Chapter 127 The Complement System
The complement system, an essential component of innate immunity, is broadly conceptualized as the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways, which interact and depend on each other for their full activity; the membrane attack complex (C5b6789), formed from activity of any pathway; the 8 serum and 4 membrane regulatory proteins that are defined to date; and 8 fully defined cell membrane receptors that bind complement components or fragments (Table 127-1). The 27 circulating components and regulators together compose about 15% of the globulin fraction of serum. The normal concentrations of serum complement components vary by age (Chapter 708); newborn infants have mild to moderate deficiencies of all components.
Table 127-1 CONSTITUENTS OF THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM
SERUM COMPONENTS
Classical Pathway
C1q
C1r
C1s
C4
C2
C3
Alternative Pathway
Factor B
Factor D
Lectin Pathway
Mannose-binding lectin (MBL), ficolins 1, 2, 3 (M, L, H, respectively)
MBL-associated serine proteases (MASPs) 1, 2
Membrane Attack Complex
C5
C6
C7
C8
C9
Regulatory Protein, Enhancing
Properdin
Regulatory Proteins, Downregulating
C1 inhibitor (C1 INH)
C4-binding protein (C4-bp)
Factor H
Factor I
S protein (vitronectin)
Clusterin
Carboxypeptidase N (anaphylatoxin inactivator)
MEMBRANE REGULATORY PROTEINS
CR1 (CD35)
Membrane cofactor protein (MCP; CD46)
Decay-accelerating factor (DAF, CD55)
CD59 (membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis; protectin)
MEMBRANE RECEPTORS
CR1 (CD35)
CR2 (CD21)
CR3 (CD11b/CD18)
CR4 (CD11c/CD18)
C3a receptor
C5a receptor
C1q receptors
Complement receptor of the Ig superfamily (CRIg)
CR, complement receptor; Ig, immunoglobulin.
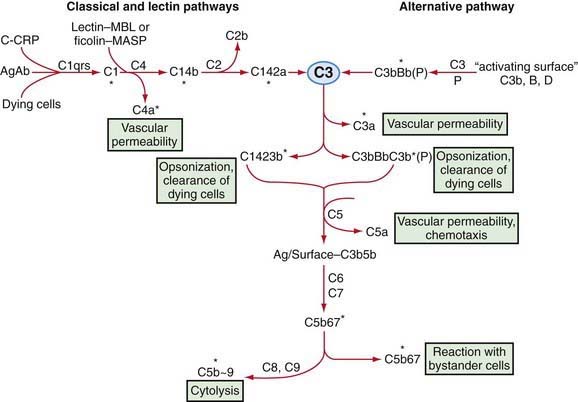
Complement is a system of interacting proteins. The biologic functions of the system depend on the interactions of individual components, which occur in sequential, cascade fashion. Activation of each component, except the 1st, depends on activation of the prior component or components in the sequence. Interaction occurs along three pathways (Fig. 127-1): the classical pathway, in the order antigen–antibody–C142356789; the lectin (carbohydrate-binding) pathway, in the order microbial carbohydrate–lectin (mannose-binding lectin [MBL] or ficolin)–MBL-associated serine protease–C42356789; and the alternative pathway, in the order activator–C3bBD–C356789. Antibody accelerates the rate of activation of the alternative pathway, but activation can occur on appropriate surfaces in the absence of antibody. The classical and the alternative pathways interact with each other through the ability of both to activate C3.
Alternative Pathway
Certain “activating surfaces” promote alternative pathway activation if C3b is fixed to them, including bacterial teichoic acid or endotoxin, virally infected cells, antigen-IgA complexes, and cardiopulmonary bypass and renal dialysis membranes. These surfaces act by protecting the C3bBb enzyme from the control otherwise exercised by factors I and H. Rabbit red blood cell membrane is such a surface, which serves as the basis for an assay of serum alternative pathway activity. Endotoxin may alter normally “nonactivating” cell surfaces in vivo so that C3bBb is relatively protected from inactivation, which may partially explain the activation of complement in patients with gram-negative bacteremia. Sialic acid on the surface of microorganisms or cells prevents formation of an effective alternative pathway C3 convertase by promoting activity of factors I and H. Nevertheless, significant activation of C3 can occur through the alternative pathway, and the resultant biologic activities are qualitatively the same as those achieved through activation by C142 (see Fig. 127-1).
Participation in Host Defense
Neutralization of endotoxin in vitro and protection from its lethal effects in experimental animals require C1 INH and later-acting components of complement, at least through C6. Finally, activation of the entire complement sequence can result in lysis of virus-infected cells, tumor cells, and most types of microorganisms. Bactericidal activity of complement has not appeared to be important to host defense, except for the occurrence of Neisseria infections in patients lacking later-acting components of complement (Chapter 128).
Karp DR, Holers VM. Complement in health and disease. In: Goldman L, Ausiello D, editors. Cecil medicine. ed 23. Philadelphia: Saunders/Elsevier; 2008:282-288.
Murphy K, Travers P, Walport M, editors. Janeway’s immunobiology, ed 7. Garland Science, New York, 2008;61-82.
Perry VH, O’Connor V. C1q: the perfect complement for a synaptic feast? Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:807-811.
Sjoberg AP, Trouw LA, Blom AM. Complement activation and inhibition: a delicate balance. Trends Immunol. 2008;30:83-90.