High-energy injuries: Motor vehicle accidents constitute ∼ 50% of cases, with seat belts increasing risk
– “High-riding” seat belt incorrectly placed over abdomen increases risk (muscle avulsion from iliac crest)
– Other traumatic injuries are common (∼ 80%), with up to 50% of patients suffering other abdominal injuries requiring surgery
 Low-energy injuries (most common in children): Impact by small blunt object (such as bicycle handlebar, i.e., handlebar hernia)
Low-energy injuries (most common in children): Impact by small blunt object (such as bicycle handlebar, i.e., handlebar hernia)
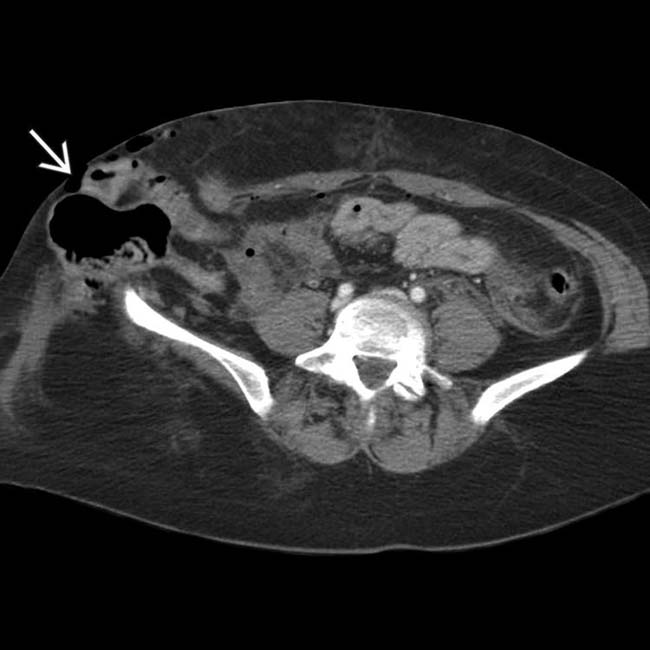
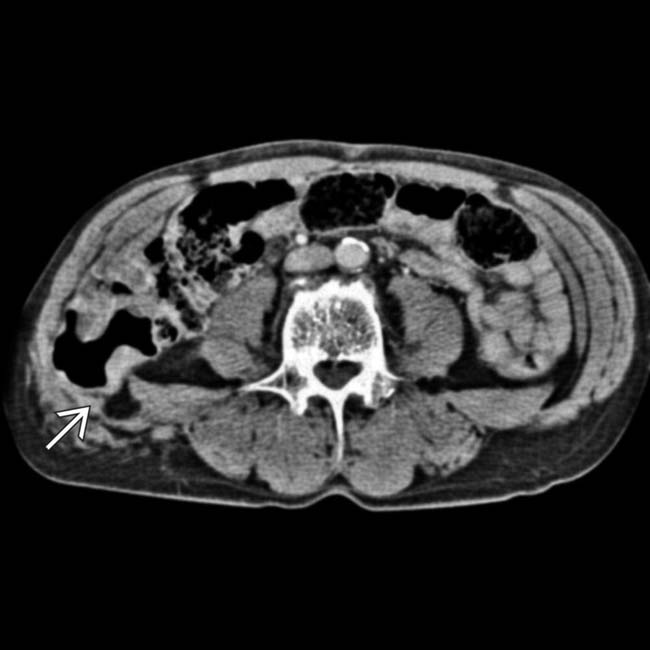
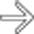
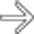
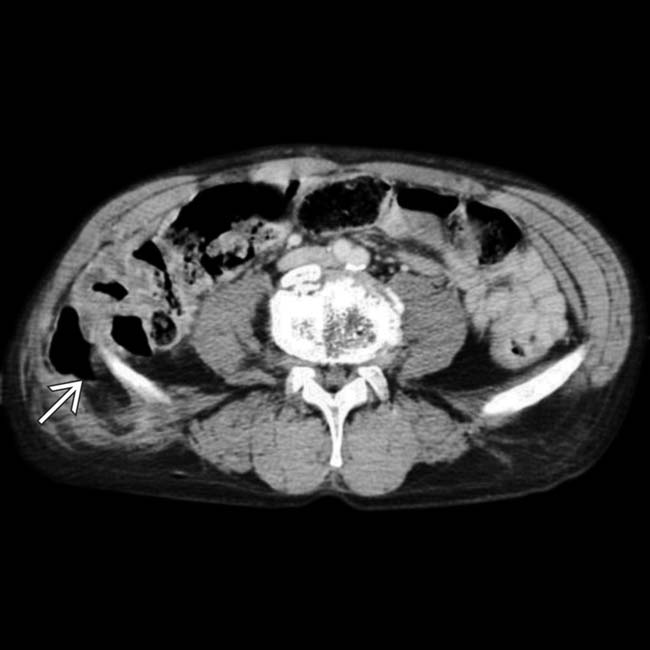
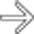 herniating through a traumatic abdominal wall defect. At surgery, several segments of small bowel had serosal tears and avulsions, requiring resection.
