Recent Posts
- Beyond the Hospital Bed: Why the Home is the Next Frontier in Senior Recovery
- More Than Just a Chart: Why Specialized Technology Matters in Modern Pediatrics
- Relationship Clarity Across Leading Psychic Websites
- The Role of Assisted Living in Managing Chronic Conditions in Older Adults
- What Is Asthma Caused By?
Categories
- Allergy and Immunology
- Anesthesiology
- Basic Science
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Cardiovascular
- Complementary Medicine
- Critical Care Medicine
- Dermatology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Hematology, Oncology and Palliative Medicine
- Internal Medicine
- Medical Education
- Neonatal – Perinatal Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nursing & Midwifery & Medical Assistant
- Obstetrics & Gynecology
- Opthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pathology
- Pediatrics
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Plastic Reconstructive Surgery
- Psychiatry
- Pulmolory and Respiratory
- Radiology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Surgery
- Test
Home » Thoracic Lymph Nodes
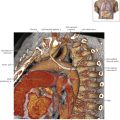
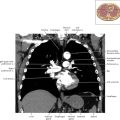
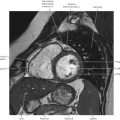
Thoracic Lymph Nodes
Published on 13/02/2015 by admin
Filed under Cardiothoracic Surgery
Last modified 22/04/2025
Print this page