Chapter 26 The Assessment and Management of Posterolateral Instability
Introduction
The high congruency of the bony structures forming the elbow, make the elbow an inherently stable joint. The stabilizing system provided by the osseous architecture and the balanced intact musculature which provides dynamic or active joint stability, is supported by strong capsule-ligamentous structures on the lateral and medial side of the elbow joint.1–6 In full flexion and extension of the elbow, the primary stability is provided by the osseous articulation, whereas the capsule-ligamentous stabilizers are the primary stabilizers in all semi-flexed positions, providing maximal stability at 90° of joint flexion.3,5–8
The most common cause of ligamentous injury of the elbow joint resulting in instability is an elbow dislocation. In adults, the elbow joint is the second most commonly dislocated major joint after the shoulder and is the most commonly dislocated joint in the paediatric age group. The incidence of elbow dislocation in the general population is estimated to be 6/100 000.4
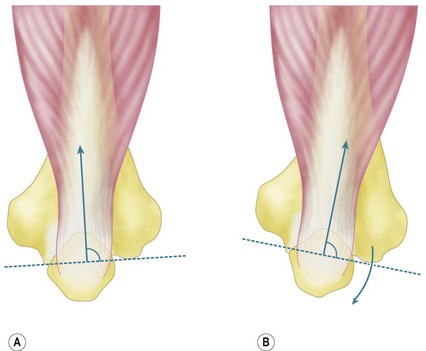
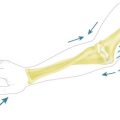
Posttraumatic chronic ligamentous instability can be divided into medial or valgus instability, postero-medial instability and posterolateral rotatory instability (PLRI). As the signs and symptoms of these entities are often subtle, the examiner must have a high index of suspicion and a thorough knowledge of the symptoms and expected findings at physical examination in order to make the diagnosis. Persistent insufficiency of the lateral collateral ligament complex (LCLC) (especially the ulnar part – the lateral ulnar collateral ligament (LUCL)) results in PLRI (Fig. 26.1A). Insufficiency of the medial collateral ligament (MCL), in particular the anterior part or AMCL, results in valgus instability (Fig. 26.1B).
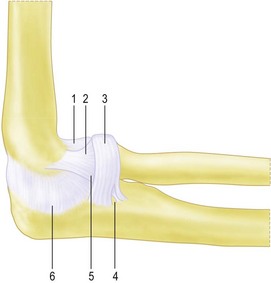
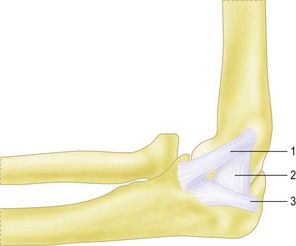
Figure 26.1 (A) The lateral collateral ligament complex (LCLC). This complex consists of:
2.Radial collateral ligament (RCL).
4.Interval between annular ligament and lateral ulnar collateral ligament (LUCL).
(B) The medial collateral ligament complex (MCLC). This complex consists of:
1.Anterior medial collateral ligament (AMCL).
Background/aetiology
During a posterolateral dislocation of the elbow joint, rupture of the ligamentous complex occurs in a circle from lateral to medial, as described by O’Driscoll et al; in stage I, the LUCL is disrupted; in stage II, the other lateral ligamentous structures as well as the anterior and posterior capsule are torn. In stage III disruption of the medial collateral ligament can be partial with disruption of the posterior bundle only (IIIA) or complete (IIIB).4
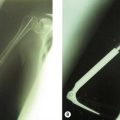
In a cubitus varus deformity the triceps contraction has been hypothesized to result in asymmetrical loading of the joint resulting in attenuation of the LCLC (Fig. 26.2). If surgical reconstruction is considered in these cases of complex instability a LCLC reconstruction alone will not restore stability. A valgus osteotomy to correct the varus deformity, in addition to a LCLC reconstruction, should be considered and is essential if the varus deformity is more than 20°. Experimental data in cadavers have shown increased strain on the LCLC with more than 25° of varus angulation and increased opening of the joint line space with more than 20° of varus angulation. In the preoperative work-up an assessment of the malunion in three directions is mandatory. Evaluation with a computed tomography (CT) scan of the injured and the uninjured complete humerus is necessary to determine the rotational deformity.
