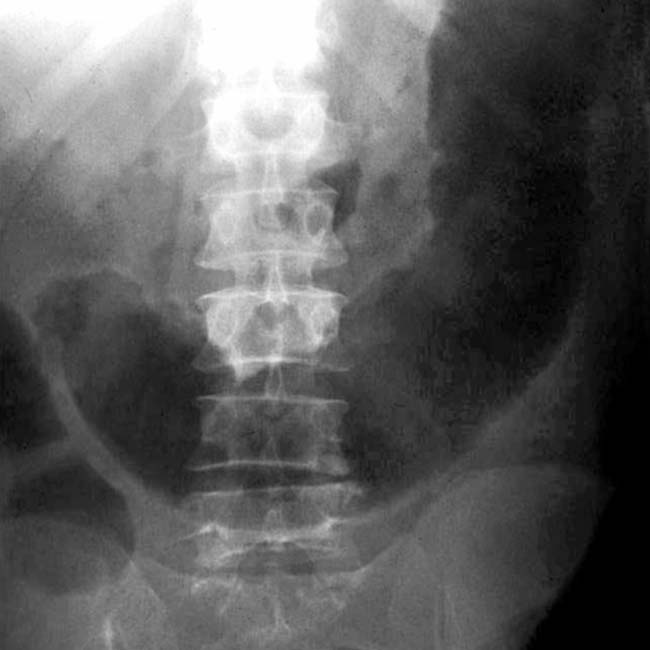
Transverse colonic folds may be thickened (edema or hemorrhage), or lost (sloughed mucosa and submucosa)
 .
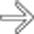
.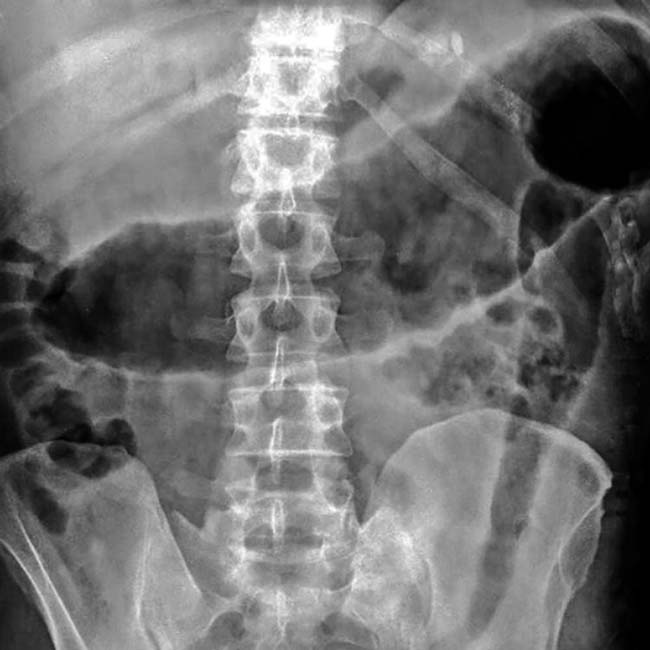
 , marked dilation of the colon with loss of transverse folds, and intraluminal high-density material
, marked dilation of the colon with loss of transverse folds, and intraluminal high-density material 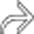 representing hemorrhage and sloughed mucosa.
representing hemorrhage and sloughed mucosa.
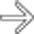
 . The colon
. The colon 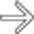 is massively distended with blood and debris and its wall is relatively thin. Soon after this scan, the colon perforated and a total colectomy was required.
is massively distended with blood and debris and its wall is relatively thin. Soon after this scan, the colon perforated and a total colectomy was required.
