CHAPTER 2 Trapeziometacarpal and Scaphotrapezial Arthroscopy Portals
Trapeziometacarpal Joint Portals
Standard Portals
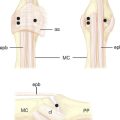
Menon initially presented his work on arthroscopy of the trapeziometacarpal joint as a meeting exhibit in 1994.1 He then published his experience with the arthroscopic management of trapeziometacarpal arthritis in 1996.2 He described two working portals: a volar portal just radial to the abductor pollicus longus tendon (APL) and a dorsal portal that is just ulnar to the APL along the line of the joint. Berger independently developed his technique for arthroscopic evaluation of the first carpometacarpal joint, which he first presented as an instructional course in 1995. He then published his clinical work in 1997. He named the volar radial portal the 1-R portal and the dorsal ulnar portal the 1-U.3 He defined the term dorsal as being in the plane of the thumb nail and volar in the plane of the distal pulp.
Radial and ulnar referred to the thumb when its nail is parallel to the fingernails, with the thumb supinated and radially abducted. He noted that the plane of the 1-R portal passes through the nonligamentous capsule just lateral to the anterior oblique ligament (AOL). This portal is preferred for viewing the dorsoradial ligament (DRL), the posterior oblique ligament (POL), and the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL). The plane of the 1-U portal, which is just posterior and ulnar to the extensor pollicus brevis (EPB), passes between the DRL and PRL. This portal provides views of the AOL and UCL. Both portals are along the radial border of the thumb, which makes it difficult to assess the lateral side of the joint.4 There is no true internervous plane because branches of the superficial radial nerve surround the field and are at risk for injury with improper technique. The radial artery courses immediately posterior and ulnar to the arthroscopic field.
Modified Radial Portal
Orrellana and Chow described a modified radial portal (RP) for improving the radial view of the TMJ.5 The RP is located just distal to the oblique ridge of the trapezium, following a line along the radial border of the flexor carpi radialis (FCR) tendon rather than the APL. In an anatomic study of six cadaver arms, the superficial radial nerve (SRN) was located a mean of 6.3 mm (range 4 to 8 mm) from the 1-U portal and 7.8 mm (range 4 to 12 mm) from the RP. The radial artery passed within 2.7 mm (range 2 to 3.5 mm) of the 1-U portal and 10 and 15 mm from the RP. To establish the RP, the scope is placed in the 1-U portal. The light source is pointed to the RP, which lies just radial to the AOL. A 22-gauge needle is inserted just distal to the ridge of the trapezium. The skin is incised, followed by blunt dissection through the capsule and insertion of the trocar and cannula, and then the arthroscope.