During surgery, the deformity is corrected in valgus, flexion or extension and rotation, depending on the preoperative assessment. Finally, iatrogenic injury as a result of surgery to the lateral side of the elbow or repeated steroid injections can result in injury to the LCLC (Table 26.1).
Table 26.1 Aetiology of lateral collateral ligament insufficiency
| Trauma | Postero-lateral dislocation of the elbow joint |
| Fracture dislocation | |
| Elbow subluxation | |
| Sprain/varus injury | |
| Chronic attenuation | Longstanding cubitus varus deformity with or without trauma |
| Longstanding inflammation of the elbow | |
| Chronic crutch users | |
| Iatrogenic | Following lateral elbow surgery, i.e. tennis elbow release or arthrolysis |
| Repeated steroid injections |
Iatrogenic lesions primarily occur after release of the common extensor tendon to treat chronic lateral epicondylitis. The ligament complex is particularly at risk in cases where ‘minimal invasive techniques’ or percutaneous techniques have been used as the surgical procedure. It is of utmost importance that surgeons are aware of the ligamentous anatomy, in order to preserve the ligament during elbow surgery. If transsection of the LCLC occurs during surgery or release of the insertion of the LCLC is necessary during a surgical procedure, the surgeon should repair the ligament as anatomically as possible. The LCLC is the primary capsular-ligamentous stabilizer of the elbow joint to varus and external rotation.3–9
The mean length of the LCLC from its origin to the annular ligament is 20 mm, and the width is approximately 8 mm.10 The insertion point on the lateral epicondyle is at the isometric point for the flexion and extension axis, and therefore the ligament is uniformly taut in the entire flexion axis.2,10 The functional anatomy of the ligament indicates that there is a superior and inferior part to the ligament and only complete division induces clinically significant joint laxity.5,6,8 The ligament complex is covered by the anconeus muscle, the supinator tendon and the musculo-tendinous insertion of the extensor carpi ulnaris and the extensor digitorum.9,10 Cohen and Hastings showed that the musculo-tendinous insertion of the extensor carpi ulnaris and the extensor digitorum covered the ligament and provided an additional stabilizing effect for the LCLC.9
A broad band originates from the undersurface of the lateral epicondyle and inserts fan-shaped into the annular ligament. This band constitutes the LCL and the LUCL. The fibres of the LUCL component, being the most posterior, pass through the annular ligament and insert on the ulna with fibres from the most inferior part of the annular ligament, inconsistently named the accessory collateral ligament.2,8,9,11,12 The insertion on the proximal part of the supinator crest, is separated from the annular ligament by a small triangular space.5,8,11 The annular ligament originates from the anterior and posterior margins of the lesser sigmoid notch and passes around the radial head, maintaining contact between the radial head and the ulna.10 In PLRI, the proximal radioulnar joint is intact. Laxity or avulsion of the ulnar part of the lateral collateral ligament leads to an increase in external rotation of the ulnohumeral joint.5 This increase in external rotation results in a secondary posterior subluxation of the radial head. This secondary subluxation, with an intact proximal radioulnar joint, must be differentiated from isolated posterior head subluxation with disruption of the proximal radioulnar joint and an intact ulnohumeral joint.13
Associated injuries with elbow dislocations are common; radial head and neck fractures occur in 5–10%, avulsions of fragments from the medial or lateral epicondyle occurs in 12% and fractures of the coronoid process occur in 10% of all dislocations. The reverse is also true and fractures around the elbow can be associated with ligamentous injury. Van Riet and Morrey in a study of an American population noted injury to the LCLC in 35 of 88 patients with radial head fractures14 and similar results were also noted in a Dutch study.15 The incidence of associated, ligamentous injuries in radial head fractures is high, especially in Mason type 3 and 4 injuries. The treating physician should be aware of this and should perform a thorough physical examination of the upper limb in every patient with a radial head fracture.
