Upper Limb (Extremity)
• Technical factors and radiation protection
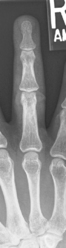
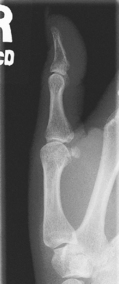
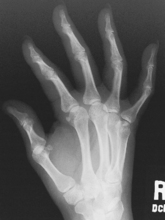
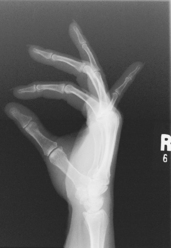
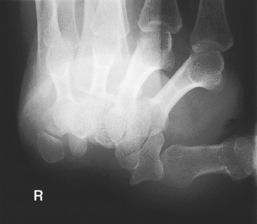
 AP axial thumb and PA hand critique
AP axial thumb and PA hand critique
 PA oblique hand and “fan” lateral hand critique
PA oblique hand and “fan” lateral hand critique
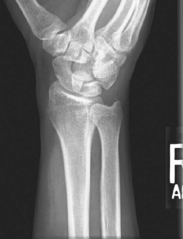
 PA axial ulnar deviation (15° and Modified Stecher) (S)
PA axial ulnar deviation (15° and Modified Stecher) (S)
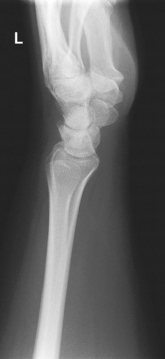
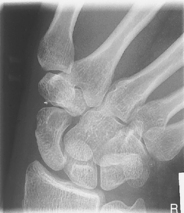
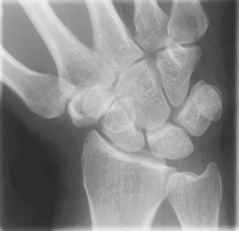
 Scaphoid projections (15° and Modified Stecher) critique
Scaphoid projections (15° and Modified Stecher) critique
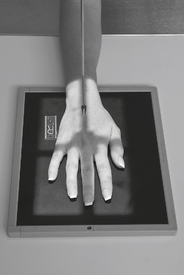
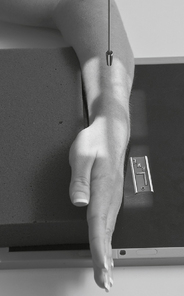
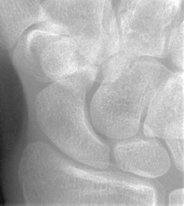
 PA wrist radial deviation critique
PA wrist radial deviation critique
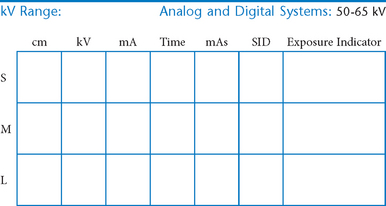
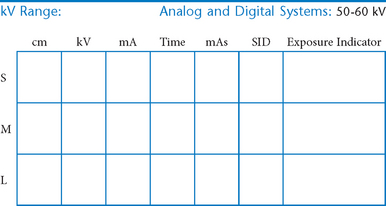
Upper Limb (Extremity)*
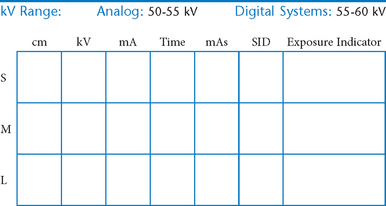
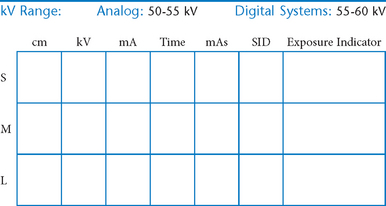
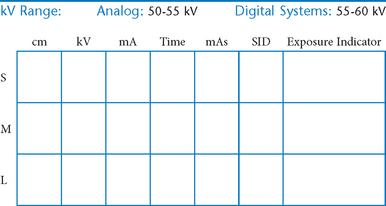
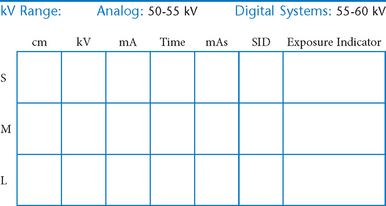
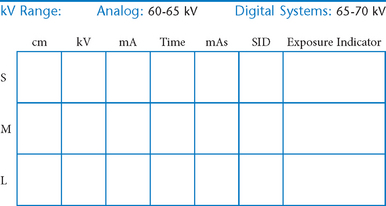
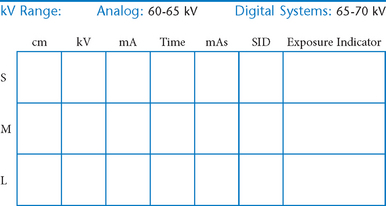
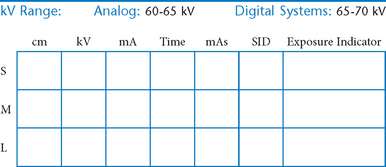
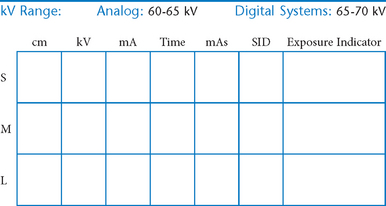