Thenar Portal
A thenar portal was subsequently described by Walsh et al.6 This portal is placed by illuminating the thenar eminence with the arthroscope in the 1-U portal, and then inserting an 18-gauge needle through the bulk of the thenar muscles at the level of the TMJ (approximately 90 degrees from the 1-U portal). This portal did not appear to violate the important deep anterior oblique ligament, which is the major restraint against thumb metacarpal dorsal subluxation. They measured the distances of the surrounding neurovascular structures to three portals in a cadaver study of seven limbs. The superficial radial nerve typically has a major volar branch (SR1) and a major dorsal branch that subdivides into a volar (SR2) and dorsal (SR3) branch. SR1 generally parallels the first extensor compartment, whereas SR2 crosses the first web space.7
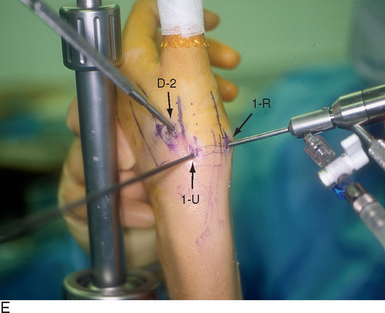
Distal/Dorsal (D-2) Portal
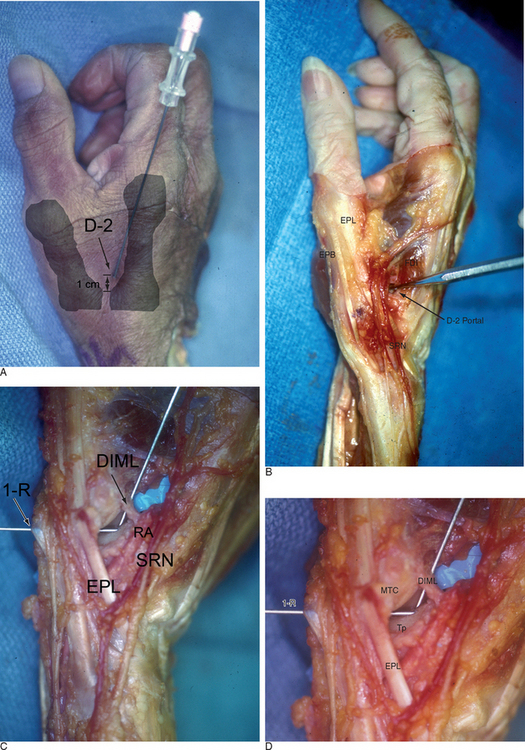
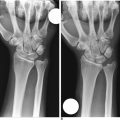
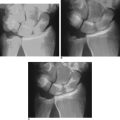
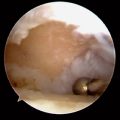
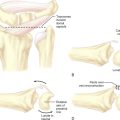
Access to medial osteophytes may sometimes be difficult. Hence, I have found the use of a distal/dorsal (D-2) accessory portal to be of some value. Its main utility is that it allows one to look down on the trapezium rather than across it, which facilitates resection of medial osteophytes. This accessory portal allows views of the dorsal capsule with rotation of the scope and facilitates triangulation of the instrumentation. It is situated in the dorsal aspect of the first web space. An anatomical study of five cadaver hands revealed that the D-2 portal surface landmark is ulnar to the EPL tendon and 1 cm distal to the V-shaped cleft at the juncture of the index and thumb metacarpal bases. The portal lies just distal to the dorsal intermetacarpal ligament (DIML).8
The DIML is an extracapsular ligament that originates from the dorsoradial aspect of the index metacarpal radial to the extensor carpi radialis longus insertion. It inserts onto the palmar-ulnar tubercle of the base of the thumb metacarpal along with the POL and UCL.4 A trocar placed through the D-2 portal was found to pass through the first dorsal interosseous muscle and penetrate the DIML, entering the joint either through or between the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) and the posterior oblique ligament (POL) (Figure 2.1a through d). Branches of the superficial radial nerve passed within 3.2 mm (range 1 to 5 mm) of this portal. The radial artery was 3.8 mm away (range 3 to 5 mm) from this portal, the FDMA was within 2.8 mm (range 2 to 4 mm) of this portal, and the cephalic vein was within 2.8 mm (range 1 to 5 mm) of this portal. On average, the D-2 portal was 17.2 mm from the 1-U portal (range 12 to 20 mm).