Presentation, investigation and treatment options
Clinical signs and symptoms of patients with an insufficiency of the LCLC vary depending on the severity of the instability, associated injuries such as radial head or coronoid fractures, and activity levels. In rare cases of LCLC insufficiency recurrent frank elbow dislocations occur. However, more often the symptoms and clinical signs of insufficiency are more subtle. It is important therefore, if an accurate diagnosis is to be made, that the surgeon is fully aware of the clinical symptoms and signs of LCLC insufficiency.16,17
Physical examination
The alignment of the elbow joint is examined in the anatomical position with the hands supinated and elbows extended. Axial alignment is assessed with the ‘carrying angle’, which is formed between the humerus and the forearm in the coronal plane. The average carrying angle is 10° for men and 15° for women although much variation exists based on age, race, sex and body weight.18–21
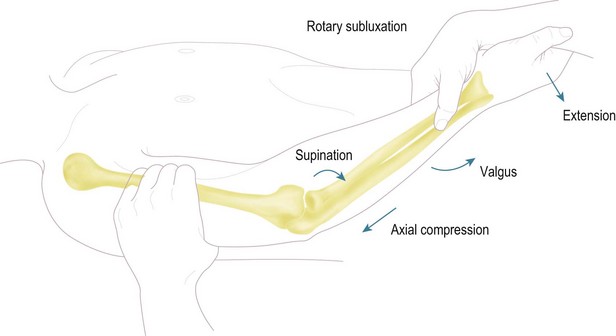
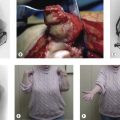
The medial and lateral ligament complexes should be tested in all patients. Pure varus stress does not allow reliable assessment of the lateral ligamentous structures. Several other physical examination manoeuvres have been described to test the LCLC.22 During the clinical examination, which will usually have a normal range of motion, the patient will often describe lateral elbow pain during forced external rotation in the semi-flexed elbow, or during the pivot shift manoeuvre described by O’Driscoll.16 This test involves applying a valgus, supination and axial load force to the elbow. As the elbow is extended, the radial head and ulna sublux from the humerus. During flexion the elbow relocates (Fig. 26.3).
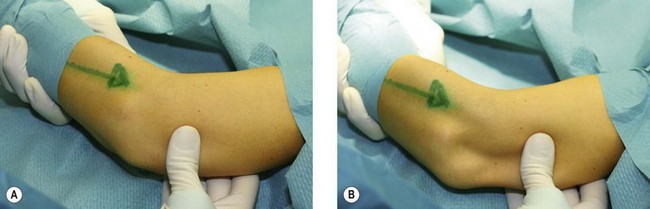
The subluxation can be seen as prominence of the radial head and dimpling of the skin between the proximal radius and humerus (Fig. 26.4). In the majority of patients this pivot shift is hard to elicit without anaesthesia although most patients with an insufficiency of LCLC report painful apprehension at 30–50° of joint flexion. Alternatively the ‘push up’ test described by Regan can be used to assess instability. The patient is asked to push their bodyweight out of an armchair while keeping the forearms in supination and shoulders abducted.23 If the patient has PLRI it is impossible to perform this test since extension of the elbow results in subluxation of the radiocapitellar joint.