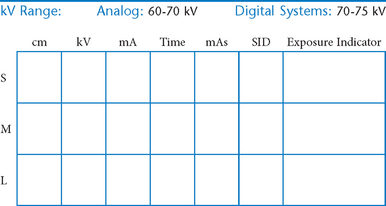
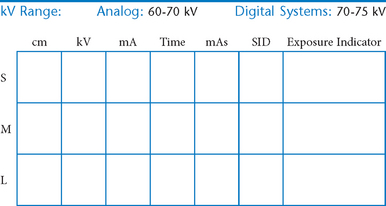
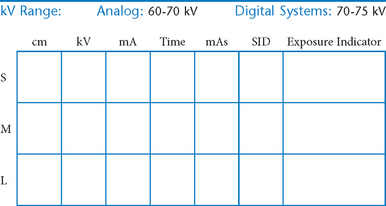
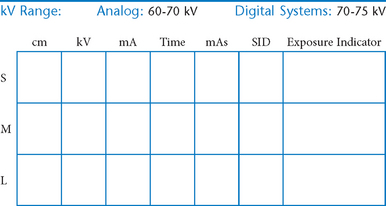
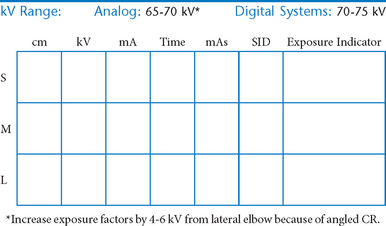
• 40-44″ (102-113 cm) SID, minimum OID
• Nongrid or TT (tabletop), detail (analog) screens
• Digital imaging requires special attention to accurate CR and part centering and close collimation.
• Immobilization (when needed)
• Multiple exposures per imaging plate: Multiple images can be placed on the same IP. When doing so, careful collimation and lead masking must be used to prevent pre-exposure or fogging of other images.
• Grid use with digital systems: Grids generally are not used with analog (film-screen) imaging for body parts measuring 10 cm or less. However, with certain digital systems, the grid may or may not be able to be removed from the receptor. In those cases, it is departmental protocol that determines if a grid is left in place or removed. Important: If a grid is used, the anatomy must be centered to it to avoid grid cutoff.
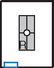
PA Fingers*
PA Oblique Fingers*
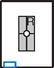
Position
• Patient seated, hand on table, elbow flexed 90° (lead shield over lap)
• Align fingers to long axis of portion of IR being exposed.
• Rotate hand 45° medially or laterally (dependent of digit examined), resting against 45° angle support block.
