37 Ulnar Nerve Block
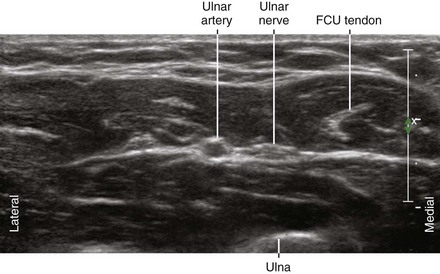
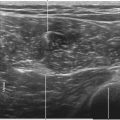
The ulnar nerve is a branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus. The ulnar nerve provides sensation of the dorsal and palmar sides of the ulnar aspect of the hand. It leaves the neurovascular bundle in the axilla to travel through the cubital tunnel. In the forearm it joins the ulnar artery on its medial side. The ulnar nerve usually lies between the ulnar artery and the flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) tendon in the forearm. The dorsal cutaneous branch leaves the ulnar nerve in the forearm proximal to the wrist.1,2 At the level of the hamate, the ulnar nerve divides into its superficial sensory branch and its deep motor branch.
Suggested Technique
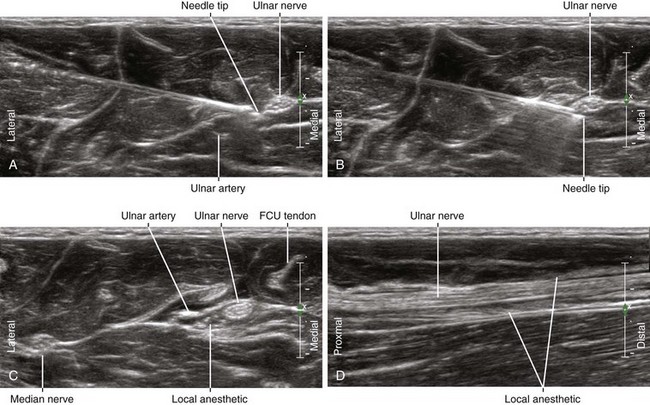
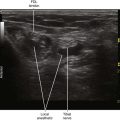
The ulnar nerve is usually blocked just proximal to its juncture with the ulnar artery in the forearm.3 In this location the nerve is either oval or triangular. The block is performed with the patient supine and the arm supinated. The needle tip is placed within the fascial plane that connects the ulnar nerve and ulnar artery using an in-plane approach from the lateral side of the forearm. To access this plane with the block needle it is best to puncture the fascia and slowly inject as the needle is pulled back.
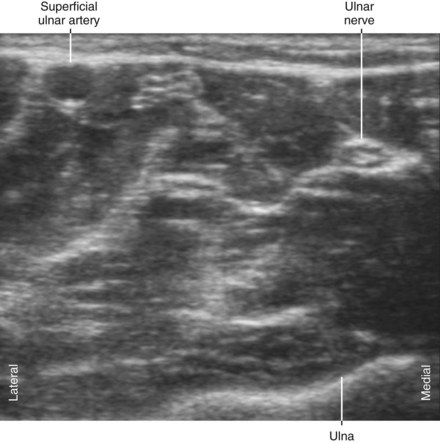
A relatively common (3%-10%) anatomic variant is superficial ulnar artery, whereby the ulnar artery lies superficial to the flexor muscles.4
Neurologic Assessment
Key Points
| Ulnar Nerve Block | The Essentials |
|---|---|
| Anatomy | The UN lies between the UA and FCU tendon. |
| The UN is about 3 mm in diameter. | |
| Image orientation | The UN lies on the ulnar (medial) side of the UA in the forearm. |
| Positioning | Arm supinated |
| Operator | Standing on the lateral (cephalad) side of the armboard |
| Display | Across the armboard |
| Transducer | High-frequency linear, 23- to 38-mm footprint |
| Initial depth setting | 25 mm |
| Needle | 25 gauge, 38 mm in length |
| Anatomic location | Mid-forearm, just proximal to where the UN and UA join |
| Approach | SAX view of UN, in-plane from lateral to medial |
| Place the needle tip between the UN and UA at their juncture. | |
| Sonographic assessment | The injection should track distally along the UN to the DCUN. |
| Anatomic variation | Superficial ulnar artery (3%-10%; when the UA lies superficial to the flexor muscles) |
1 Botte MJ, Cohen MS, Lavernia CJ, et al. The dorsal branch of the ulnar nerve: an anatomic study. J Hand Surg (Am). 1990;15:603–607.
2 Grossman JA, Yen L, Rapaport D. The dorsal cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve: an anatomic clarification with six case reports. Chir Main. 1998;17:154–158.
3 Gray AT, Schafhalter-Zoppoth I. Ultrasound guidance for ulnar nerve block in the forearm. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2003;28:335–339.
4 Schafhalter-Zoppoth I, Gray AT. Ultrasound-guided ulnar nerve block in the presence of a superficial ulnar artery. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2004;29:297–298.