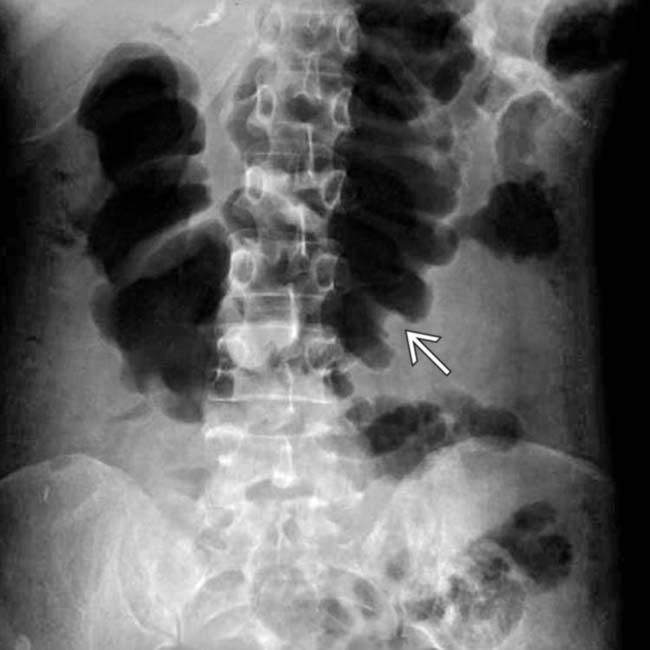
 , suggesting mucosal sloughing or pseudopolyps.
, suggesting mucosal sloughing or pseudopolyps.
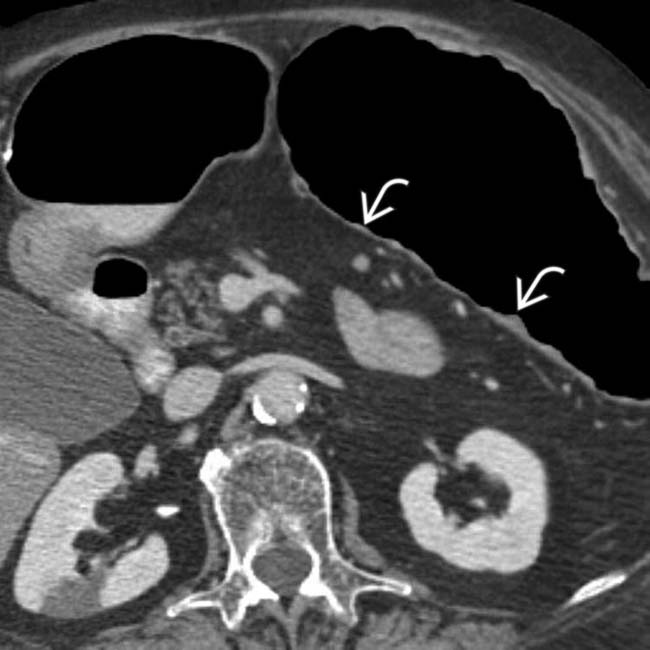
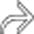 within the dilated, thin-walled transverse colon.
within the dilated, thin-walled transverse colon.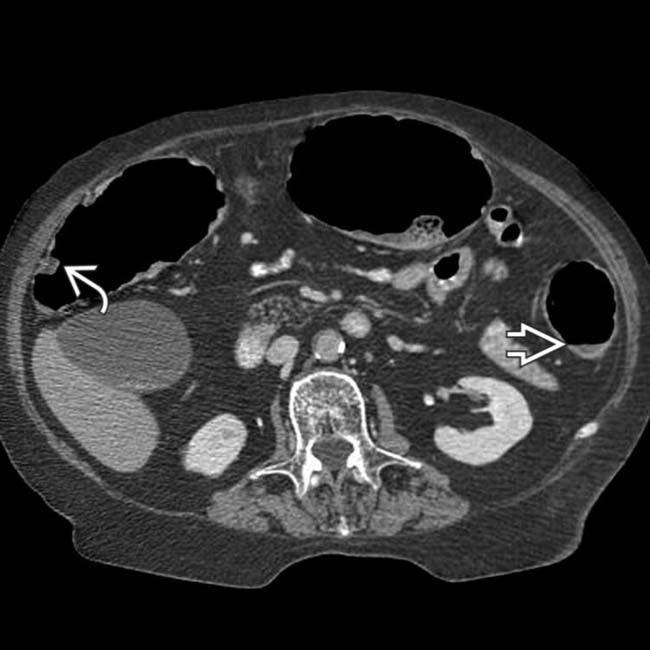
 , distention and thinning of the walls of the colon, as well as more mucosal pseudopolyps
, distention and thinning of the walls of the colon, as well as more mucosal pseudopolyps  .
