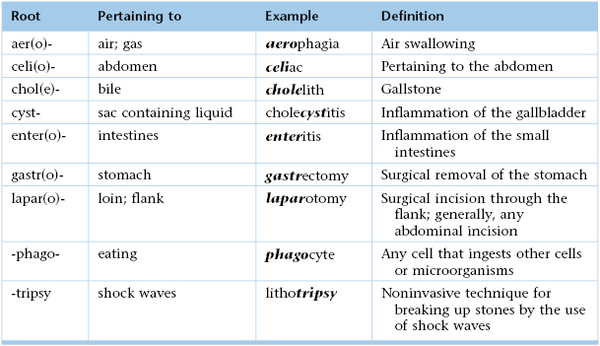
Chapter 14
The Abdomen
A good eater must be a good man; for a good eater must have good digestion, and good digestion depends upon a good conscience.
Benjamin Disraeli (1804–1881)
General Considerations
Diseases of the abdomen are common. In the United States, approximately 10% of the adult male population is affected by peptic ulcer disease. Diverticular disease affects 5% of the population older than 40. Colorectal cancer is the third most common malignant neoplasm (9% of all cancers) affecting American men and women. It is the third most common cause of cancer deaths in men (8%) and in women (9%). In 2011, approximately 141,210 new cases of cancer of the colon and rectum were diagnosed, and there were 49,380 deaths from colorectal cancer.
In the general American population, the lifetime probability for development of colorectal cancer is approximately 5.5%, or 1 per 18 people. The risk for this type of cancer differs widely among individuals. The highest incidence is in African Americans, who have a rate of 50.4 cases per 100,000 population. The incidence for the white population is second, at 43.9 per 100,000. The lowest incidence is in the Native American population, at 16.4 per 100,000. Some patients, such as those with congenital polyposis or ulcerative colitis, have a predisposition to the development of cancer of the colon, frequently at an early age. The lifetime risk of colonic cancer in patients with polyposis coli is 100%. The incidence of polyposis in the population of the United States varies from 1 per 7000 to 1 per 10,000 live births. The risk for development of colonic cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis is 20% per decade of life. Diet has been shown to have a relationship to the incidence of colonic cancer. Individuals on a low-fiber and high-fat diet are at higher risk. Earlier physical diagnosis has been clearly shown to lower the mortality rates for colorectal cancer.
In 2011, in addition to deaths related to cancer of the colon and rectum, deaths from cancer of the liver and intrahepatic bile ducts accounted for 4% (19,590 patients) of all cancer deaths in men. More than 80% of these cases are hepatocellular carcinoma, originating from hepatocytes. The incidence of liver cancer has been increasing by 3.4% per year in men and by 3% per year in women since 1992. In contrast to most common cancer sites, incidence rates are highest among Asian Americans, Pacific Islanders, and Hispanics. In the United States and other western countries, alcohol-related cirrhosis and possibly nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associated with obesity account for the majority of liver cancer cases. Chronic infections with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) are associated with less than half of liver cancer cases in the United States, although they are the major risk factors for the disease worldwide. Other risk factors for liver cancer, particularly in developing nations, include parasitic infections (e.g., schistosomiasis and liver flukes) and consumption of food contaminated with aflatoxin, a toxin produced by mold during the storage of agricultural products in a warm, humid environment.
Also in 2011 there were 9250 new cases of gall bladder and biliary tract cancer reported in men and women with 3300 deaths. There were also 44,030 new cases of pancreatic cancer and 37,660 deaths, which account for 6% of all cancer deaths in men and for 7% of all cancer deaths in women in the United States. The death rate for pancreatic cancer increased from 2003 to 2007 by 0.7% per year in men and by 0.1% per year in women. Tobacco smoking and smokeless tobacco use increase the risk of pancreatic cancer; incidence rates are about twice as high for cigarette smokers as for nonsmokers. There were 16,980 new cases of esophageal cancer, with a 4 : 1 male/female ratio and 14,710 deaths, which makes esophageal cancer the seventh leading cause of cancer deaths in men (4% of all cancer deaths).