• Separate fingers; ensure that affected finger(s) is (are) parallel to IR.
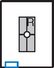
Lateral Fingers*
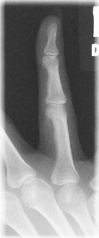
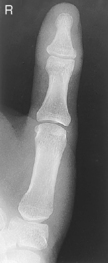
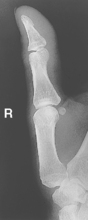
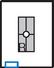
AP Thumb*
PA Oblique Thumb*
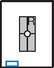
Lateral Thumb*
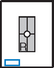
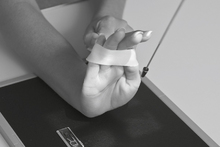
AP Axial Thumb*
Note: This is a special projection to better demonstrate the first carpometacarpal joint region.
Position
• Patient seated or standing, hand rotated internally placing posterior surface of thumb directly on IR
• Align thumb to long axis of portion of IR being exposed.
• Extend fingers and hold back with other hand to prevent superimposing base of thumb and 1st CMC joint region (a key positioning requirement).
PA Hand*
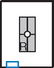
PA Oblique Hand*
Lateral Hand (Fan and Extension Lateral)*
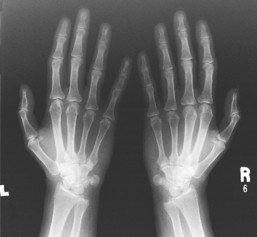
AP Oblique Bilateral Hand*
PA Wrist*
PA Oblique Wrist*
Lateral Wrist*
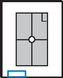
PA Axial Wrist—UInar Deviation and Modified Stecher (Scaphoid)*
Note: See p. 26, 8th ed textbook for joint movement terminology.
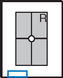
PA Axial Scaphoid (Ulnar Deviation with 15° and Modified Stecher)
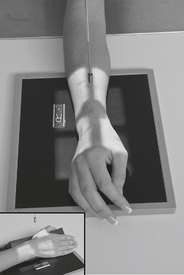
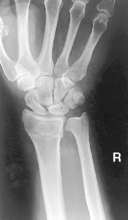
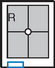
PA Wrist—Radial Deviation*
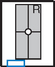
Note: See p. 26, 8th ed textbook, for explanation on wrist joint movement terminology.
Wrist—Carpal Canal*
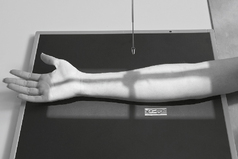
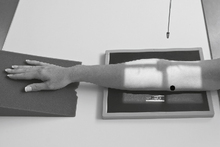
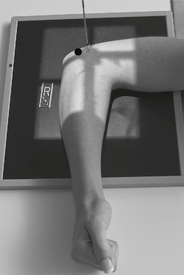
AP Forearm*

Lateral Forearm*
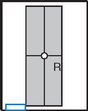
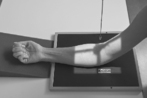
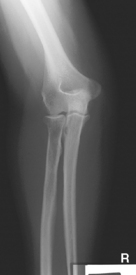
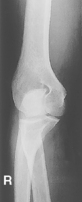
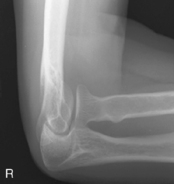
AP Elbow*
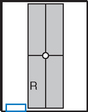
Position
• Elbow extended and hand supinated (shield across lap)
• Lean laterally as needed for true AP (palpate epicondyles)
• If elbow cannot be fully extended, take two AP projections as shown (Figs. 2-44 and 2-45) with CR perpendicular to distal humerus on one, and perpendicular to proximal forearm on another.
