CHAPTER 21 Tuberosity Reduction and Fixation
Greater and lesser tuberosity complications are primary obstacles to achieving a satisfactory result after unconstrained arthroplasty for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures.1 Tuberosity malunion and nonunion are situations to be avoided. The first step in avoiding these complications is placement of the tuberosities at their correct anatomic location through proper preoperative planning and accurate humeral prosthetic positioning (Chapters 18 and 20). The second step in avoiding these complications is through tuberosity fixation. Tuberosity fixation consists of two major components: use of a reliable and reproducible suture fixation technique to provide initial fracture stability, and use of bone graft to assist in tuberosity healing and provide long-term fracture stability. This chapter details our preferred tuberosity fixation technique and the use of bone graft to enhance tuberosity position and healing.
PREPARATION OF BONE GRAFT
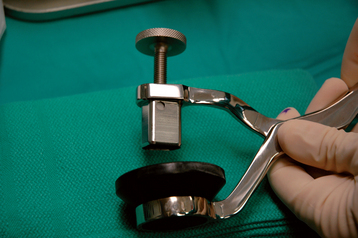
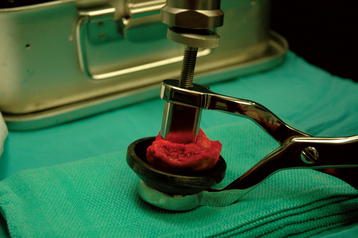
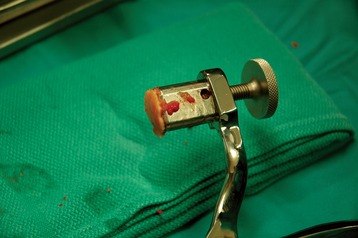
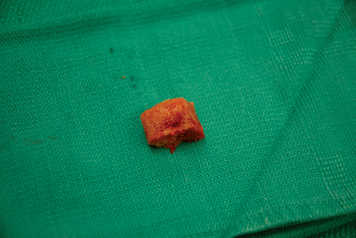
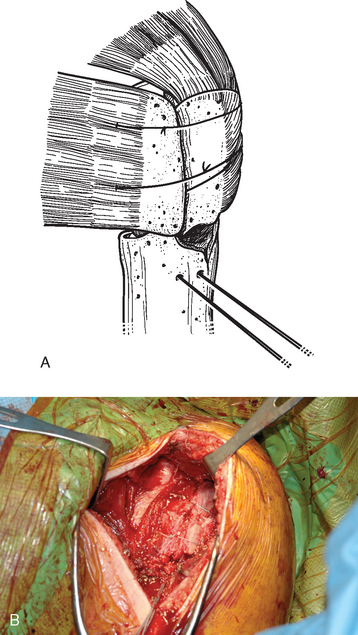
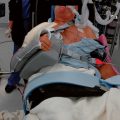
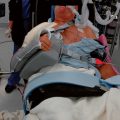
A specially designed bone graft cutter is used to harvest bone graft plugs from the humeral head fragment. The thumbscrew of the bone graft cutter is completely recessed, and the cutting edge is advanced through the humeral head from cancellous surface to articular surface with a mallet (Figs. 21-1 and 21-2). After the cutting edge of the bone graft cutter has been advanced completely through the humeral head, the remaining humeral head is removed from the cutter and preserved. The thumbscrew of the bone graft cutter is advanced slightly to extrude just the portion of the bone graft plug covered with articular cartilage (Fig. 21-3). The articular cartilage is removed from the bone graft plug with a large biting rongeur (Fig. 21-4). The bone graft plug is then fully extruded from the bone graft cutter (Fig. 21-5). This process is repeated for a second bone graft plug.
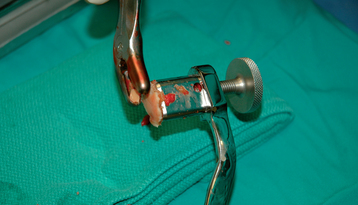
Figure 21-4 The articular cartilage is removed from the bone graft plug with a large biting rongeur.
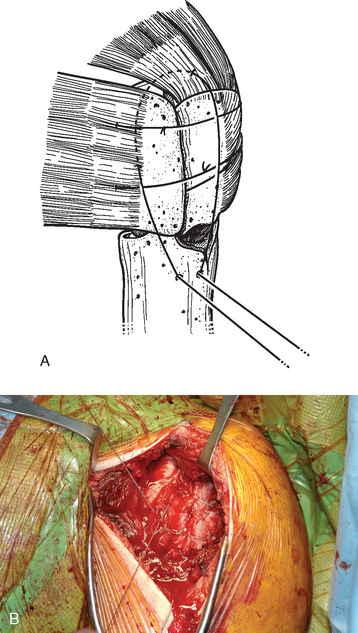
The remaining cancellous bone in the humeral head fragment is removed with a large biting rongeur and morselized (Fig. 21-6). Care is taken to not include articular cartilage in the morselized bone graft. One of the bone graft plugs is gently impacted into the fenestration of the humeral prosthesis that had previously been cemented into place, as described in Chapter 20 (Fig. 21-7).