A similar test is the ‘table top’ test. The patient reports apprehension when asked to perform a press-up with the elbow pointing laterally. Pain and apprehension occurs as the elbow reaches approximate 40° of flexion, and these symptoms improve or resolve when the test is repeated using the thumb of the examiner to push over the radial head, preventing posterior subluxation.24
In cases of doubt, evaluation under anesthesia in combination with arthroscopy can be performed. Positive results of the pivot shift test, posterolateral drawer test or fluoroscopically proven lateral joint line opening of more than 2 mm or fluoroscopically proven posterolateral subluxation support the diagnosis of insufficiency of the LCLC.22
Investigations
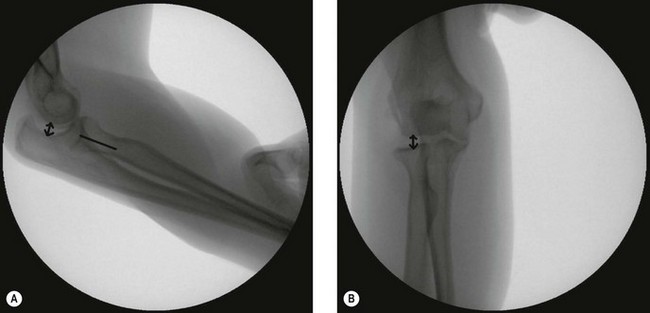
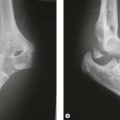
The diagnosis of LCLC insufficiency is made primarily by the history and physical findings. Imaging studies such as radiographs, dynamic radiographs and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) only serves to support the clinical suspicion of LCLC insufficiency. Classically, the elbow appears normal on anteroposterior (AP) radiographs. However, standard radiographs are mandatory to rule out associated pathology that includes radial head or coronoid fractures or malformation of the distal humerus, radial head or coronoid process. The axial malalignment of cubitus varus is easily detected on standard AP views, especially if compared with the uninjured side. In rare cases a static or fixed subluxation or dislocation of the elbow joint will be found on standard radiographs. In the minority of patients with insufficiency of the LCLC a bony avulsion of the LCLC is seen on a standard AP view, usually at the humeral side. In children this avulsion is, in most cases, an avulsion of the lateral apophysis. On lateral radiographs, the radial head may appear to be situated posteriorly to the capitellum, especially if the forearm is in full supination and in addition there may be slight widening of the radiohumeral joint. Stress radiographs performed under anesthesia can be useful. The integrity of the MCLC should be evaluated first; opening of the medial joint line by more than 2 mm indicates insufficiency of the medial ligamentous complex.25 Second, the forearm is placed in full supination and varus in order to determine the amount of lateral joint line opening. More than 2 mm indicates LCLC insufficiency. Finally, forced supination under valgus load is applied. In patients with LCLC injury, lateral fluoroscopy shows that the radial head is no longer aligned with the centre of the capitellum.
MRI and CT are not routinely used in the evaluation of the integrity of the LUCL.16 Some studies have identified selective deficiency of the LCLC, however, negative findings on MRI does not exclude insufficiency of the lateral ligamentous complex.26 MRI can be useful for the detection of chondral damage to the capitellum secondary to the recurrent subluxation of the radial head. CT will not contribute to the diagnosis of LCLC insufficiency but can be useful to assess osseous defects. Loose flecks of bone within the joint after a posterolateral dislocation usually indicate an avulsed fragment from the epicondyle or a fragment of the articular surface. Such fragments should be removed or replaced depending on the findings at the time of LCLC surgery.27
The assessment of the elbow under anaesthesia enables the pivot shift test and drawer sign to be appropriately performed in order to confirm the diagnosis (Fig. 26.4). In patients under anaesthesia these tests are universally positive in insufficiency of the LCLC.22 Fluoroscopy can be used to document the lateral joint line opening (more than 2 mm) or posterolateral subluxation (radial head is not aligned with the centre of the capitellum) (Fig. 26.5).
Treatment options
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment of a simple posterior dislocation of the elbow or acute isolated LCLC injury is advocated.16 Treatment consists of a short period (1–2 weeks) of immobilization with the forearm pronated in a long arm cast to control pain and stability After this period the elbow is assessed for stability. In stages 1–3a (see Introduction), in which the AMCL is intact and valgus stability is present progressive unlimited flexion and extension is permitted. In stage 3b the elbow is unstable in extension and a hinged brace in pronation is applied with an extension block of 30°. This extension block is gradually diminished to 0° over a period of 2–4 weeks. Adjustable flexion and extension splints can be used if a full range of motion has not been attained within 2–3 months after trauma. Rehabilitation of the LCLC deficient elbow should be performed with the forearm pronated and with avoidance of external rotatory and varus loads on the elbow.28 For the first 3 months after injury rotation of the forearm is advised only with the elbow flexed.
