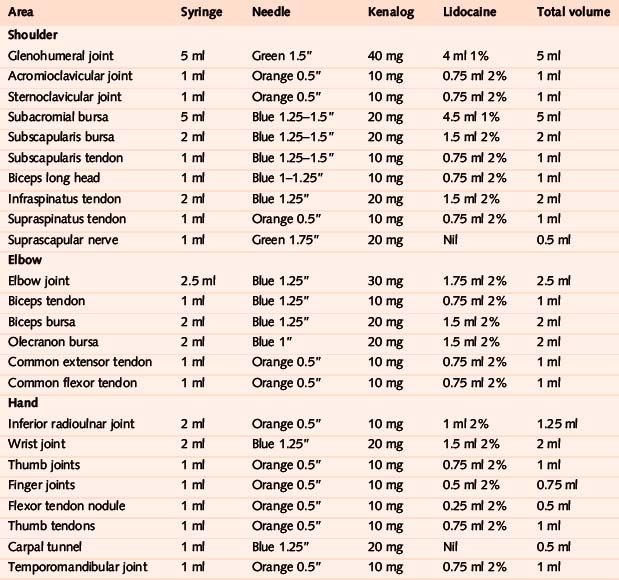
Glenohumeral joint
Acute or chronic capsulitis – ‘frozen shoulder’
Causes and findings
Technique
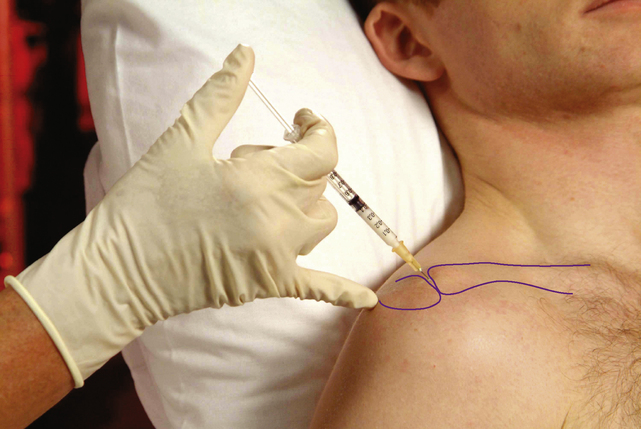
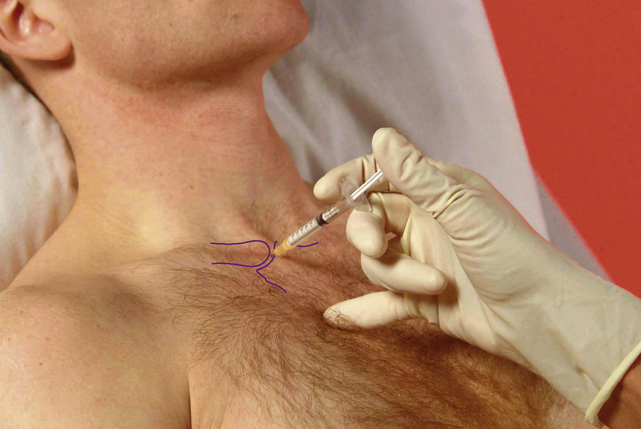
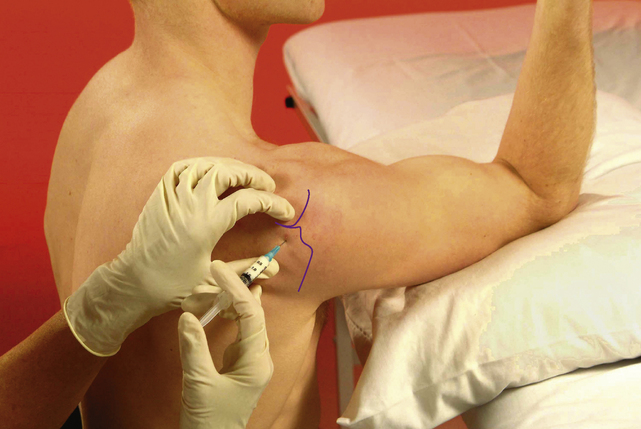
Acromioclavicular joint
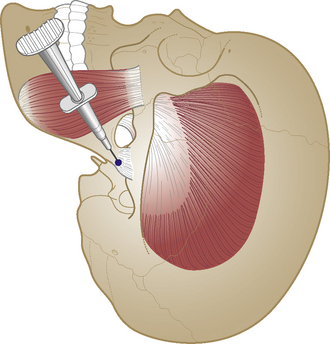
Subacromial bursa
Chronic bursitis
Causes and findings
Comments
In our experience, this is the most common injectable lesion seen in orthopaedic medicine (Appendix 2). Results are usually excellent; relief of pain after one injection is usual but the rehabilitation programme must be maintained. If, rarely, the symptoms persist after two injections, the shoulder should be scanned because a cuff tear might be present. In thin patients, the fluid sometimes causes visible swelling around the edge of the acromion.