herniating through a traumatic abdominal wall defect. At surgery, several segments of small bowel had serosal tears and avulsions, requiring resection.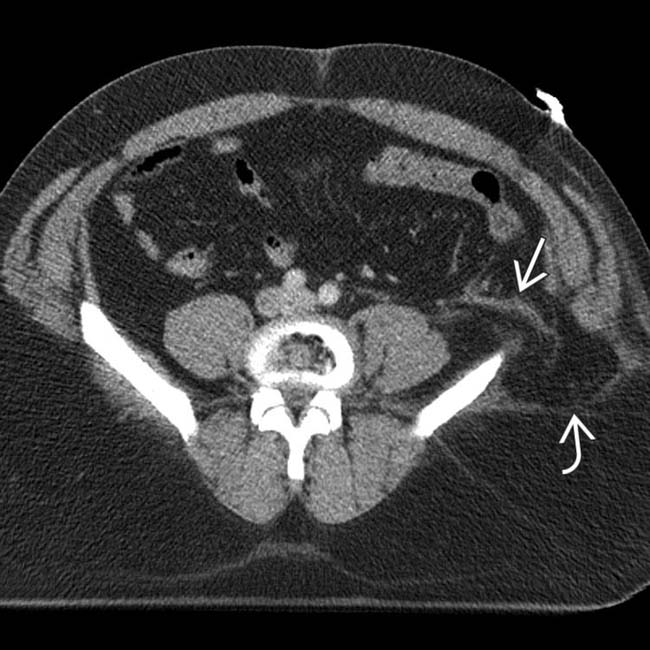
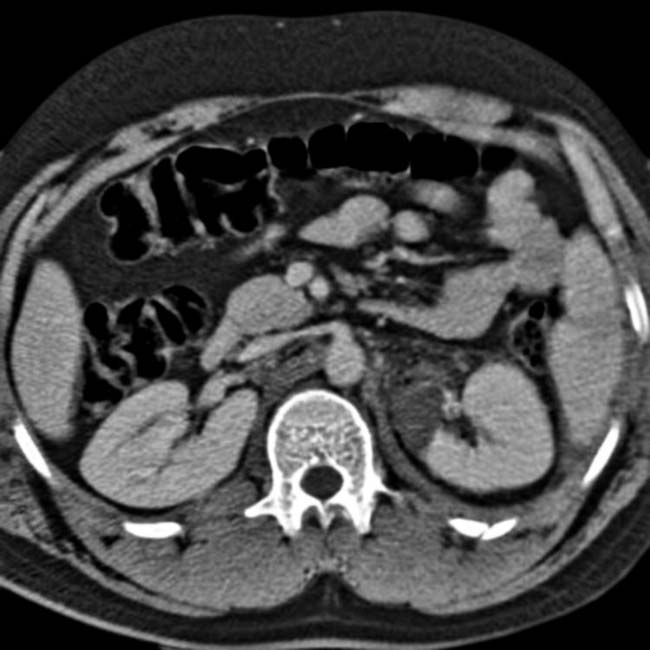
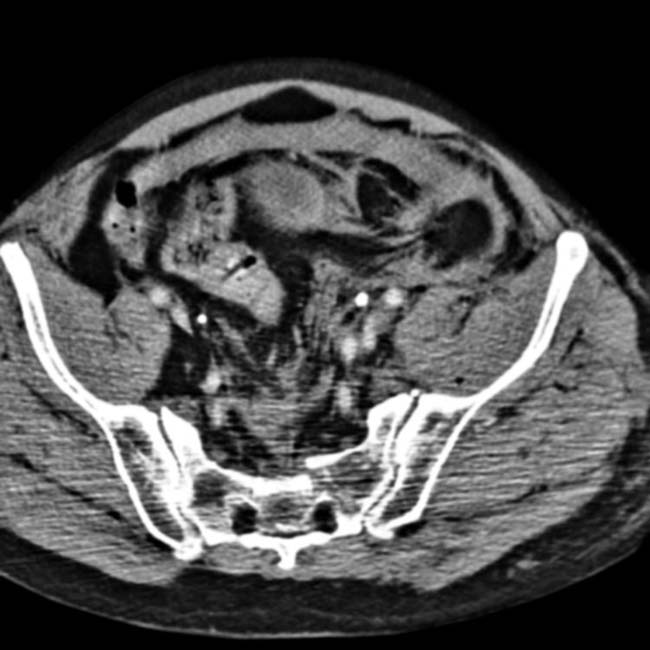
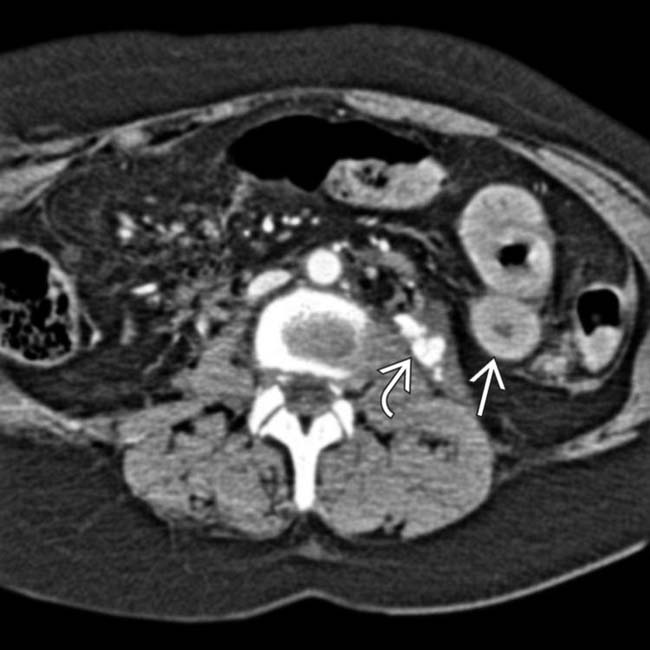
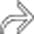 . Also noted is infiltration of the intraabdominal fat
. Also noted is infiltration of the intraabdominal fat  adjacent to the hernia. At surgery, a serosal tear of the descending colon was identified.
