Chapter 19 Unipedicular Approach for Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
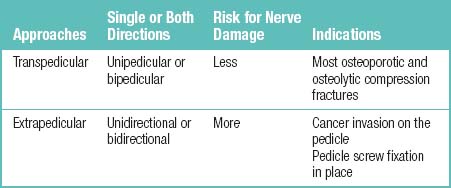
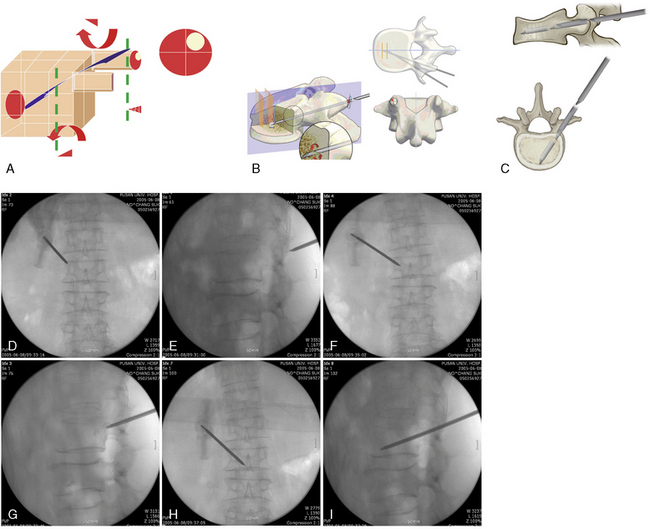
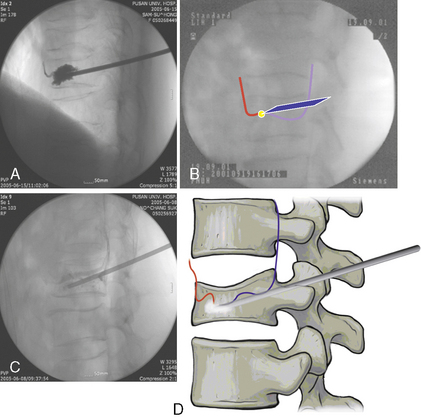
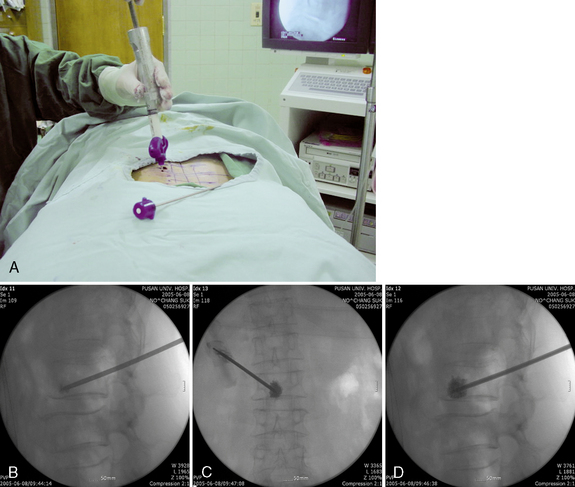
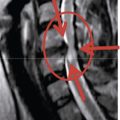
Unipedicular vertebroplasty is a percutaneous unipedicular approach [1,2] for introducing polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) cement into the collapsed vertebral body to provide reinforcement that will relieve pain immediately. There are two distinct approaches for percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP), the transpedicular approach and the extrapedicular approach (Table 19.1). These approaches are further described in Table 19.2 and Figure 19-1.
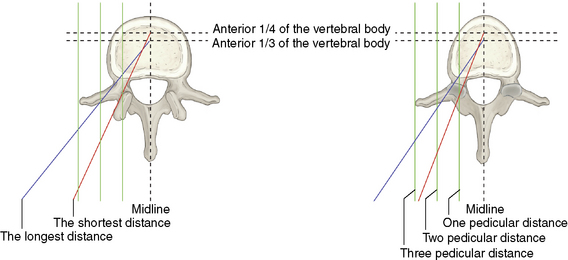
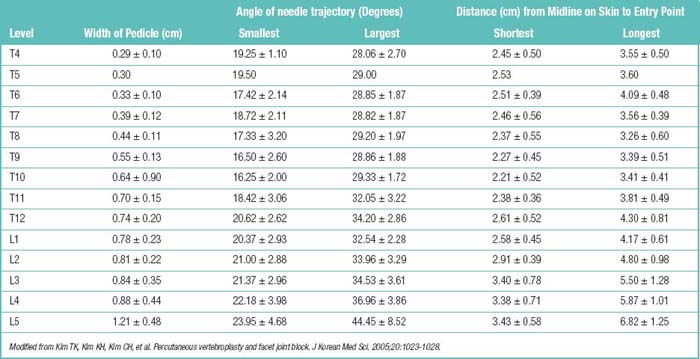
Table 19.2 Computed Tomography or Magnetic Resonance Imaging Parameters for Needle Placement in Unipedicular Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
The action mechanisms for pain relief from PVP are as follows:
Preoperative prepations
Preoperative Examination and Medications
Physical examination should reveal the following findings:
Imaging diagnosis consists of the following modalities:
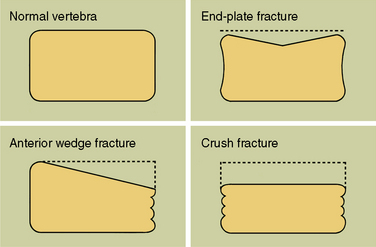
 Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging should show fracture lines or fatty changes on the vertebrae
Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging should show fracture lines or fatty changes on the vertebraeComplications
Possible complications of PVP and their treatment or prevention are as follows:
 Subsequent adjacent fractures in adjacent vertebrae due to lower BMD in the patient with osteoporosis or to active lesions in the patient with malignant metastasis; common medications for osteoporotic and metastatic osteolysis can be prescribed to prevent this occurrence.