Surgical treatment
Acute LCLC deficiency
Acute ligamentous repair or reconstruction is only rarely necessary.29 It is indicated for persistent instability that does not permit early motion. It usually occurs in combination with fractures of the radial head or coronoid process. Refixation or an imbrication procedure are appropriate. The origin of the LCLC is elevated and re-sutured to the isometric point on the lateral epicondyle with heavy sutures. These sutures can be passed through the anatomical insertion on the humeral side using bone tunnels or the ligament can be reattached with bone anchors. If following repair, concern remains regarding the stability of the elbow, a hinged external fixator can be applied.30
Chronic LCLC deficiency
In chronic LCLC deficiency with recurrent dislocations or subluxations, there is no role for conservative treatment and operative reinsertion or reconstruction of the LCLC is mandatory.31–33 LCLC reconstruction is indicated rather than repair, when attenuation or deficiency of the LCLC complex exists to the extent that imbrication or reattachment of the soft tissues will not achieve structural stability. In cases of severe cubitus varus (greater than 20°) or severe coronoid deficiency ligament reconstruction alone is not sufficient.
Reconstruction with a tendon graft is also contraindicated in the first 4–6 weeks after trauma (first dislocation or fracture dislocation) since direct repair, as described by Osborne, is usually satisfactory.34
Surgical techniques and rehabilitation
Refixation or imbrication
The patient is placed supine on the operating table with the arm supported on an arm table. Under tourniquet control the joint is exposed through Kocher’s interval. The avulsed origin of the LCLC is identified, elevated and re-sutured to the isometric point on the lateral epicondyle with two heavy, non-absorbable sutures. The sutures are passed through the anterior and posterior part of the LCLC, and the overlying common extensor-supinator fibres and fixed through bone tunnels to the isometric point of the lateral epicondyle of the distal humerus.22
Ligamentous reconstruction with a graft
Graft selection
Several types of tendon graft can be used for ligament reconstruction. These include palmaris longus, which has been used historically,32,35 and hamstring tendon which has the disadvantage of donor site morbidity.36 Tendon allografts such as plantaris and semitendinosus seem to have similar outcomes to autograft and have the advantage that they eliminate donor site morbidity and reduce surgical time.22 However, some patients are not willing to accept allograft for personal or religious reasons. Furthermore the cost of allograft differs from country to country and this can play a part in decision making.
Several authors have reported the use of triceps fascia as a graft for reconstruction with reinforcement of the remnants of the LCLC.31,33 This graft measures about 10 cm in length and 1.5 cm in width, and is harvested from the middle-third part of the triceps tendon, without damaging the lamina splendens (the muscular septum between the lateral head and medial/long head of the triceps). The graft can be harvested using a 3 cm extension of the same incision that is used for the ligament reconstruction. The problems of donor site morbidity and the disadvantages of allograft are overcome with the use of a triceps graft.
A recent cadaveric study has shown that triceps graft offers sufficient strength to be used in ligament reconstruction of the elbow.37 In this study the tendon was split into thirds and its tensile properties were recorded using a materials testing machine. The lateral portion was significantly thinner and less stiff than the medial and central portions (p < 0.05). It failed at significantly lower ultimate load than the central portion (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences between the medial, central and lateral portions of the triceps tendons with regards to ultimate stress (p = 0.20) or modulus of elasticity (p = 0.64). Data from the study were compared with the available literature regarding tensile elbow ligaments. The failure load of the strongest ligament of the elbow joint, the anterior band of the medial collateral ligament, has been reported to be 260 N. The failure load of the lateral collateral ligament of the elbow joint has been reported to be 232 N. All three portions of the triceps tendon that were tested were found to be stronger and therefore able to withstand sufficient forces when used to reconstruct the MCL or LCL. The palmaris longus tendon, which is frequently used to reconstruct elbow ligaments, has been reported to fail at loads of 357 N, almost half of the strength that the central strip of triceps tendon offers (704 N).