adjacent to the hernia. At surgery, a serosal tear of the descending colon was identified.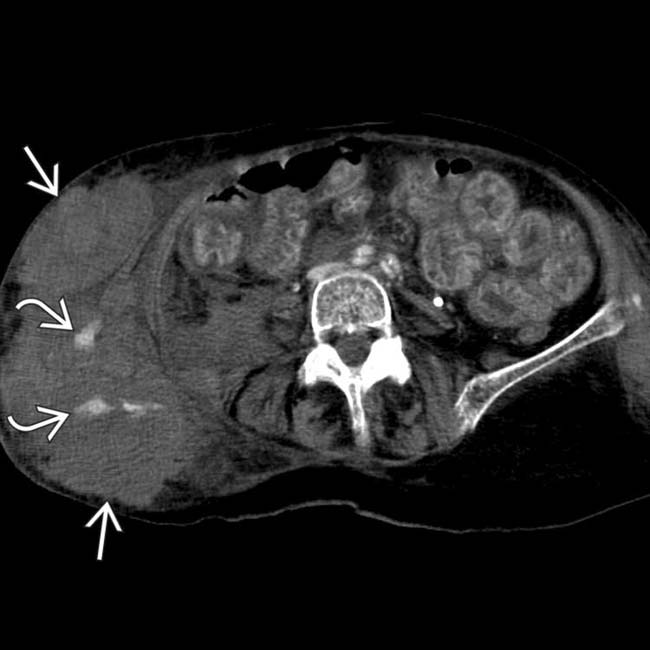
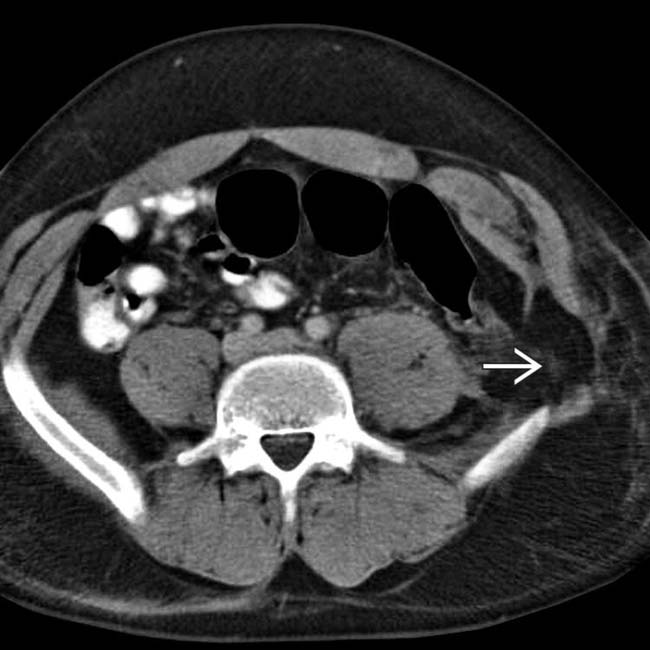
 herniated through a traumatic hernia of the right abdominal wall. Active arterial bleeding
herniated through a traumatic hernia of the right abdominal wall. Active arterial bleeding  is evident. Much of the herniated bowel was not viable at the time of surgery.