Structure and Physiology
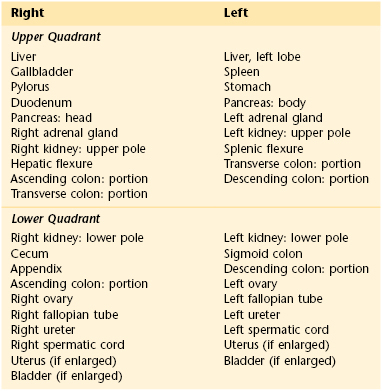
For descriptive purposes, the abdominal cavity is usually divided visually into four quadrants. Two imaginary perpendicular lines cross at the umbilicus to divide the abdomen into the right upper and right lower quadrants and the left upper and left lower quadrants. One line extends from the sternum to the pubic bone through the umbilicus. The second line is at right angles to the first at the level of the umbilicus. The four quadrants formed and the abdominal organs within each quadrant are shown in Figure 14-1.
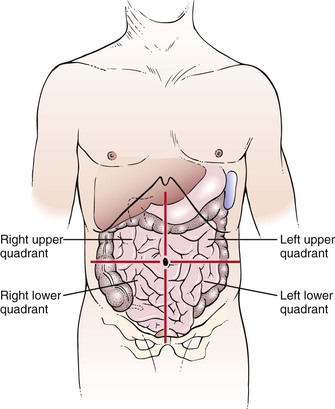
Figure 14–1 The four abdominal quadrants.
Another method of description divides the abdomen into nine areas: epigastric, umbilical, suprapubic, right and left hypochondrium, right and left lumbar, and right and left inguinal. Two imaginary lines are drawn by extending the midclavicular lines to the middle of the inguinal ligaments. These lines form the lateral extent of the rectus abdominis muscles. At right angles to these lines, two parallel lines are drawn: one at the costal margins and the other at the anterosuperior iliac spines. The nine-area system is shown in Figure 14-2.
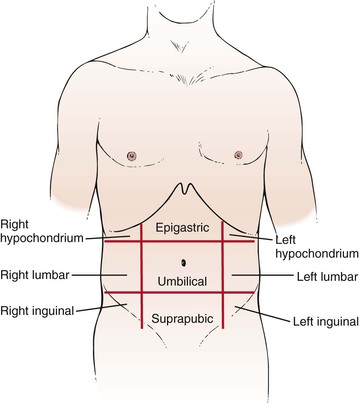
Figure 14–2 The nine abdominal areas.
The examiner should recognize the abdominal structures that are located in each area. Table 14-1 lists the organs present in each of the four quadrants.
Because the kidneys, duodenum, and pancreas are posterior organs, it is unlikely that abnormalities in these organs can be palpated in adults. In children, in whom the abdominal muscles are less developed, renal masses, especially on the right side, can often be palpated.
As food passes into the esophagus, an obstructing lesion can produce dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing. Gastroesophageal reflux can lead to heartburn. Upon entry of partially digested food into the stomach, the stomach relaxes. A failure of this relaxation may lead to early satiety or pain. The stomach functions as a food reservoir, secreting gastric juice and providing peristaltic activity with its muscular wall. Between 2 and 3 L of gastric juice is produced daily by the stomach lining and affects the digestion of proteins. The semifluid, creamy material produced by gastric digestion of food is called chyme. Secretion of gastric juice may produce pain if a gastric ulcer is present. Intermittent emptying of the stomach occurs when intragastric pressure overcomes the resistance of the pyloric sphincter. Emptying is normally complete within 6 hours after eating. Any obstruction to gastric emptying may produce vomiting.