Surgical technique for reconstruction with a graft
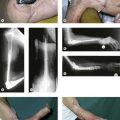
The patient is placed supine position on the operating table. Intravenous antibiotics are given 30 minutes before incision. A tourniquet is applied and the elbow joint exposed through Kocher’s interval. The anconeus is separated posteriorly from the extensor carpi ulnaris (Fig. 26.6). The ulnar attachment of the LUCL is palpated at the tubercle of the supinator crest and dissected. The tubercle is felt by stressing the elbow in varus and external rotation. On the humeral side, the supracondylar ridge is exposed posteriorly and anteriorly.
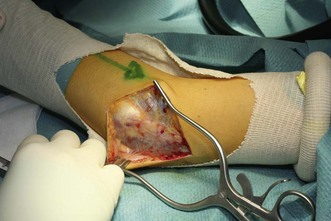
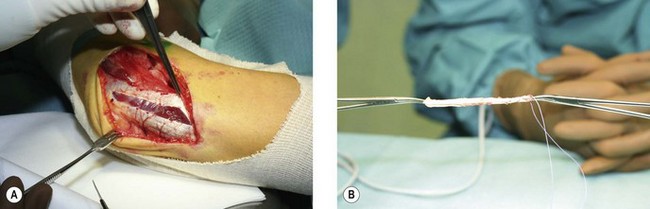
The common extensor origin is partially reflected to expose the capsule. The capsule is in most cases attenuated. The capsule and common extensor tendon are incised longitudinally just anterior to the posterior border of the tendon. The capsule is marked with stay-sutures to allow plication before fixing the graft. The entire LCLC is either stretched or detached from the humerus. The tissue of the LCLC is generally of poor quality, and necessitates reconstruction with a graft. The type of graft used is surgeon dependent but for the last few years I have been using a triceps graft for LCLC. The graft is harvested from the middle-third part of the triceps tendon without damaging the lamina splendens and measures about 10 cm in length by 1.5 cm in width (Fig. 26.7). The graft is folded along its long axis and both ends of the graft are braided with nonabsorbable sutures. The defect in the triceps fascia is closed using side-to-side absorbable stitches.
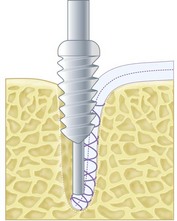
The insertion site for the tendon graft on the ulna is then prepared. A 5.5 mm ulnar drill hole is made just at the tubercle of the supinator crest, the second cortex is not penetrated with the drill. The graft is fixed using a bioabsorbable 5.5 mm interference screw (Fig. 26.8). The point of isometry is determined by holding the graft with a hemostat at the humeral origin during flexion and extension. During flexion and extension the graft must be tensioned throughout the whole range of motion. At the point of isometry, a 5.5 mm drill hole is made in the distal humerus. This drill hole is directed to the anterior part of the lateral column. With a suture retriever the sutures in the graft are passed through the tunnel. The humeral end of the graft is docked in the humeral tunnel. Before tightening the tendon graft, the capsule is closed and plicated. Closing the capsule is essential to prevent the graft from rubbing on the radial head or capitellum. The graft is tensioned with the elbow in 40° of flexion and full pronation. The graft is fixed on the humeral side with a bioabsorbable 5.5 mm screw.
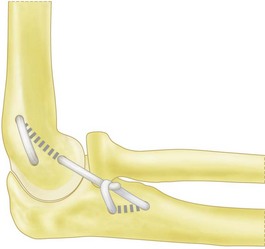
The remnants of the LCLC can be used to reinforced the triceps tendon graft. Olsen and co-workers described an alternative technique using triceps. The midportion of the graft is tunnelled in the lateral condyle and the two distal legs of the graft are fixed on the proximal part of the supinator crest, using bone anchors. The reconstruction is tensioned at 90° of elbow flexion, and finally the two legs are sewed to each other using nonabsorbable sutures. Other authors have reported equally good results using different graft fixation techniques but the basic principle is the same, with a reconstruction of the ligamentous structure originating at the humeral epicondyle and inserting on the proximal supinator crest (Fig. 26.9).