TECHNIQUE FOR REDUCTION AND FIXATION OF THE TUBEROSITIES
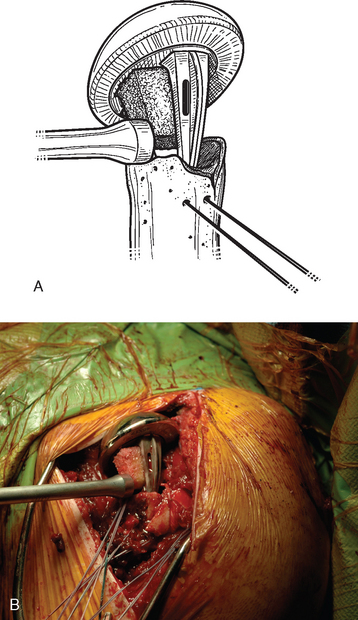
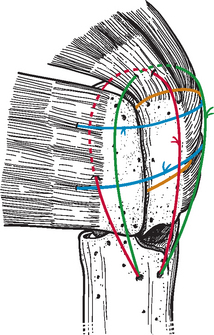
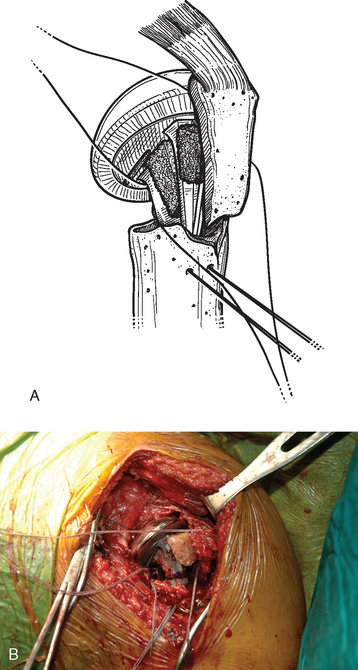
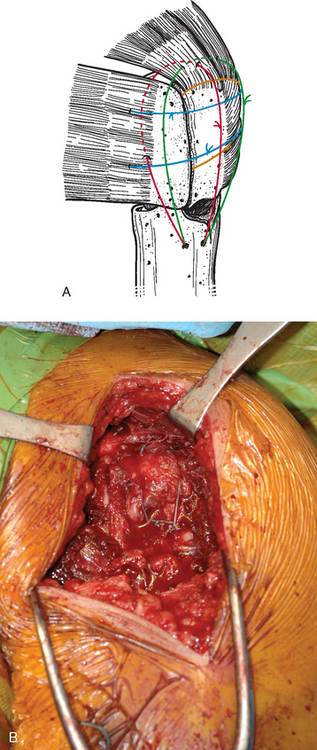
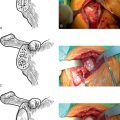
Fixation of the tuberosities is achieved with a reproducible suture fixation technique consisting of four horizontal cerclage sutures (two around the greater tuberosity and two around the greater and lesser tuberosities) and two vertical cerclage sutures (Fig. 21-8). The sutures to be used for horizontal cerclage were previously placed when control of the greater tuberosity was initially achieved (Chapter 19) and consist of two strands of no. 2 braided permanent suture placed through the rotator cuff at the junction of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus and two strands of no. 2 braided permanent suture placed through the rotator cuff at the junction of the infraspinatus and teres minor. The vertical cerclage sutures consist of the two strands of no. 2 nonabsorbable braided suture placed in the humeral diaphysis before humeral implant cementation, as described in Chapter 20.