.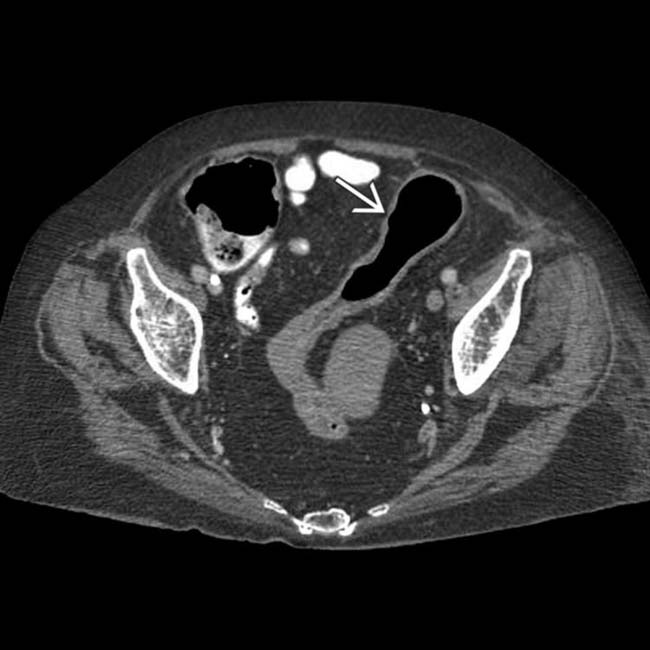
 . Because of symptoms that were refractory to medical management, as well as these CT findings, the patient had a total colectomy.
. Because of symptoms that were refractory to medical management, as well as these CT findings, the patient had a total colectomy.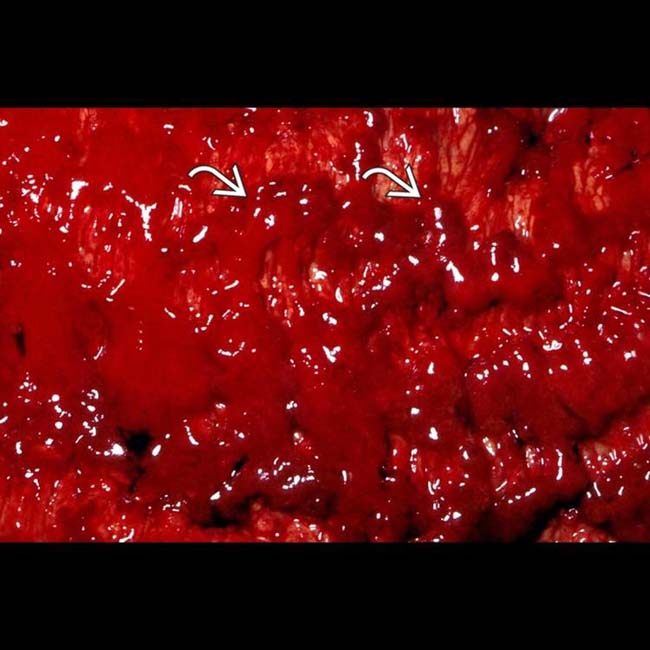
 in a case of toxic megacolon.
in a case of toxic megacolon.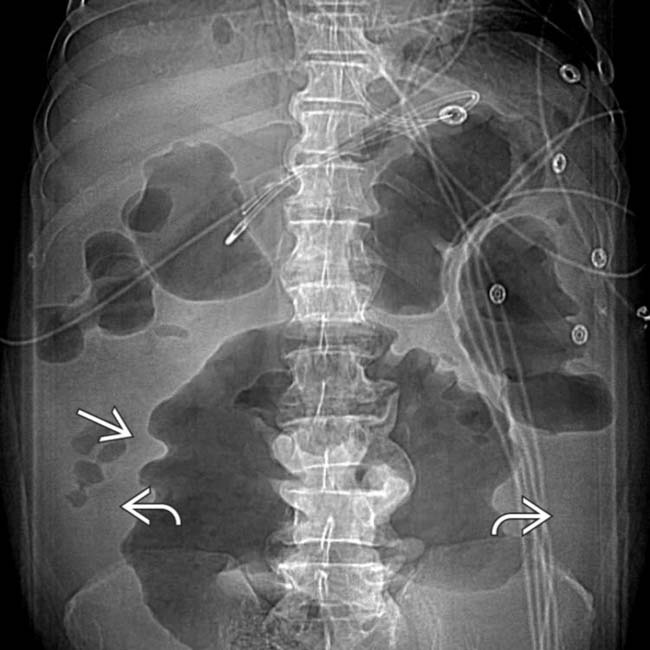
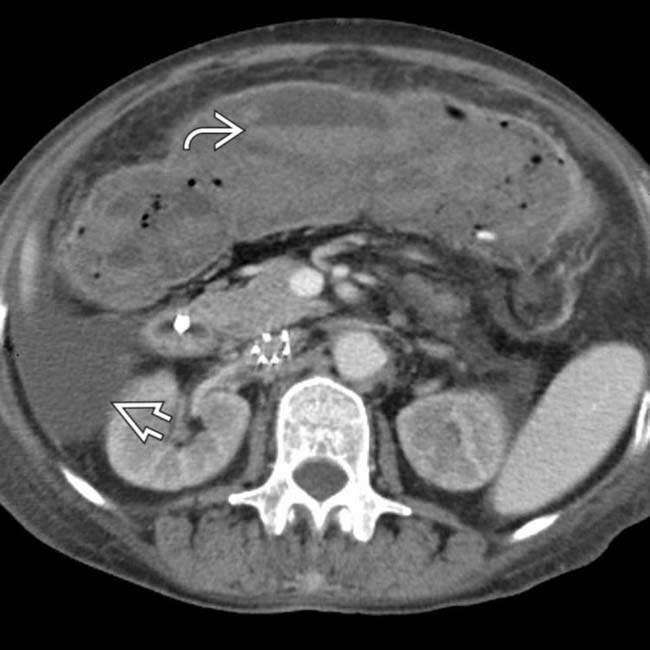
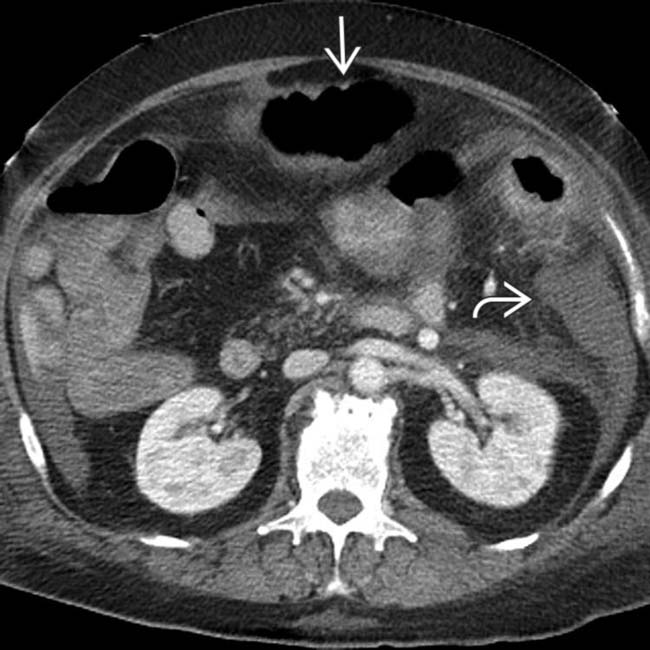