Subsequent adjacent fractures in adjacent vertebrae due to lower BMD in the patient with osteoporosis or to active lesions in the patient with malignant metastasis; common medications for osteoporotic and metastatic osteolysis can be prescribed to prevent this occurrence. Transient neuropraxia or spinal cord damage due to damage or contusion from vertebral needle passage; anticonvulsant medications can be prescribed for this rare complication.
Transient neuropraxia or spinal cord damage due to damage or contusion from vertebral needle passage; anticonvulsant medications can be prescribed for this rare complication. Transient hypotension due to sympathetic nerve ablation from polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) heating and toxin; this complication is rare but preparations should be made for a hypotensive event.
Transient hypotension due to sympathetic nerve ablation from polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) heating and toxin; this complication is rare but preparations should be made for a hypotensive event. Pulmonary embolism due to leakage of PMMA into the vertebral vein; because of this rare but potentially lethal complication, it is necessary to make preparations for emergency open operation.
Pulmonary embolism due to leakage of PMMA into the vertebral vein; because of this rare but potentially lethal complication, it is necessary to make preparations for emergency open operation.Procedure
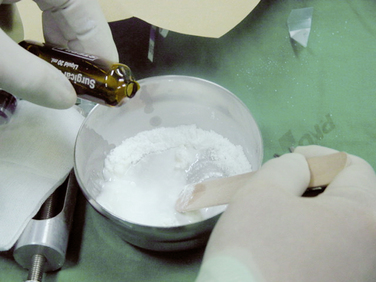
Figure 19–9 Mixing of bone cement and barium powder with solvent to form a mixture of toothpaste-like consistency.
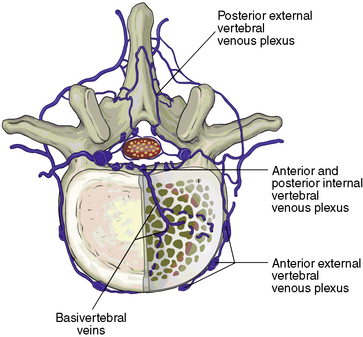
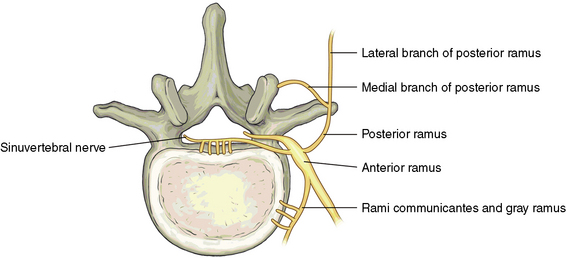
Related anatomy and physiology
The following aspects of anatomy and physiology are important for PVP:
Key points
 The introduction of a 20% solution of bone cement by volume results in a significant increase in the compressive strength of the vertebral body.
The introduction of a 20% solution of bone cement by volume results in a significant increase in the compressive strength of the vertebral body. Cement leakage is frequently noted with the 20% cement solution, especially in patients with higher BMD.
Cement leakage is frequently noted with the 20% cement solution, especially in patients with higher BMD. Unipedicular vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are comparable to bipedicular techniques in restoring vertebral body strength, stiffness, and height.
Unipedicular vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are comparable to bipedicular techniques in restoring vertebral body strength, stiffness, and height.1 Steinmann J., Tingey C.T., Cruz G., Dai Q. Biomechanical comparison of unipedicular versus bipedicular kyphoplasty. Spine. 2005;30:201-205.
2 Higgins K.B., Harten R.D., Langrana N.A., Reiter M.F. Biomechanical effects of unipedicular vertebroplasty on intact vertebrae. Spine. 2003;28:1540-1547. discussion 1548