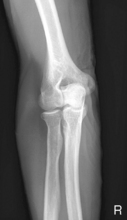
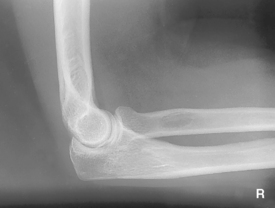
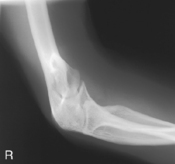
Lateral Elbow*
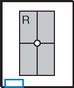
Lateral Elbow
Trauma Axial Lateral Elbow*
Trauma Axial Lateral Elbow
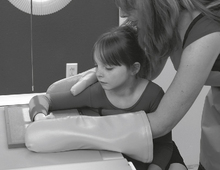
Pediatric AP Upper Limb*
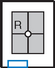
Position
• Supine position, arm abducted away from body, lead shield over pelvic area
• Include entire limb unless a specific joint or bone is indicated.
• Immobilize with clear flexible-type retention band and sandbags, or with tape.
• Use parental assistance only if necessary, provide lead gloves and apron.
Pediatric Lateral Upper Limb*
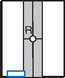
Position
• Supine position with arm abducted away from body, lead shield over pelvic area
• Include entire limb unless a specific joint or bone is indicated.
• Immobilize with clear flexible-type retention band and sandbags or with tape.
• Flex elbow and rotate entire arm into a lateral position.
• Use parental assistance only if necessary, provide lead gloves and apron.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, pp. 136 and 137.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 141.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 142.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 143.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 144.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 145.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 146.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 147.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 149.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 150.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 151.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 153.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 154.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 155.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 156.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, pp. 157 and 158.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 159.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 160.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 162.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 163.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, pp. 164 and 165.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, pp. 166 and 167.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 168.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 170.

 PA fingers (R)
PA fingers (R) PA oblique fingers (R)
PA oblique fingers (R) PA and PA oblique critique
PA and PA oblique critique Lateral fingers (R)
Lateral fingers (R) AP (R)
AP (R) Lateral finger and AP thumb critique
Lateral finger and AP thumb critique PA oblique (R)
PA oblique (R) Lateral (R)
Lateral (R) PA oblique and lateral thumb critique
PA oblique and lateral thumb critique AP axial (modified Roberts method) (S)
AP axial (modified Roberts method) (S) PA (R)
PA (R) PA oblique (R)
PA oblique (R) Lateral (“fan”) (R)
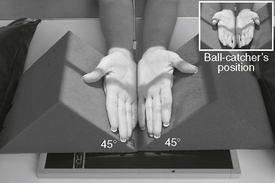
Lateral (“fan”) (R) AP oblique bilateral (Norgaard/ball-catcher’s) (S)
AP oblique bilateral (Norgaard/ball-catcher’s) (S) AP oblique bilateral critique
AP oblique bilateral critique PA (R)
PA (R) PA oblique (R)
PA oblique (R) PA and PA oblique critique
PA and PA oblique critique Lateral (R)
Lateral (R) Lateral critique
Lateral critique PA radial deviation (S)
PA radial deviation (S) Tangential carpal canal (Gaynor-Hart method) (S)
Tangential carpal canal (Gaynor-Hart method) (S) Tangential carpal canal critique
Tangential carpal canal critique AP (R)
AP (R) Lateral (R)
Lateral (R) AP and lateral critique
AP and lateral critique AP (R)
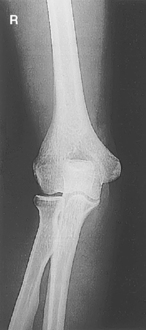
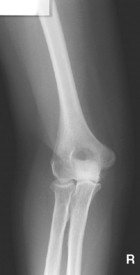
AP (R) AP critique
AP critique AP partially flexed critique
AP partially flexed critique AP oblique (medial and lateral) (R)
AP oblique (medial and lateral) (R) AP medial and lateral elbow critique
AP medial and lateral elbow critique Lateral elbow (R)
Lateral elbow (R) Lateral elbow critique
Lateral elbow critique Trauma axial lateral (Coyle method) (S)
Trauma axial lateral (Coyle method) (S) Trauma axial lateral (Coyle method) critique
Trauma axial lateral (Coyle method) critique AP (S)
AP (S) Lateral (S)
Lateral (S)