 due to ascites. The colon is diffusely dilated with a loss of the normal transverse fold pattern. The folds that are seen are grossly thickened and have a “thumbprint” appearance
due to ascites. The colon is diffusely dilated with a loss of the normal transverse fold pattern. The folds that are seen are grossly thickened and have a “thumbprint” appearance  .
.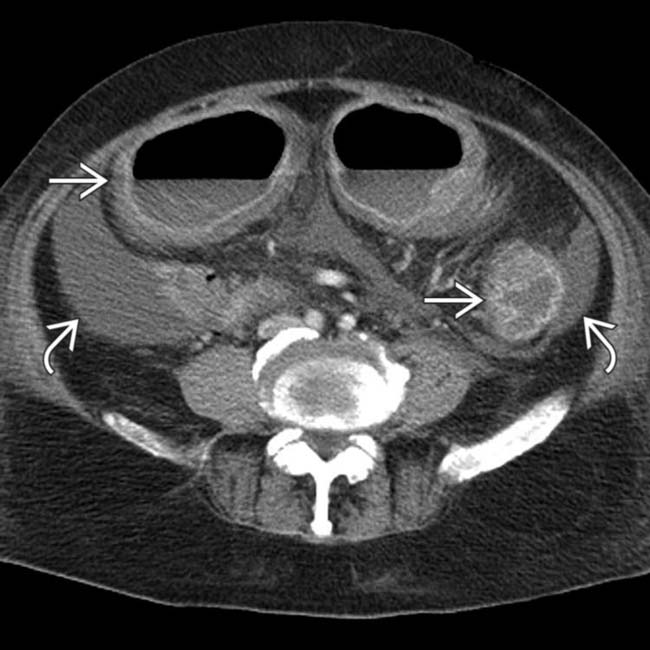
 . No normal transverse folds are evident. Ascites fills the paracolic gutters
. No normal transverse folds are evident. Ascites fills the paracolic gutters  , accounting for the bulging flanks seen on plain films.