is evident. Much of the herniated bowel was not viable at the time of surgery.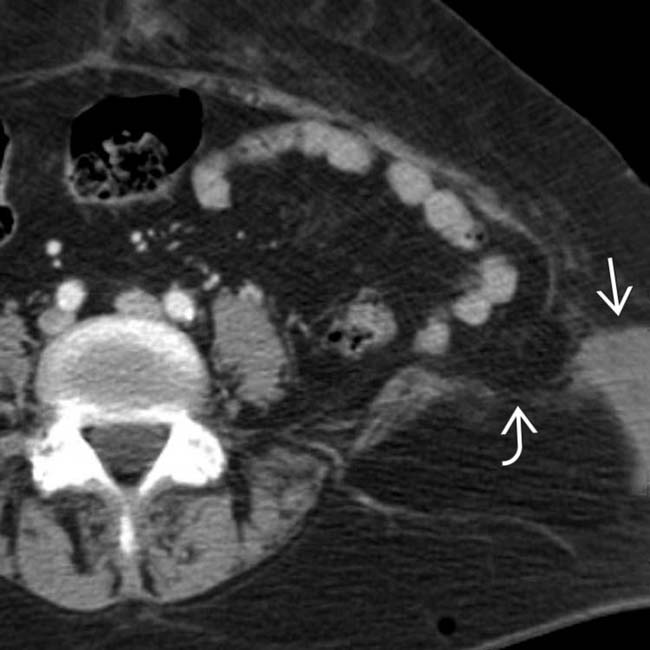
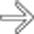
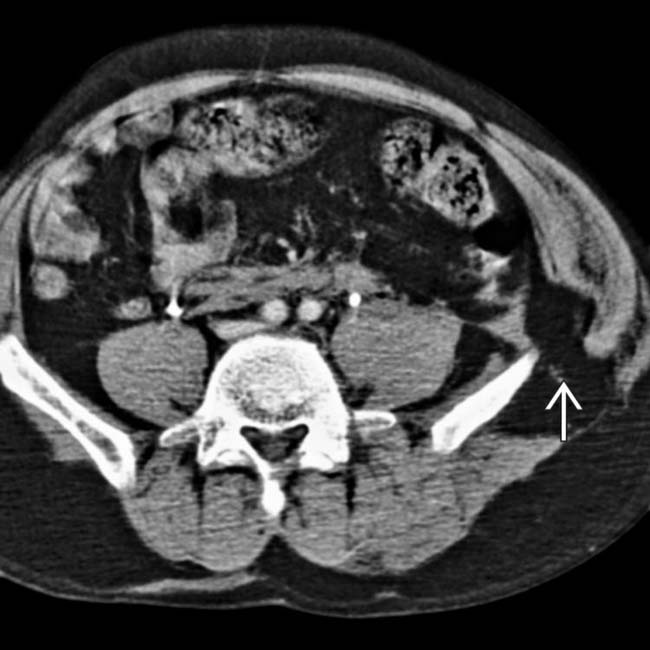
 in the left lower quadrant, with the muscles avulsed from their attachment to the iliac crest. Note the presence of adjacent subcutaneous hematoma
in the left lower quadrant, with the muscles avulsed from their attachment to the iliac crest. Note the presence of adjacent subcutaneous hematoma 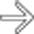 . This is a typical example of a seat belt injury.
. This is a typical example of a seat belt injury.PATHOLOGY
General Features
• Etiology
 Most hernias develop due to combination of sudden increase in intraabdominal pressure, direct force of traumatic impact, acceleration-deceleration shear injury, and compressive force of seat belt
Most hernias develop due to combination of sudden increase in intraabdominal pressure, direct force of traumatic impact, acceleration-deceleration shear injury, and compressive force of seat belt
 High-energy injuries: ∼ 50% of cases result from motor vehicle accidents, with seat belts increasing risk
High-energy injuries: ∼ 50% of cases result from motor vehicle accidents, with seat belts increasing risk
 Most hernias develop due to combination of sudden increase in intraabdominal pressure, direct force of traumatic impact, acceleration-deceleration shear injury, and compressive force of seat belt
Most hernias develop due to combination of sudden increase in intraabdominal pressure, direct force of traumatic impact, acceleration-deceleration shear injury, and compressive force of seat belt
 High-energy injuries: ∼ 50% of cases result from motor vehicle accidents, with seat belts increasing risk
High-energy injuries: ∼ 50% of cases result from motor vehicle accidents, with seat belts increasing risk
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
 .
.
























 .
.
 .
.
 .
.
 from mesenteric or retroperitoneal arteries. Several segments of small bowel
from mesenteric or retroperitoneal arteries. Several segments of small bowel  show mural hemorrhage, and bleeding is present between bowel loops.
show mural hemorrhage, and bleeding is present between bowel loops.