The entry of chyme from the stomach into the duodenum stimulates the secretion of pancreatic enzymes and contraction of the gallbladder. The flow of pancreatic juice is maximal approximately 2 hours after a meal; the daily output is 1 to 2 L. The three enzymes of chyme—lipase, amylase, and trypsin—are responsible for the digestion of fats, starches, and proteins, respectively. In cases of pancreatic insufficiency, the stool is pale and bulky and has an odor that is more offensive than normal. The chyme and the neutralizing effect of these enzymes reduce the acidity of the duodenal contents and relieve the pain of peptic duodenal ulcer. The pain from an acutely inflamed gallbladder or from pancreatitis worsens at this phase of the digestive cycle.
The digested food continues its course through the small intestine, in which further digestion and absorption occur. Failure of bile production or its release from the gallbladder results in decreased digestion and absorption of fats, leading to diarrhea. Gallstones may form as a result of diet or hereditary predisposition.
The liver produces bile, detoxifies the byproducts of the digestion of food, and metabolizes proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates. The daily output of bile is approximately 1 L. In the absence of normal liver function, jaundice, ascites, and coma may result.
The jejunum and ileum further digest and absorb the nutrients. Bile acids and vitamin B12 are absorbed in the ileum. The dark color of stool is caused by the presence of stercobilin, a metabolite of bilirubin, that is secreted in the bile. If bile does not flow into the small intestine, the stools become pale brown to gray and are called acholic, or free from bile.
Review of Specific Symptoms
The most common symptoms of abdominal disease are as follows:
Pain
Pain is probably the most important symptom of abdominal disease. Although abdominal neoplasia may be painless, most abdominal disease manifests itself with some amount of pain. Pain can result from mucosal irritation, smooth muscle spasm, peritoneal irritation, capsular swelling, or direct nerve stimulation. Abdominal pain necessitates speedy diagnosis and therapy.
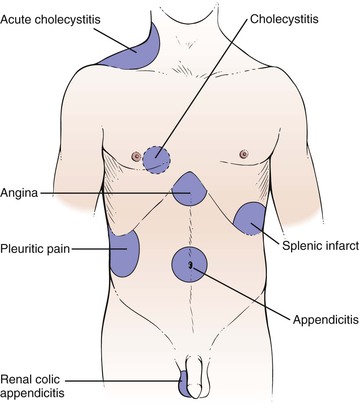
There are three broad categories of abdominal pain: visceral, parietal, and referred. Visceral pain develops when hollow abdominal organs such as the gall bladder, stomach, or intestines contract forcefully or their walls are stretched. If the capsule of the liver or spleen is stretched, visceral pain can also develop. For the patient, it may be difficult to localize such pain. It can be described typically as gnawing, burning, or aching. When severe, nausea, vomiting, and sweating may develop. Parietal pain stems from inflammation of the peritoneum. The pain is extremely severe, and the patient is often more able to localize the pain over a specific organ. The patient lies extremely still, boardlike, as any movement tends to exacerbate the pain. Referred pain is a term used to describe pain originating in the internal organs but described by the patient as being located in the abdominal or chest wall, shoulder, jaw, or other areas supplied by the somatic nerves. Pain appears to originate in areas supplied by the somatic nerves entering the spinal cord at the same segment as the sensory nerves from the organ responsible for the pain. The pain is usually localized. For example, right shoulder pain or right scapular pain may result from acute cholecystitis; testicular pain may result from renal colic or from appendicitis. The common sites for referred pain are shown in Figure 14-3. The locations of pain in abdominal disease are summarized in Table 14-2.
Table 14–2
Location of Pain in Abdominal Disease
| Area of Pain | Affected Organ | Clinical Example |
| Substernal | Esophagus | Esophagitis |
| Shoulder | Diaphragm | Subphrenic abscess |
| Epigastric | Stomach Duodenum Gallbladder Liver Bile ducts Pancreas |
Peptic gastric ulcer Peptic duodenal ulcer Cholecystitis Hepatitis Cholangitis Pancreatitis |
| Right scapula | Biliary tract | Biliary colic |
| Midback | Aorta Pancreas |
Aortic dissection Pancreatitis |
| Periumbilical | Small intestine | Obstruction |
| Hypogastrium | Colon | Ulcerative colitis Diverticulitis |
| Sacrum | Rectum | Proctitis Perirectal abscess |
When a patient complains of abdominal pain, ask the following questions:
“Has the pain changed its location since it started?”