, accounting for the bulging flanks seen on plain films.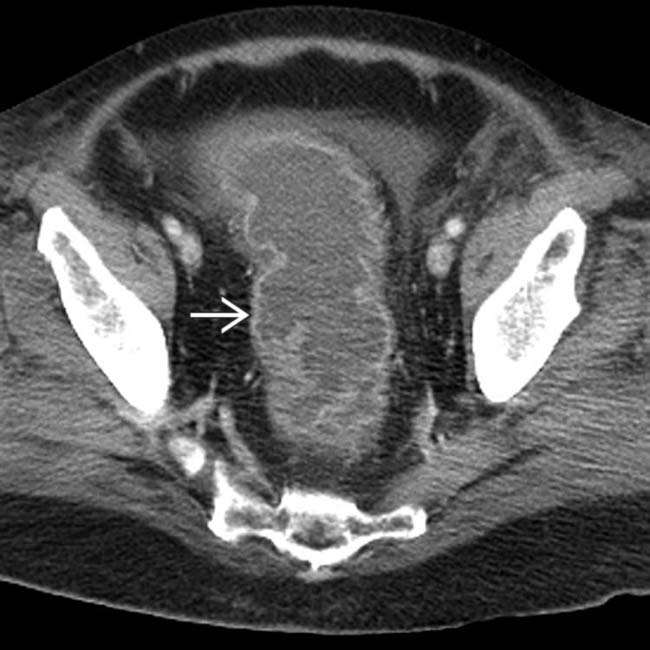
 .
.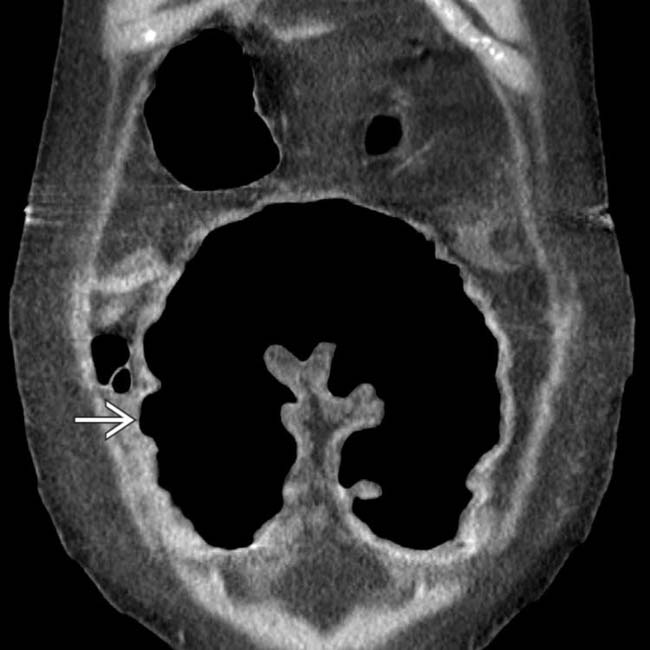
 with a complete loss of its normal transverse fold pattern.
