Chapter 18 The Menopause
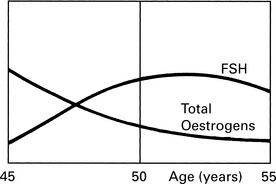
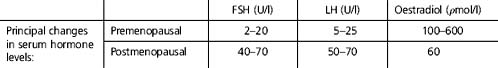
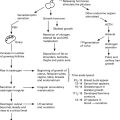
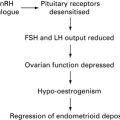
The menopause
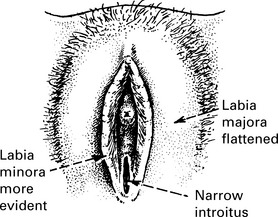
Changes in the genital tract
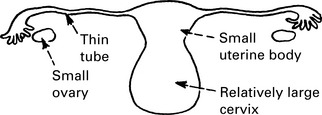
Uterus: The uterus becomes small with a relatively large cervix – a return to infantile proportions.
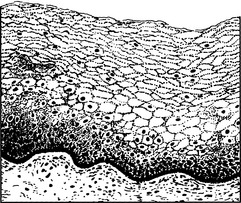
Normal premenopausal vaginal epithelium. Note the thick cornified layer.
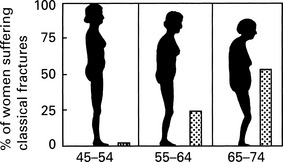
Osteoporosis
Risk factors for osteoporosis are:
Bone Densitometry
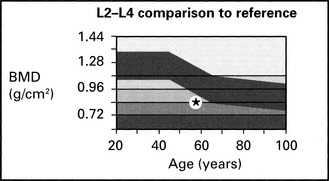
| L2–L4 BMD (g/cm2) | 0.809 ± 0.01 |
| L2–L4% young adult | 67 ± 3 |
| L2–L4% age matched | 79 ± 3 |
At –3.26 SD of young adult, there is definite osteoporosis of lumbar spine
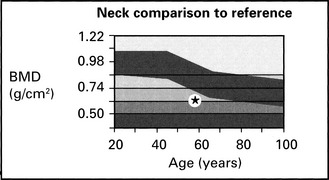
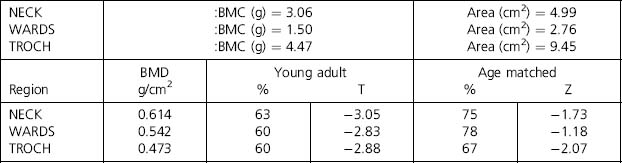
| Neck BMD (g/cm2) | 0.614 ± 0.02 |
| Neck % young adult | 63 ± 3 |
| Neck % age matched | 75 ± 3 |
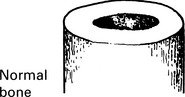
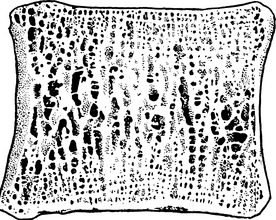
Osteoporosis at all three sites in this hip
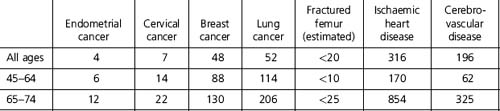
Cardiovascular disease and the menopause
Carbohydrate metabolismoestrogen reduced insulin resistance.
Hormone replacement therapy
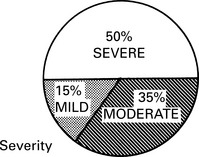
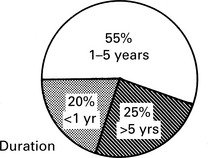
Severity of symptoms and quality of life
| Contraindications | Relative contraindications |
| Pregnancy | Cerebrovascular accident |
| Uninvestigated abnormal vaginal bleeding | Severe migraine |
| Breast cancer or other oestrogen-dependent tumour | Thrombophilia |
| Venous thromboembolic disease | |
| Myocardial infarction or unstable angina | |
| Severe liver disease |
Screening
Screening before and on HRT is similar to well-woman screening.
Women should be encouraged to take part in national breast and cervical screening programmes.
Pelvic examination should be performed only where clinically indicated.
Pros and cons of different routes
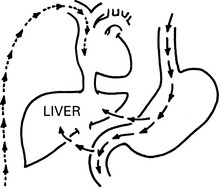
Oral
Transdermal and Percutaneous
Vaginal Preparations
Potent oestrogens given vaginally have systemic effects.
Vaginal preparations relieve atrophic vaginitis, trigonitis, vaginal dryness and dyspareunia.