“Do you feel the pain in any other part of your body?”
“How long have you had the pain?”
“Have you had recurrent episodes of abdominal pain?”
“Did the pain start suddenly?”
“Can you describe the pain? Is it sharp? Dull? Burning? Cramping?”
“Is the pain continuous? Does it come in waves?”
“Has there been any change in the severity or nature of the pain since it began?”
If the patient is a woman, ask this question:
If the woman is of child-bearing age and is sexually active, ask the question:
It is crucial to determine the location of the pain at its onset, its localization, its character, and its radiation. Commonly, when an abdominal organ ruptures, pain is felt “all over the belly,” without localization to a specific area. Pain arising from the small intestine is commonly felt in the umbilical or epigastric regions; for example, pain from acute appendicitis begins at the umbilicus.
In time, pain may become localized to other areas. Pain from acute appendicitis travels from the umbilicus to the right lower quadrant approximately 1 to 3 hours after the initial event. Pain in the chest followed by abdominal pain should raise the suspicion of a dissecting aortic aneurysm.
Note the nature of the pain. Pain caused by a perforated gastric ulcer is often described as “burning,” dissecting aneurysm as “tearing,” intestinal obstruction as “gripping,” pyelonephritis as “dull” or “aching,” and biliary or renal colic as “crampy” or “constricting.”
The time of occurrence and factors that aggravate or alleviate the symptoms (e.g., meals or defecation) are particularly important. Periodic epigastric pain occurring 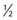 to 1 hour after eating is a classic symptom of gastric peptic ulcers. Patients with a duodenal peptic ulcer have pain 2 to 3 hours after eating or before the next meal. Food tends to lessen the pain, especially in duodenal ulcers. Perforation of a duodenal ulcer to the pancreas may produce backache, simulating an orthopedic problem. Nocturnal pain is a classic symptom of duodenal peptic ulcer disease. Pain after eating may also be associated with vascular disease of the abdominal viscera. Patients with this condition are older and have postprandial pain, anorexia, and weight loss. This triad is seen in abdominal angina resulting from obstructive vascular disease in the celiac axis or the superior mesenteric artery. Table 14-3 summarizes the important maneuvers for ameliorating abdominal pain.
to 1 hour after eating is a classic symptom of gastric peptic ulcers. Patients with a duodenal peptic ulcer have pain 2 to 3 hours after eating or before the next meal. Food tends to lessen the pain, especially in duodenal ulcers. Perforation of a duodenal ulcer to the pancreas may produce backache, simulating an orthopedic problem. Nocturnal pain is a classic symptom of duodenal peptic ulcer disease. Pain after eating may also be associated with vascular disease of the abdominal viscera. Patients with this condition are older and have postprandial pain, anorexia, and weight loss. This triad is seen in abdominal angina resulting from obstructive vascular disease in the celiac axis or the superior mesenteric artery. Table 14-3 summarizes the important maneuvers for ameliorating abdominal pain.
Table 14–3
Maneuvers for Ameliorating Abdominal Pain
| Maneuver | Affected Organ | Clinical Example |
| Belching | Stomach | Gastric distention |
| Eating | Stomach, duodenum | Peptic ulcer |
| Vomiting | Stomach, duodenum | Pyloric obstruction |
| Leaning forward | Retroperitoneal structures | Pancreatic cancer Pancreatitis |
| Flexion of knees | Peritoneum | Peritonitis |
| Flexion of right thigh | Right psoas muscle | Appendicitis |
| Flexion of left thigh | Left psoas muscle | Diverticulitis |
Determine whether the abdominal pain is associated with anything else such as before meals, while eating, or after meals.