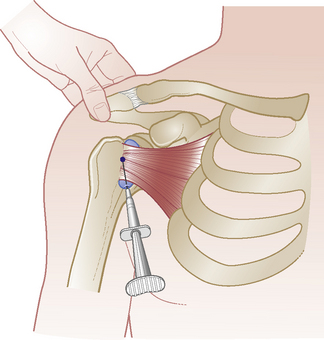
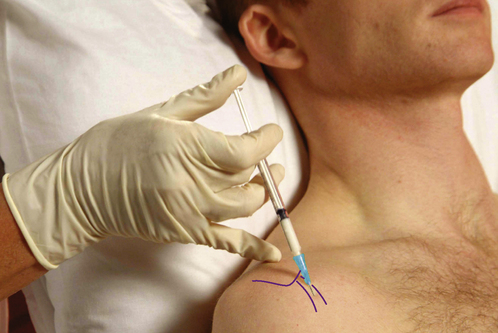
Subscapularis bursa and tendon
Acute or chronic tendinopathy or bursitis
Technique
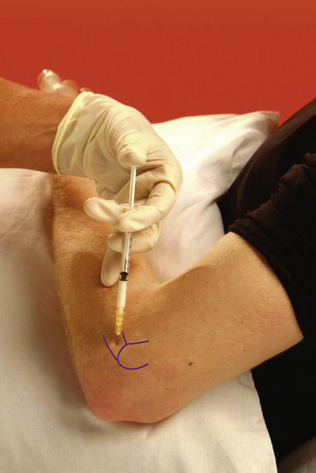
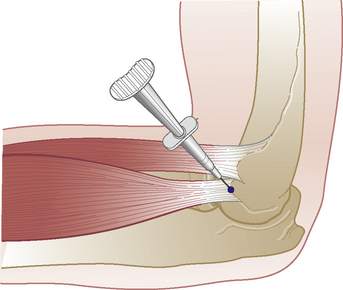
Biceps – long head
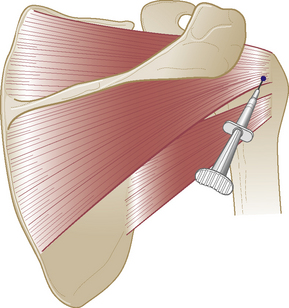
Infraspinatus tendon
Chronic tendinopathy
Technique
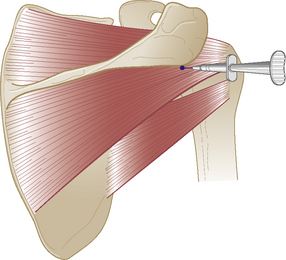
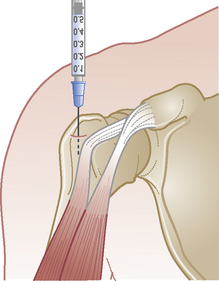
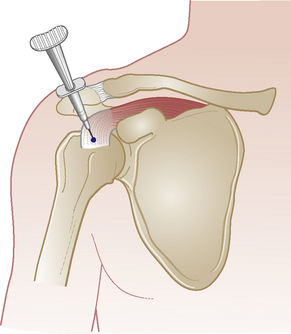
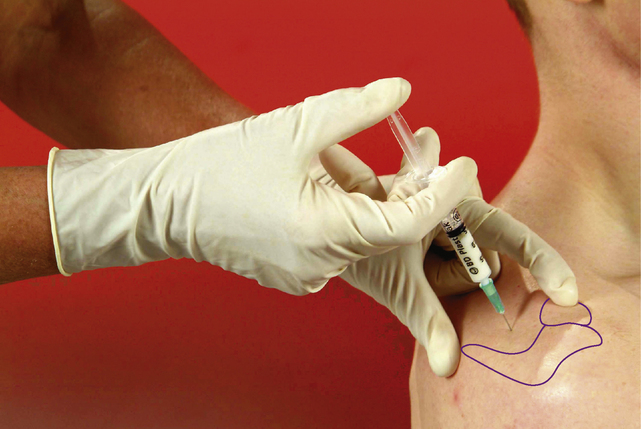
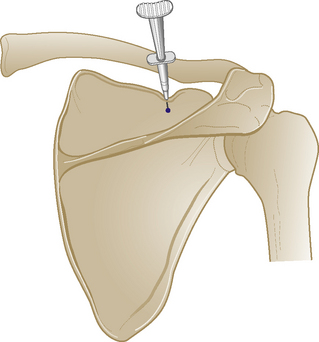
Supraspinatus tendon
Chronic tendinopathy