An alternative approach that is frequently used is a double bundle technique. On the ulnar side two holes are prepared, one near the tubercle on the supinator crest and the other 1.25 cm proximally, at the base of the annular ligament. The holes are joined using a curved awl or burr. The isometric point on the humeral epicondyle is then identified using a suture passed thought these two holes. The isometric ligament origin is then determined: this is the point at which the suture remains taut in both flexion and extension. In 40° of flexion and pronation the graft is passed through the ulnar holes and fixed on the humeral side by a docking technique or converging bone tunnels.22,38
Rehabilitation
In most institutions the same postoperative rehabilitation protocol is used for both imbrication, refixation and reconstruction of the LCLC. In general the elbow is immobilized after surgery for 2–4 weeks in a long arm cast with the forearm in pronation.31,33,35 Different authors describe the use of a hinged brace for an additional 9 weeks or the use of a removable long arm cast for protection. In revision surgery or in cases with severe instability or generalized laxity, the risk of failure is higher and an additional 6 weeks of immobilization is indicated. Using triceps tendon and interference screws, I originally immobilized the elbow in a long arm cast for a period of 3 weeks with the forearm in slight pronation instead of full pronation to prevent loss of supination.
Outcome including literature review
Nestor and co-workers in 1992 used palmaris tendon for PLRI reconstruction in 11 patients and achieved stability in 10 patients.32 More recently the Mayo Clinic has published 44 cases with a mean follow-up of 6 years. Ligament repair and imbrication was performed in 12 cases and reconstruction in 32. Surgery restored stability in all but five patients.35 Olsen, using triceps tendon as a graft, reported 89% excellent results among 18 reconstructions of the LCLC. According to the Mayo score, 94% were satisfied with the outcome and 78% obtained subjective and objective stability.31
In 2001 a report on the outcome of surgical treatment for tardy posterolateral rotatory instability in combination with a posttraumatic cubitus varus deformity was published. Twenty-one elbows were treated with reconstruction of the LCLC combined with an osteotomy. At the most recent follow-up, three patients had persistent posterolateral rotatory instability and two of these were rated as poor due to arthritis with severe pain.39
1 Morrey BF, An KN. Articular and ligamentous contributions to the stability of the elbow joint. Am J Sports Med. 1983;11:315-319.
2 Morrey BF, An KN. Functional anatomy of the ligaments of the elbow. Clin Ort Rel Res. 1985;201:84-90.
3 Morrey BF, Tanaka S, An KN. Valgus stability of the elbow: a definition of primary and secondary constraints. Clin Orthop. 1991;265:187-195.
4 O’Driscoll SW, Morrey BF, Korinek S, et al. Elbow subluxation and dislocation. A spectrum of instability. Clin Orthop. 1992;280:186-197.
5 Olsen BS, Søjbjerg JO, Dalstra M, et al. Kinematics of the lateral ligamentous constraints of the elbow joint. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1996;5:333-341.
6 Olsen BS, Søjbjerg JO, Vaesel MT, et al. Posterolateral elbow instability. The basic kinematics. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1998;7:19-29.
7 Deutch SR, Jensen SL, Tyrdal S, et al. Elbow joint stability following experimental osteoligamentous injury and reconstruction. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12:466-471.
8 Dunning CE, Zarzour ZDS, Paterseon SD, et al. Ligamentous stabilizers against posterolateral rotatory instability of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 2001;83:1823-1828.
9 Cohen MS, Hastings H. Rotatory instability of the elbow. The anatomy and role of the lateral stabilizers. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1997;79:225-233.
10 Morrey BF. Anatomy of the elbow joint. In Morrey BF, Sanchez-Sotelo J, editors: The elbow and its disorders, 3rd ed, Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 2009.
11 Olsen BS, Vaesel MT, Helmig P, et al. The lateral collateral ligament of the elbow joint. Anatomy and kinematics. An experimental study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1996;5:103-112.
12 King GJW, Morrey BF, An KN. Stabilizers of the elbow. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1993;3:165-174.