Suprapubic pain may be caused by urinary bladder disorders such as a bladder infection or cystitis. The pain is often described as dull pressure as is commonly associated with burning during urination, incontinence, frequency, flank pain, fever, nausea, or vomiting.
Ureteral pain is extremely severe and colicky. The patient cannot find a comfortable position. It results from sudden distention of the ureter and renal pelvis, and is generally caused by acute obstruction such as from a kidney stone. Always inquire about associated fever, chills, or hematuria. More questions related to abdominal pain in a woman are described in Chapter 16, Female Genitalia.
Nausea and Vomiting
Vomiting may be caused by severe irritation of the peritoneum resulting from the perforation of an abdominal organ; from obstruction of the bile duct, ureter, or intestine; or from toxins. Vomiting resulting from a perforation is commonly not massive. Obstruction of the bile duct or other tube produces stretching of the muscular wall, resulting in episodic vomiting that occurs at the height of the pain. Intestinal obstruction prevents the intestinal contents from passing distally; consequently, vomiting may result in the expulsion of intestinal contents. Toxins generally cause persistent vomiting. Not all abdominal emergencies cause vomiting. Intraperitoneal bleeding may occur in the absence of vomiting. Vomiting is frequently also caused by inflammation of intra-abdominal structures, as well as by extra-abdominal conditions, including drug toxicity, central nervous system disorders, myocardial infarction, and pregnancy. Ask the following questions if a patient complains of nausea, vomiting, or both:
“How long have you had nausea or vomiting?”
“What is the color of the vomit?”
“Is there any unusually foul odor to the vomitus?”
“Do you have nausea without vomiting?”
If the patient is a woman, ask this question:
If the patient is of child-bearing age and sexually active, ask the question:
The relationship of the pain to vomiting is important and may help in providing the diagnosis. In acute appendicitis, pain precedes the vomiting usually by a few hours. The character of the vomitus may aid in determining its cause. Acute gastritis causes the patient to vomit stomach contents. Biliary colic produces bilious, or greenish-yellow, vomitus. Intestinal obstruction often causes the patient to expel bilious vomitus, followed by feculent-smelling fluid. Feculent vomitus is usually caused by intestinal obstruction.
Nausea without vomiting is a common symptom in patients with hepatocellular disease, pregnancy, and metastatic disease. Nausea may be associated with a hearing loss and tinnitus in patients with Ménière’s disease. More questions related to nausea and vomiting in a woman are described in Chapter 16, Female Genitalia.
Change in Bowel Movements
Take a careful history of bowel habits. A change in bowel movements necessitates further elaboration. Ask these questions of the patient with acute onset of diarrhea:
“How long have you had the diarrhea?”
“How many bowel movements do you have a day?”
“Did the diarrhea start suddenly?”
“Did the diarrhea begin after a meal?” If yes, “What did you eat?”
“Are the stools watery? Bloody? Malodorous?”
“Is the diarrhea associated with abdominal pain? Loss of appetite? Nausea? Vomiting?”
The acute onset of diarrhea after a meal suggests an acute infection or toxin. Watery stools are often associated with inflammatory processes of the small bowel and colon. Shigellosis is a disease of the colon that produces bloody diarrhea. Amebiasis is also associated with bloody diarrhea.
The patient with chronic diarrhea should be asked the following:
“How long have you had diarrhea?”
“Do you have periods of diarrhea alternating with constipation?”
“Are the stools watery? Loose? Floating? Malodorous?”
“Have you noticed blood in the stools? Mucus? Undigested food?”
“What is the color of the stools?”
“How many bowel movements do you have a day?”
“Does the diarrhea occur after eating?”
“What happens when you fast? Do you still have diarrhea?”
“Is the diarrhea associated with abdominal pain? Abdominal distention? Nausea? Vomiting?”
“Have you noticed that the diarrhea is worse at certain times of the day?”
