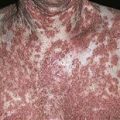
76
Tinea of the groin
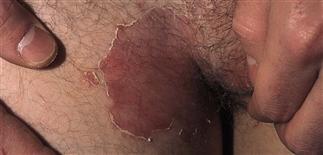
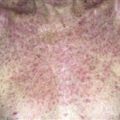
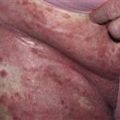
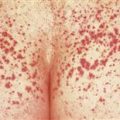
Infection starts in inguinal crease and spreads on to thigh. One or both sides involved. Many patients are unaware of infection. Fine scale is present over surface; well-defined scaling border shown.
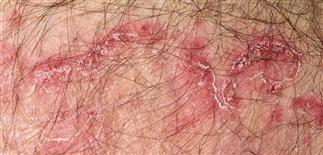
Fungal infections slowly progress. The advancing border is red with a fringe of scale. To obtain a specimen for potassium hydroxide examination, scrape the border scale with a #15 surgical blade.
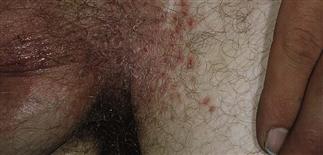
Think of Candida infections if patient presents with erythema in the groin extending to scrotum and thigh. Satellite pustules can occur with tinea; more common in acute yeast infection.

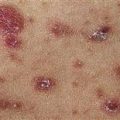
Erythrasma is a bacterial infection that looks like tinea. The brown-red patches fluoresce coral red under a Wood’s light. Prescribe topical clindamycin or benzoyl peroxide wash.
DESCRIPTION
Fungal infection of the crural fold that slowly migrates on to the thighs is known as tinea cruris or ‘jock itch.’
HISTORY
• Common in adult men, occasionally seen in obese women, rare in children. • Many infections are asymptomatic. Itching increases when inflamed. • Warmth and perspiration in summer and multiple layers of clothing in winter predispose to infection. Acute inflammation may appear shortly after wearing tight clothing. • Steroid creams provide temporary relief but will alter the typical presentation. Bizarre patterns of inflammation called tinea incognito may result. Prolonged use of steroid creams or combination steroid-antifungal preparations (e.g. Lotrisone) can cause striae. This is an irreversible change.
PHYSICAL FINDINGS
• A unilateral or bilateral half-moon-shaped patch with a well-defined scaling, and sometimes a vesicular border, begins in the crural fold and slowly extends onto thighs. Skin within the border turns red-brown, is less scaly, and may develop papules. • The infection can extend onto the buttocks and gluteal cleft. The scrotum is rarely involved. This is in contrast to Candida infections, which extend on to the thigh and scrotum and show pustules beyond the border. • Intertrigo from irritation is symmetric, involving both inner thigh and scrotum. There is no active scaling border. Psoriasis resembles intertrigo. • Erythrasma caused by Corynebacterium minutissimum infection presents as a brown, half-moon-shaped plaque with a fine scale on the surface. Wood’s light examination shows a coral-red fluorescence. • A clinical diagnosis of tinea will be made in many cases. Specimens for potassium hydroxide examination should be taken from the advancing scaling border.
TREATMENT
• Infection improves or clears if warmth and moisture are eliminated. • Most over-the-counter antifungal creams are effective. Use creams that are active against both Candida species and dermatophyte fungi (econazole, ketoconazole, miconazole, clotrimazole). Apply twice daily for 10–14 days. • Moist, itching infections improve rapidly with a cool, wet, tap water or Burow’s dressing for 20–30 min two to six times daily until skin has been dried. • Resistant infections respond to itraconazole 200 mg b.i.d. for 1–2 weeks, terbinafine 250 mg q.d. for 1–2 weeks, or fluconazole 150 mg once a week for 2–4 weeks. • Steroid creams may be used for a few days to control acute inflammation. Limit the amount prescribed. Infection may get worse and striae will form with chronic or repetitive use. • Absorbent powders, not necessarily medicated (Zeasorb), help control moisture and prevent reinfection.