Chapter 57. Triage
Triage is the sorting of casualties according to clinical priorities and is a dynamic process which can be used to assess priorities for treatment and for evacuation. Triage should be undertaken whenever the number of casualties exceeds the number of skilled helpers available. Different triage methods are available depending on the circumstances: generally triage ‘sieve’ is applied then refined, using triage ‘sort’.
Priorities
The systems of priorities in common use are referred to as the treatment (T) system and the priority (P) system:
Definitions
Use of the fourth category
Whether or not the expectant category is used is a decision for the senior personnel involved (the ambulance and medical incident officers at the scene and the chief triage officer at the hospital). Patients in the expectant category will be treated and transported after those in the T1 category but before those in the T2 and T3 categories.
Triage at major incidents
There may be a large number of casualties at a major incident and thus an enormous number of decisions need to be made as quickly and efficiently as possible.
Apply triage ‘sieve’ then triage ‘sort’
Triage sieve
• Anybody that can walk is a Category 3 for the time being
• Any patient who is not breathing has their airway opened. If they still do not breathe then they are dead
• The rest can be divided into Category 1 and Category 2, depending on their breathing and pulse.
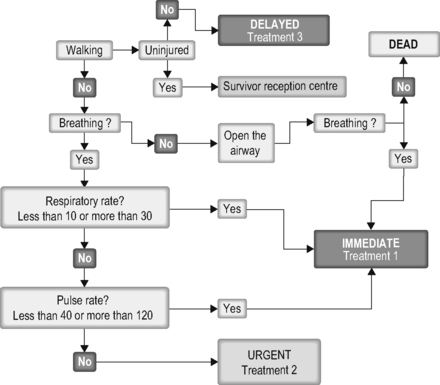 |
| Figure 57.1. |
| The triage sieve – summary. |
Triage sort
Following the triage sieve, on arrival in the casualty clearing centre, patients are triaged using a more detailed method. This is the triage sort which is based on three parameters:
Respiratory rate
Systolic blood pressure
Glasgow Coma Scale.
A score for each of these is assigned to the patient.
The sum of these three scores is the triage revised trauma score (TRTS). This method can be used to assign triage priorities.
Although more time consuming than the triage sieve, the triage sort is more accurate and can be used to prioritise further treatment and evacuation.
CRAMS
An alternative triage system used by some UK ambulance services is the CRAMS system:
C – Circulation
R – Respiration
A – Abdomen and thorax
M – Motor response
S – Speech
The CRAMS score is calculated by adding the five values together. The triage category is then assigned as shown in Table 57.1.
| Description | Colour | T system | P system |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate | Red | 1 | 1 |
| Urgent | Yellow | 2 | 2 |
| Delayed | Green | 3 | 3 |
| Expectant | Blue | 4 | |
| Dead | White |
| Priority | CRAMS score | Mortality (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate (red) | <6 | 15–100 |
| Urgent (yellow) | 7 | 3 |
| Delayed (green) | 8–10 | 0–0.5 |
Circulation
2 Normal capillary refill or systolic BP >100 mmHg
1 Delayed capillary refill or systolic BP 85–99 mmHg
0 No capillary refill or systolic BP <85 mmHg
Respiration
2 Normal respiration
1 Laboured, shallow or rate above 20/min
0 Respiration absent
Abdomen thorax
2 Abdomen not tender
1 Abdomen tender
0 Abdomen rigid, flail chest or penetrating injury
Motor response
2 Normal (obeys commands)
1 Responds only to pain
0 Postures or no response
Speech
2 Normal speech (oriented)
1 Confused or inappropriate
0 Nil or unintelligible sounds
Triage labelling
The patients must be labelled to allow orderly evacuation and to prevent duplication of effort. Cruciform triage cards allow category/colour allocation and allow for the allocation to be changed as required.
For further information, see Ch. 59 in Emergency Care: A Textbook for Paramedics.