Diarrhea and constipation frequently alternate in patients with colon cancer or diverticulitis. Loose bowel movements are common in diseases of the left colon, whereas watery movements are seen in severe inflammatory bowel disease and protein-losing enteropathies. Floating stools may result from malabsorption syndromes. Patients with ulcerative colitis commonly have stool mixed with blood and mucus. Any inflammatory process of the small bowel or colon can manifest with blood mixed with stool or undigested food. Irritable bowel syndrome classically produces more diarrhea in the morning.
Patients complaining of constipation should be asked these questions:
“How long have you been constipated?”
“How often do you have a bowel movement?”
“What is the size of your stools?”
“What is the color of your stools?”
“Is the stool ever mixed with blood? Mucus?”
“Have you noticed periods of constipation alternating with periods of diarrhea?”
Change in the caliber of the stool is significant. “Pencil”-diameter stools may result from an anal or a distal rectal carcinoma. A change in the color of stools is important. As is discussed later, pale brown to gray stools indicate an absence of bile. This can result from an obstruction to bile flow from the gallbladder or from decreased production of bile. Weight changes are important with the symptom of constipation. An increase in weight may indicate decreased metabolism seen in hypothyroidism; a decrease in weight may be associated with cancer of the colon or other hypermetabolic conditions.
Black feces can also be caused by a number of medications, such as bismuth subsalicylate (the active ingredient in Pepto-Bismol®) and dietary iron supplements, or foods such as black licorice, or blueberries.
Rectal Bleeding
Rectal bleeding may be manifested by bright red blood, blood mixed with stool, or black, tarry stools. Bright red blood per rectum,1 also known as hematochezia, can occur from colonic tumors, diverticular disease, or ulcerative colitis. Blood mixed with stool can be the result of ulcerative colitis, diverticular disease, tumors, or hemorrhoids. Ask the patient who describes rectal bleeding the following questions:
“How long have you noticed bright red blood in your stools?”
“Is the blood mixed with the stool?”
“Are there streaks of blood on the surface of the stool?”
Melena is a black, tarry stool that results from bleeding above the first section of the duodenum, with partial digestion of the hemoglobin. Inquire about the presence of melena. A useful way of questioning is to show the patient the black tubing on the stethoscope and ask, “Have your bowel movements ever been this color?” If asked directly whether the bowel movements have ever been black, the patient may answer in the affirmative, equating dark (normal) stools with black stools. Ask these questions of a patient who describes melena:
“Have you passed more than one black, tarry stool?” If yes, “When?”
“How long have you been having black, tarry stools?”
The answers to these questions can provide some information regarding the acuteness and the amount of the hemorrhage. Lightheadedness, nausea, and diaphoresis are seen with rapid gastrointestinal bleeding and hypotension.
The presence of silver-colored stools is rare but pathognomonic of acholic stools with melena, a condition strongly suggestive of cancer of the ampulla of Vater in the duodenum. The cancer produces biliary obstruction (acholic stools), and the cancerous fronds are sloughed, causing bleeding (melanotic stools). This combination produces feces that are tarnished-silver or aluminum paint–like in color.
Jaundice
The presence of jaundice (icterus) must alert the examiner that there is either liver parenchymal disease or an obstruction to bile flow. The presence of icterus, or jaundice, results from a decreased excretion of conjugated bilirubin into the bile. This can result from intrahepatic biliary obstruction, known as medical jaundice, or from extrahepatic biliary obstruction, known as surgical jaundice. In any patient with icterus, the examiner should search for clues by asking the following questions:
“How long have you been jaundiced?”
“Did the jaundice develop rapidly?”
“Is the jaundice associated with chills? Fever? Itching? Weight loss?”
“In the past year have you had any transfusions? Tattooing? Inoculations?”
“Do you use any recreational drugs?” If yes, “Do you use any drugs intravenously?”
“Do you eat raw shellfish? Oysters?”
“Have you been jaundiced before?”
“Has your urine changed color since you noticed that you were jaundiced?”
“What is the color of your stools?”
