Chapter 60 Ulcerative Colitis
INTRODUCTION
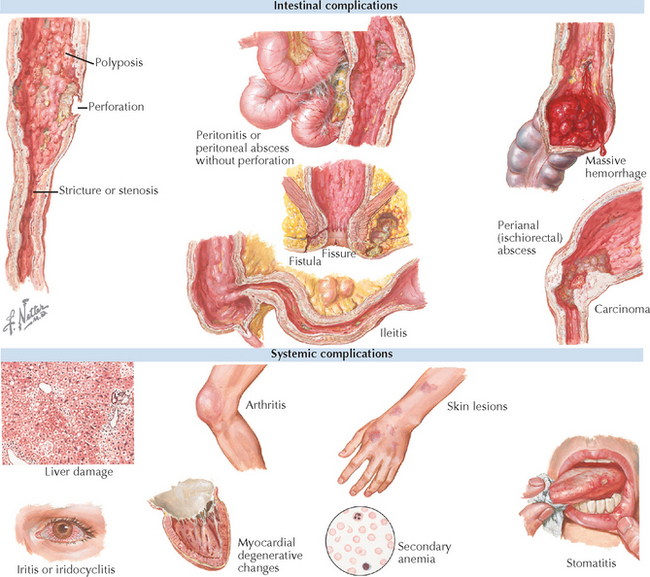
Description: Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease characterized by an inflammation limited to the mucosa of the large bowel and found primarily in the descending colon and rectum (although the entire colon may be involved). The disease is characterized by intermittent bouts of symptoms interspersed by periods of quiescence.
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH
Differential Diagnosis
MANAGEMENT AND THERAPY
Nonpharmacologic
General Measures: Evaluation and control of inflammation, prevention of complications, maintenance of nutrition (including adequate iron intake).
Specific Measures: Severe exacerbations may require hospitalization. Patients whose disease is refractory to antibiotic therapy may require surgical resection. (Between 25% and 40% of patients with ulcerative colitis eventually undergo colectomy because of massive bleeding, severe illness, rupture of the colon, or risk of cancer.)
Drug(s) of Choice
Alternative Drugs
Azathioprine and 6-mercapto-purine (6-MP) may be used for patients who have not responded to 5-ASAs or corticosteroids or who are dependent on corticosteroids. Other oral 5-ASA derivatives are being studied. Antidiarrheal agents (diphenoxylate-atropine and loperamide) may be used but may precipitate toxic megacolon. Preliminary studies with Tetomilast (OPC-6535), a novel thiazole compound, failed to achieve statistically significant effects, but trends suggest possible utility.
FOLLOW-UP
Patient Monitoring: Normal health maintenance, periodic follow-up to monitor status of disease and possible complications. Colonoscopy to watch for the possible development of cancer should be performed every 1 to 2 years beginning 7 to 8 years after the onset of disease. Annual testing of liver function is desirable.
MISCELLANEOUS
Pregnancy Considerations: No effect on pregnancy. Of patients with inactive disease, 30% have relapses during pregnancy, 15% in the first trimester. Treatment with sulfasalazine does not affect the outcome of the pregnancy. It is recommended that pregnancy be delayed until the disease is in remission.
Ardizzone S, Maconi G, Russo A, et al. Randomised controlled trial of azathioprine and 5-aminosalicylic acid for treatment of steroid dependent ulcerative colitis. Gut. 2006;55:47. Epub 2005 Jun 21
Rutgeerts P, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, et al. Infliximab for induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2462.
van Staa TP, Card T, Logan RF, Leufkens HG. 5-Aminosalicylate use and colorectal cancer risk in inflammatory bowel disease: a large epidemiological study. Gut. 2005;54:1573. Epub 2005 Jun 30