Thyroid pathophysiology
Introduction
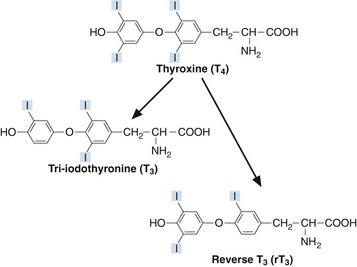
Thyroxine (T4) and tri-iodothyronine (T3) are together known as the ‘thyroid hormones’. They are synthesized in the thyroid gland by iodination and coupling of two tyrosine molecules whilst attached to a complex protein called thyroglobulin. T4 has four iodine atoms while T3 has three (Fig 44.1).
Goitre
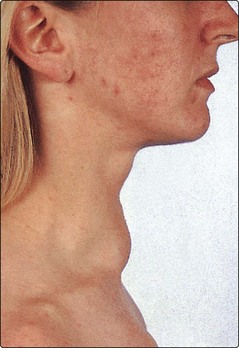
A goitre is an enlarged thyroid gland (Fig 44.2). This may be associated with hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism or a euthyroid state. Globally, iodine deficiency is the commonest cause of goitre. The WHO estimates that approximately 2 billion people have an inadequate iodine intake making it the commonest preventable cause of neuro-developmental problems. In many developed countries this problem has been overcome by the addition of iodine to a staple food such as iodised salt.
Thyroid function tests
 TSH. Measurement of TSH is a good example of how better technology has helped in the diagnosis and monitoring of disease. Early assays for TSH were unable to measure low concentrations of the hormone – the detection limits of the radioimmunoassays overlapped significantly with concentrations of the low end of the reference interval in healthy subjects. Now, very sensitive TSH assays can detect much lower concentrations and it is possible to tell with a greater degree of certainty whether TSH secretion really is lower than normal.
TSH. Measurement of TSH is a good example of how better technology has helped in the diagnosis and monitoring of disease. Early assays for TSH were unable to measure low concentrations of the hormone – the detection limits of the radioimmunoassays overlapped significantly with concentrations of the low end of the reference interval in healthy subjects. Now, very sensitive TSH assays can detect much lower concentrations and it is possible to tell with a greater degree of certainty whether TSH secretion really is lower than normal.
 Total T4 or free T4. Following the introduction of replacement thyroxine or of anti-thyroid treatment, e.g. carbimazole, or indeed following any alteration in dosage, TSH may take many weeks to unsuppress and adjust to its new level. During this time, it is essential to have some estimate of T4 status. This applies particularly to the monitoring of anti-thyroid treatment; patients can become profoundly hypothyroid quite quickly.
Total T4 or free T4. Following the introduction of replacement thyroxine or of anti-thyroid treatment, e.g. carbimazole, or indeed following any alteration in dosage, TSH may take many weeks to unsuppress and adjust to its new level. During this time, it is essential to have some estimate of T4 status. This applies particularly to the monitoring of anti-thyroid treatment; patients can become profoundly hypothyroid quite quickly.
 Total T3 or free T3. Occasionally it may be useful to have an estimate of T3 status in addition to T4. In hyperthyroidism, the rise in T3 is almost always disproportionate to the rise in T4; an estimate of T3 status may permit earlier identification of thyrotoxicosis. In some patients only the T3 rises – the T4 remains within the reference interval (T3 toxicosis).
Total T3 or free T3. Occasionally it may be useful to have an estimate of T3 status in addition to T4. In hyperthyroidism, the rise in T3 is almost always disproportionate to the rise in T4; an estimate of T3 status may permit earlier identification of thyrotoxicosis. In some patients only the T3 rises – the T4 remains within the reference interval (T3 toxicosis).
 Antibodies. The titre of autoantibodies to thyroid tissue antigens may be helpful in the diagnosis and monitoring of autoimmune thyroid disease. Anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) may be useful in hypothyroidism and stimulating thyroid receptor antibodies in thyrotoxicosis.
Antibodies. The titre of autoantibodies to thyroid tissue antigens may be helpful in the diagnosis and monitoring of autoimmune thyroid disease. Anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) may be useful in hypothyroidism and stimulating thyroid receptor antibodies in thyrotoxicosis.
Drugs and the thyroid
Various drugs affect thyroid function tests. The effects of some of these are summarized in Table 44.1.
Table 44.1
Drugs affecting thyroid function tests
| Drug | Mechanism | Major effects |
| Amiodarone | Reduced peripheral deiodination Amiodarone can also stimulate or inhibit release of thyroid hormones from thyroid |
↑T4,↓T3, transient ↑ in TSH Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism |
| Lithium | Reduced thyroid uptake of iodine Reduced release of thyroid hormone |
Goitre Hypothyroidism |
| Anticonvulsants (phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital) | Displace T4 and T3 from binding proteins | ↑ free T4, ↑ free T3 |
| Heparin | Releases lipoprotein lipase into plasma with resultant increase in free fatty acids. These displace T4 and T3 from binding proteins | ↑ free T4, ↑ free T3 |
| Aspirin | In high concentrations displaces T4 from transthyretin | ↑ free T4 |