13 Rahusen F, Verheul C, Eygendaal D. Functional after treatment of an isolated, traumatic, dorsal dislocation of the radial head. Treatment rationale by a specialized physiotherapist. Fysiotherapeutische Casuïstiek. 2004;11:1016-1018.
14 Van Riet R, Morrey BF, O’Driscoll SW, et al. Associated injuries complicating radial head fractures: a demographic study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;441:351-355.
15 Kaas L, van Riet R, Vroemen JPAM, et al. The incidence of associated fractures of the upper limb in fractures of the radial head. Strat Traum Limb Recon. 2008;5:59-61.
16 O’Driscoll SW, Bell DF, Morrey BF. Posterolateral rotatory instability of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1991;73:440-446.
17 Charalambous CP, Stanley JK. Posterolateral rotatory instability of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2008;90:272-279.
18 Atkinson WB, Elftman H. The caring angle of the human arm as a secondary sex character. Anat Rec. 1945;91:49.
19 Beals RK. The normal carrying angle of the elbow. Clin Orthop. 1976;119:194.
20 Keats TE, Teeslink R, Diamond AE, et al. Normal axial relationships of the major joints. Radiology. 1966;87:904.
21 Lanz T, Wachsmuth W. Praktishe anatomie (edited). Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1959.
22 Sanchez-Sotelo J. Treatment of LCL injuries. In Morrey BF, Sanchez-Sotelo J, editors: The elbow and its disorders, 3rd ed, Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 2009.
23 Regan W, Lapner PC. Prospective evaluation of two diagnostic apprehension signs for posterolateral instability of the elbow. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15:344-350.
24 Arvind C, Hargreaves D. Table top relocation rest – new clinical test for posterolateral rotator instability of the elbow. J shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15:500.
25 Eygendaal D, Valstar ER, Söjbjerg JO, et al. Biomechanical evaluation with R.S.A. of the medial collateral ligament of the elbow. Clin Ort Rel Res. 2002;396:100-105.
26 Potter HG, Weiland AJ, Schatsz JO, et al. Posterolateral rotatory instability of the elbow; usefulness of MR imaging in diagnosis. Radiology. 1997;204:185.
27 Joseffson PO, Johnell O, Wendeberg B. Ligamentous injuries in dislocation of the elbow joint. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 1987;221:221-225.
28 King T. Recurrent dislocation of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 1953;35:50.
29 Cohen MS, Hasting H. Acute elbow dislocation: evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1998;6:15-23.
30 Koslowsky TC, Mader K, Siedek M, et al. Treatment of bilateral elbow dislocation using external fixation with motion capacity: a report of 2 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(7):499-502.
31 Olsen BS, Søjbjerg JO. The treatment of recurrent posterolateral instability of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2003;85:342-346.
32 Nestor BJ, O’Driscoll SW, Morrey BF. Ligamentous reconstruction for posterolateral rotatory instability of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1992;74:1235-1241.
33 Eygendaal D. Ligamentous reconstruction around the elbow using triceps tendon. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75:516-523.
34 Osborne G, Cotterill P. Recurrent dislocation of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 1966;48:340-346.
35 Sanchez-Sotello J, Morrey BF, O’Driscoll SW. Ligamentous repair and reconstruction for posterolateral rotatory instability of the elbow. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2005;87:54-61.
36 van Riet RP, Bain GI, Baird R, et al. Simultaneous reconstruction of medial and lateral elbow ligaments for instability using a circumferential graft. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2006;10(4):239-244.
37 Baumfeld JA, Zobitz ME, van Riet RP, et al. Triceps tendon properties and its potential as an autograft. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(5):697-699.
38 Stanley D. Lateral collateral ligament injury. In: Celli A, Celli L, Morrey BF, editors. Treatment of elbow lesions. Milan: Springer-Verlag, 2008.
39 O’Driscoll SW, Spinner RJ, McKee MD, et al. Tardy posterolateral rotator instability of the elbow due to cubitus varus. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 2001;83:1358.