“Do you have any friends or relations who are also jaundiced?”
“What type of work do you do? What other types of work have you done?”
Viral hepatitis is associated with nausea, vomiting, a loss of appetite, and an aversion to smoking. Hepatitis A has a fecal-oral route of transmission and an incubation period of 2 to 6 weeks. It may be linked to ingestion of raw shellfish. HBV is blood-borne and has an incubation period of 1 to 6 months. Health professionals are at increased risk for hepatitis. Any contact with an individual with viral hepatitis places a person at a higher risk of contracting viral hepatitis. HCV is the most common chronic blood-borne infection in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has estimated that during the 1980s, as many as 230,000 new infections have occurred in this country. It is estimated that as many as 3.9 million Americans have the antibody to HCV and are currently asymptomatic. They are, however, at risk for chronic liver disease, the tenth leading cause of death in the United States. Approximately 40% of chronic liver disease is HCV related and results in 8000 to 10,000 deaths a year. End-stage liver disease secondary to HCV infection is the most common indication for liver transplantation. Because most of these individuals are younger than 50 years, it is anticipated that by 2020, there will be a marked increase in the number of patients with chronic liver disease.
Slowly developing jaundice that is accompanied by pale stools and cola-colored urine is obstructive jaundice, either intrahepatic or extrahepatic. Jaundice accompanied by fever and chills is considered cholangitis until proved otherwise. Cholangitis may result from stasis of bile in the bile duct that results from a gallstone or from cancer of the head of the pancreas. Determine whether chemicals are used in a patient’s occupation or hobbies because they may be related to the cause of the jaundice. Many industrial chemicals and drugs have been associated with liver disease. These agents may be responsible for a viral hepatitis–like illness, cholestasis, or for granulomas or hepatic tumors. Occupational exposure to carbon tetrachloride and vinyl chloride is well known to cause liver disease. Ask questions related to alcohol abuse. These are described in Chapter 1, The Interviewer’s Questions.
Abdominal Distention
Abdominal distention may be related to increased gas in the gastrointestinal tract or to the presence of ascites. Increased gas can result from malabsorption, irritable colon, or air swallowing (aerophagia). Ascites can have a variety of causes, such as cirrhosis, congestive heart failure, portal hypertension, peritonitis, or neoplasia. To try to identify the cause of abdominal distention, ask these questions:
“How long have you noticed your abdomen to be distended?”
“Is the distention intermittent?”
“Is the distention related to eating?”
“Is the distention lessened by belching or by passing gas from below?”
Gaseous distention related to eating is intermittent and is relieved by the passage of flatus or belching. A patient with ascites has the insidious development of increased abdominal girth, noted through a progressive increase in belt size. Loss of appetite is often associated with cirrhosis and malignancy, although end-stage congestive heart failure may produce this symptom as well. Shortness of breath and ascites may be symptoms of congestive heart failure, but the shortness of breath may be the result of a decrease in pulmonary capacity owing to ascites from another cause. Questions related to alcohol abuse are most appropriate and are outlined in Chapter 1, The Interviewer’s Questions.
Mass
An abdominal mass may be a neoplasm or a hernia. An abdominal hernia is a protrusion from the peritoneal cavity into which peritoneal contents are extruded. The contents may be omentum, intestine, or bladder wall. An abdominal hernia may be inguinal, femoral, umbilical, or internal, depending on its location. The most common complaint is swelling, which may or may not be painful. An inguinal hernia may manifest as a mass in the groin or scrotum. The major complications of a hernia are intestinal obstruction and intestinal strangulation from interference of blood supply. A hernia is termed reducible when it can be emptied of its contents by pressure or a change in posture.
The sign or symptom of a pulsatile abdominal mass should alert the examiner to the possibility of an aortic aneurysm.