Scaphotrapeziotrapezoidal Joint Portals
STT-U Portal
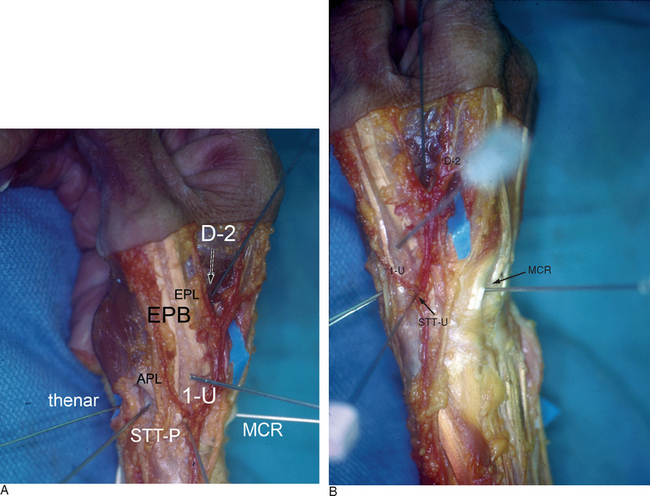
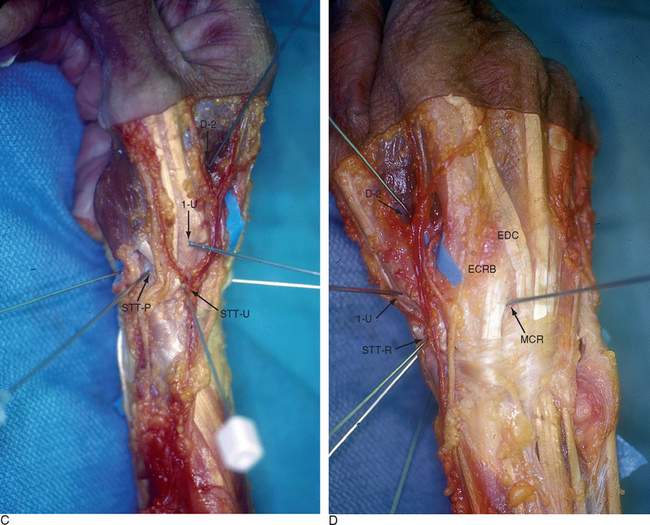
Bowers and Whipple have described a scaphotrapeziotrapezoidal joint (STT-U) portal they used to facilitate arthroscopic resections of the distal scaphoid with scaphotrapezial osteoarthritis. They used this portal in conjunction with the radial midcarpal portal (RMC) for evaluation and treatment of disorders of the STT joint. The STT-U portal is located in line with the midshaft axis of the index metacarpal, just ulnar to the EPL.9 Entry into this portal requires traction on the index finger. Leaving the EPL to the radial side of the STT portal protects the radial artery in the snuffbox from injury.
STT-R Portal
A radial portal for STT arthroscopy (STT-R) has also been recently reported.10 This portal is radial to the abductor pollicus longus (APL) tendon at the level of the STT joint. Access to the joint is facilitated by use of a 1.9-mm 30E angled arthroscope. Cadaver dissections demonstrated that maintaining a position palmar and radial to the APL tendon at the STT joint level avoids the radial artery by a mean of 8.8 mm (range 6 to 10 mm). The angle between the two portals is 130E, which facilitates triangulation of the instrumentation. As with the 1-/,2 portal, branches of the superficial radial nerve virtually surround the arthroscopic field. Hence, blunt dissection of the capsule and knowledge of the regional anatomy are essential.
STT-P Portal
Baré and co-workers described another accessory palmar portal (STT-P) based on a dissection of 10 cadaver arms.11 They identified a safe portal of entry that was midway between the radial styloid and the base of the first metacarpal, 3 mm ulnar to the APL tendon and 6 mm radial to the scaphoid tubercle. The trocar is inserted into the ST joint, aiming toward the base of the fifth metacarpal while holding the thumb in extension and adduction. This portal lay 7.6 mm (range 5 to 11 mm) from the radial artery, 6.5 mm (range 4 to 11 mm) from the superficial branch of the radial artery, and 11.6 mm (range 3 to 20 mm) from the closest radial sensory nerve branch.
Bain et al. used a portal that was radial to the EPL tendon (STT-R), along with the RMC, for arthroscopic debridement of isolated STT OA.12 They recommended a 1.5-cm skin incision to enable safe blunt dissection.