Technique
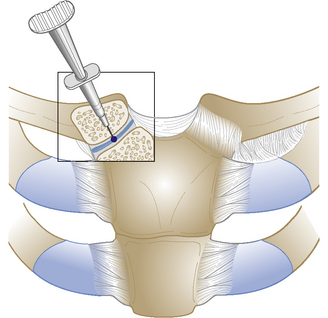
Suprascapular nerve
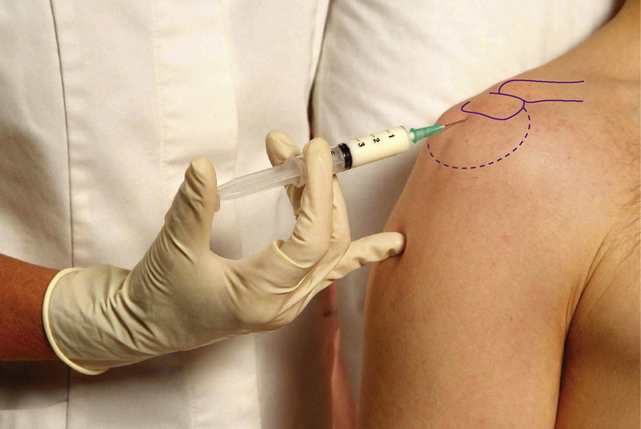
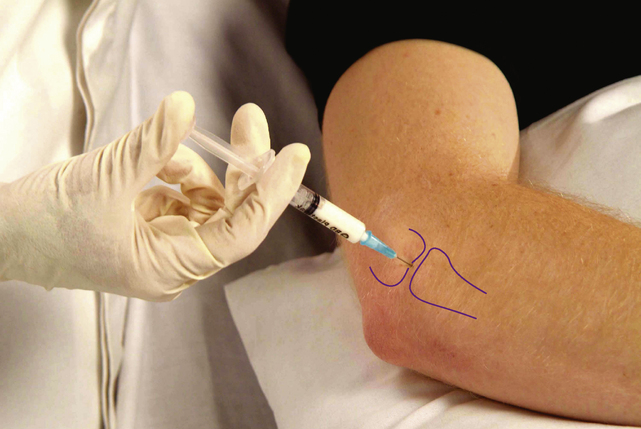
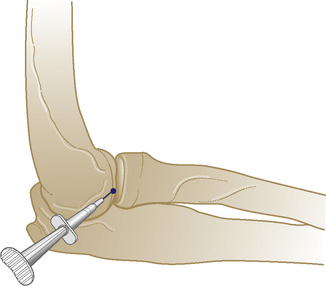
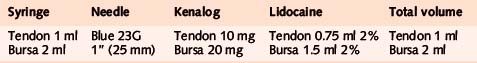
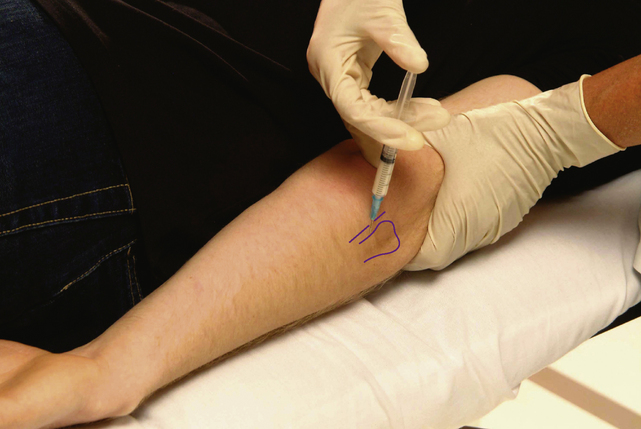
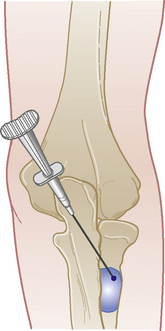
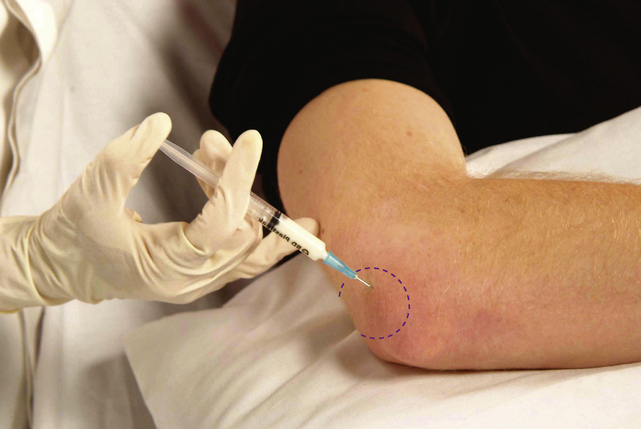
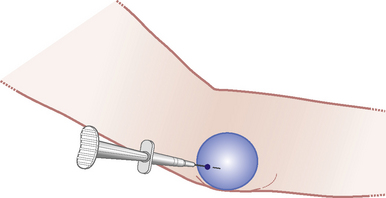
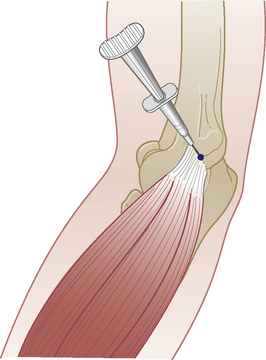
Elbow joint
Acute or chronic capsulitis
Technique
Comments
This is not a very common injection but may be useful after trauma or fracture of the radial head.