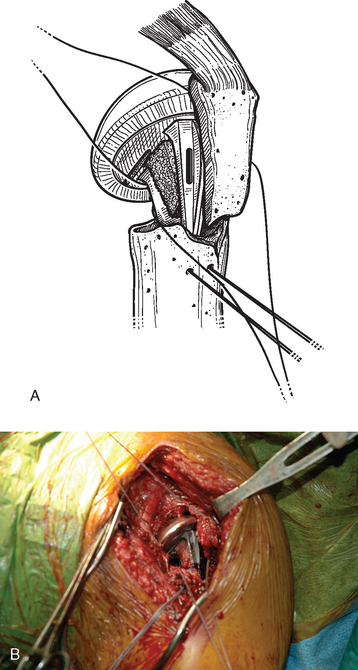
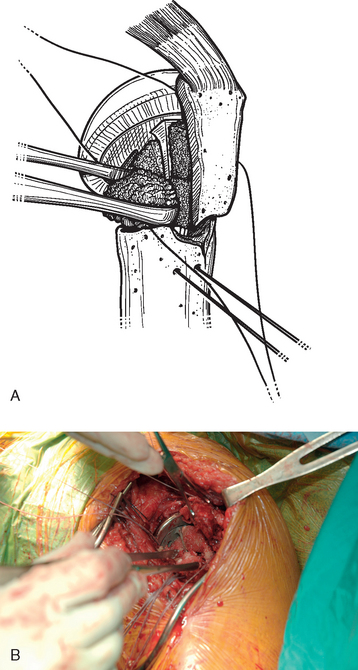
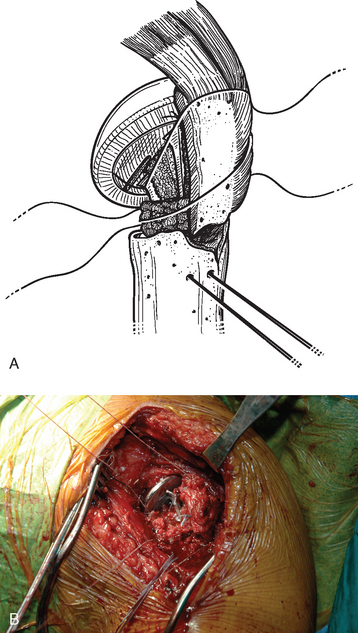
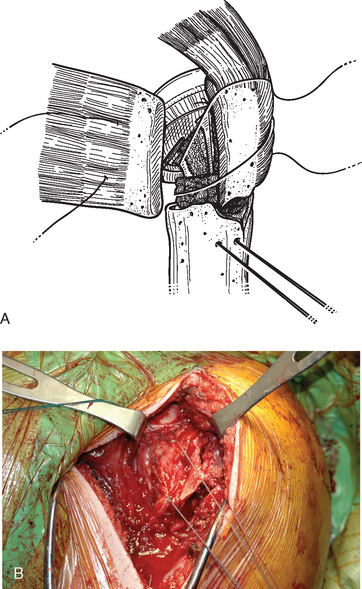
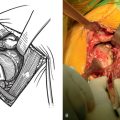
The sutures controlling the greater tuberosity are passed around the smooth polished medial aspect of the prosthetic neck (Fig. 21-9). The second of the two bone graft plugs is placed lateral to the neck of the prosthesis to accommodate for bone loss in the greater tuberosity and to place the greater tuberosity in a more anatomic lateral position (Fig. 21-10). The morselized bone graft is placed along the diaphyseal fracture line to promote healing of the greater and lesser tuberosities to the humeral shaft (Fig. 21-11). The greater tuberosity is gently grasped with Lahey forceps and reduced into position lateral to the second bone graft plug (Fig. 21-12). Two of the sutures controlling the greater tuberosity, one superior and one inferior, are tied to fixate the greater tuberosity (Fig. 21-13). The remaining two sutures, one superior and one inferior, are passed through the subscapularis tendon just medial to its osseous insertion on the lesser tuberosity (Fig. 21-14). The lesser tuberosity is reduced with the previously placed stay sutures, and the circumferential sutures are tied to secure the tuberosity (Fig. 21-15). Tuberosity fixation is completed with the two sutures previously placed through drill holes in the humeral diaphysis. One suture is passed through the subscapularis and supraspinatus tendons just medial to their osseous insertion and then tied (Fig. 21-16). The second suture is passed through the infraspinatus and supraspinatus tendons just medial to their osseous insertion and then tied (Fig. 21-17). Security of the tuberosities must be evaluated by checking the mobility of the shoulder after tuberosity repair. The tuberosities and prosthetic humeral head implant should move as one unit.
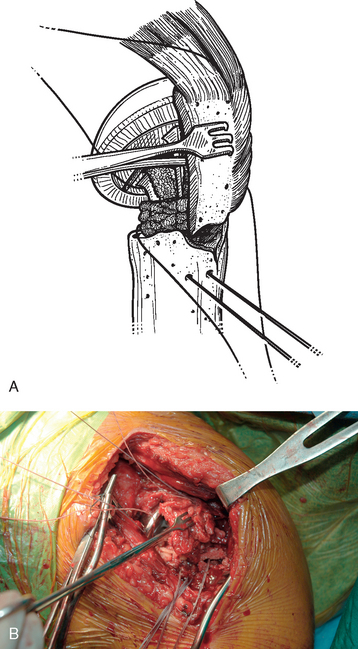
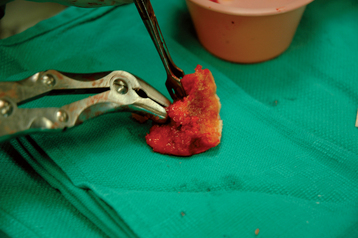
Figure 21-12 A and B, The greater tuberosity is reduced into position lateral to the second bone graft plug with Lahey forceps.