Methodology
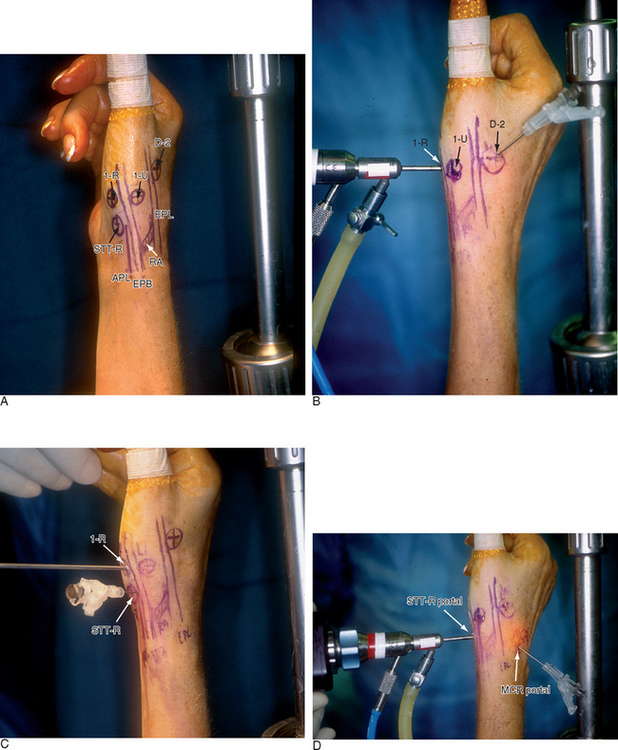
The patient is positioned supine on the operating table, with the arm extended on a hand table. The thumb is suspended by Chinese finger traps with 5 pounds of counter-traction, which forces the wrist into ulnar deviation. A traction tower facilitates this procedure, although any means of traction will suffice. The relevant landmarks are palpated and outlined, including the proximal and dorsal edge of the thumb metacarpal base, the APL and EPL tendons, and the radial artery in the snuffbox.
To establish the D-2 portal, the junction of the base of the index and thumb metacarpal is palpated just distal and ulnar to the extensor pollicus longus (EPL) tendon. The entry site is marked, with the tourniquet down to allow palpation or Doppler of the radial artery. A 22-gauge needle is inserted at this juncture, angling proximally radial and palmar to penetrate the joint space (which is viewed from the 1-R or 1-U portal). A small skin incision is made and tenotomy scissors are used to spread the soft tissue and pierce the joint capsule. This is followed by use of a blunt trocar and cannula and then the arthroscope (or hook probe, motorized shaver, or 2.9-mm bur) (Figure 2.3a through e).
1 Menon J. Arthroscopic evaluation of the first carpometacarpal joint. J Hand Surg [Am]. 1998;23:57.
2 Menon J. Arthroscopic management of trapeziometacarpal joint arthritis of the thumb. Arthroscopy. 1996;12:581-587.
3 Berger RA. A technique for arthroscopic evaluation of the first carpometacarpal joint. J Hand Surg [Am]. 1997;22:1077-1080.
4 Bettinger PC, Berger RA. Functional ligamentous anatomy of the trapezium and trapeziometacarpal joint (gross and arthroscopic). Hand Clin. 2001;17:151-168. vii
5 Orellana MA, Chow JC. Arthroscopic visualization of the thumb carpometacarpal joint: Introduction and evaluation of a new radial portal. Arthroscopy. 2003;19:583-591.
6 Walsh EF, Akelman E, Fleming BC, DaSilva MF. Thumb carpometacarpal arthroscopy: A topographic, anatomic study of the thenar portal. J Hand Surg [Am]. 2005;30:373-379.
7 Steinberg BD, Plancher KD, Idler RS. Percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation through the snuff box: An anatomic study. J Hand Surg [Am]. 1995;20:57-62.
8 Slutsky DJ. The use of a dorsal distal portal in trapeziometacarpal arthroscopy. Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery. In press 2007.
9 Bowers WH. Arthroscopic anatomy of the wrist. In: McGinty J, editor. Operative Arthroscopy. New York: Raven Press; 1991:613-623.
10 Carro LP, Golano P, Farinas O, Cerezal L, Hidalgo C. The radial portal for scaphotrapeziotrapezoid arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2003;19:547-553.
11 Bare J, Graham AJ, Tham SK. Scaphotrapezial joint arthroscopy: A palmar portal. J Hand Surg [Am]. 2003;28:605-609.
12 Ashwood N, Bain GI, Fogg Q. Results of arthroscopic debridement for isolated scaphotrapeziotrapezoid arthritis. J Hand Surg [Am]. 2003;28:729-732.