with a complete loss of its normal transverse fold pattern.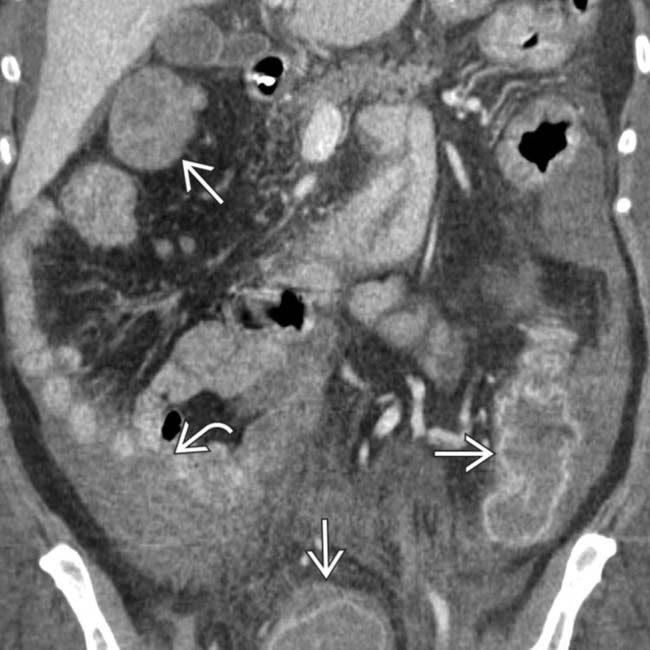
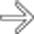
 and ascites
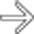
and ascites  . These CT and clinical features are classic for toxic megacolon due to infectious colitis (C. difficile), confirmed at urgent colectomy. The colonic mucosa showed extensive necrosis and sloughing, but no frank perforation was found.
. These CT and clinical features are classic for toxic megacolon due to infectious colitis (C. difficile), confirmed at urgent colectomy. The colonic mucosa showed extensive necrosis and sloughing, but no frank perforation was found.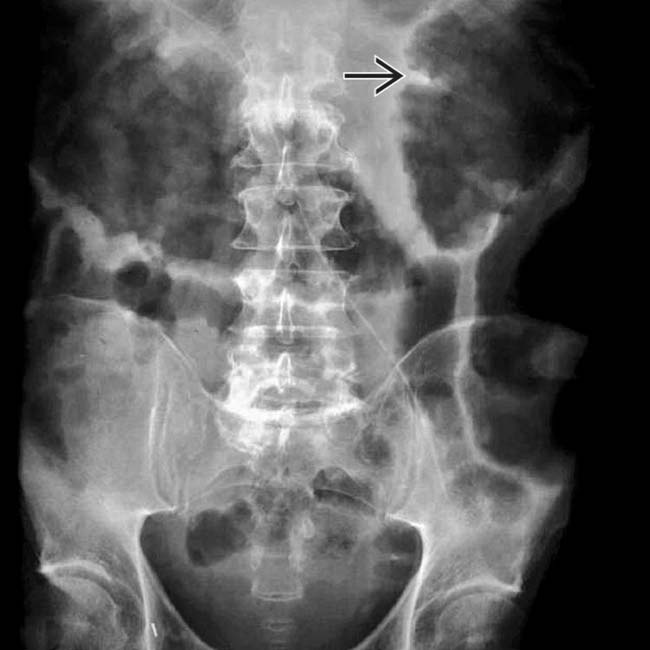
 due to subserosal and omental edema.
due to subserosal and omental edema.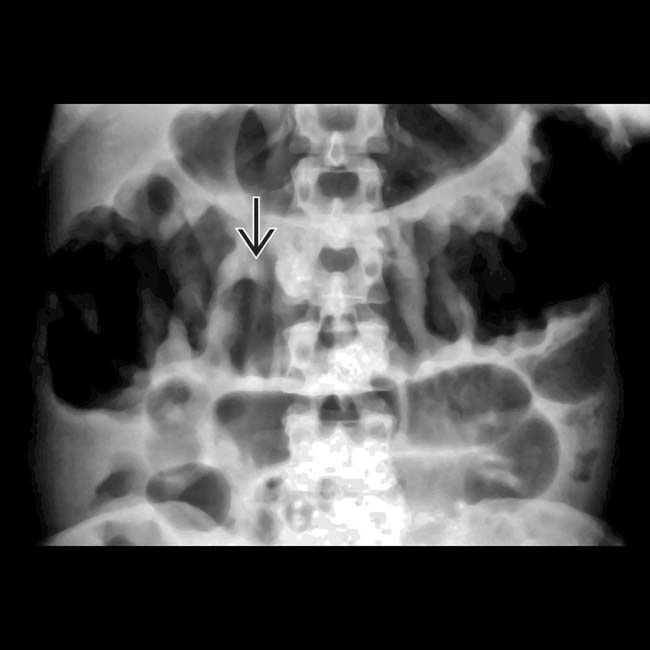
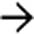 .
.
 .
.
 indicating edematous mucosa.
indicating edematous mucosa.



























 and colonic distension
and colonic distension  .
.