Pruritus
Pruritus, or itching, is a common symptom. Generalized itching may be a symptom of a diffuse skin disorder2 or a manifestation of chronic renal or hepatic disease. In 50% of individuals with generalized pruritus, a systemic disease is the cause. Intense pruritus may be associated with lymphoma or Hodgkin’s disease, as well as with malignancies of the gastrointestinal tract. Thyroid dysfunction can also cause generalized pruritus. Medications such as opiates, hydroxychloroquine, aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and any of a large number of medications that are metabolized by the liver can cause generalized itching.
In older individuals, pruritus may also be caused by dry skin alone. Pruritus ani is localized itching of the anal skin. It has many causes, including fistulas, fissures, psoriasis, intestinal parasites, frequent liquid stools, anal perspiration, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, and diabetes. Pruritus ani may be caused by eating certain foods, smoking, and drinking alcoholic beverages, especially beer and wine. Some of the food items that have been associated with pruritus ani include coffee, tea, carbonated beverages, milk products, tomatoes and tomato products such as ketchup, cheeses, nuts, and chocolate. Cleanliness is almost never a factor.
Loss of Appetite
Loss of appetite or intolerance to certain or all foods is important to ascertain. Patients with hepatitis often note a lack of appetite, as well as a loss of interest in smoking if they had a smoking habit previously. Patients will commonly describe an unpleasant taste or a fullness in their abdomen after eating only a light meal.
Impact of Inflammatory Bowel Disease on the Patient
Inflammatory bowel disease constitutes a group of diseases of unknown cause. The symptoms produced depend on the location, extent, and acuteness of the inflammatory lesions. The common presenting features are fever, anorexia, weight loss, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, rectal urgency, and rectal bleeding. It is a chronic, potentially disabling illness, often resulting in the need for multiple surgeries, in fistula formation, and in cancer.
Inflammatory bowel disease may lead to long absences from school or work, disruption of family life, malabsorption, malnutrition, and multiple hospitalizations. A patient can have 10 to 30 watery or bloody bowel movements each day. As a consequence, patients with inflammatory bowel disease can have many psychological problems, particularly when they are young adults. Because of malabsorption, the prevalence of osteopenia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease ranges from 40% to 50%; osteoporosis is present in 5% to 30% of all patients. Fractures of the hip, spine, and distal radius occur. One study revealed that the incidence of fractures among persons with inflammatory bowel disease is 40% greater than in the general population.
Sexual development may be delayed as a result of malnutrition. Social development is also delayed. The necessity of constantly having to remain near a bathroom inhibits patients’ abilities to develop normal dating patterns. Many of these patients are socially immature, and social introversion is common. By necessity, they remain at home. Their lives revolve around their bowel habits.
In most cases, there is a positive correlation between the severity of the physical disease and the extent of emotional disturbance. Dependency is the most reported characteristic of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Repressed rage, suppression of feelings, and anxieties are also common. It is reported that many patients have a constant desire to rid themselves of events in their lives. This characteristic can be acted out through the diarrhea. Another characteristic of these patients is to be obsessive-compulsive. The marked obsessive character becomes even more obvious when the patient is ill. It is typical for patients to worry incessantly about what is happening in their bowels. The patients are intelligent, often having read much literature, including medical textbooks, about their disease.
Denial is usually not a prominent symptom. In contrast, these patients concentrate obsessively on the details of their bowel habits.
Sexual problems are common. Interest and participation in sexual activity tend to be at a low level. Many of these individuals prefer to be fondled like a child and largely reject any genital contact. Patients are prone to regard sexual activity in anal terms, such as “dirty,” “unclean,” or “soiling.” They are squeamish about body contact, odors, and secretions. The loss of libido and decreased sexual drive may be related to their fear of bowel action during intercourse, of perineal pain, or that sexual intercourse may in some way further damage the bowel.
The frequent hospitalizations cause anxiety and depression, which exacerbate the disease. The fear of cancer may be the basis of depression, which is a common response to the disease. It is well established that emotional factors are important in maintaining and prolonging an existing attack. Schoolwork deteriorates as young patients are forced to miss more and more school, further increasing their anxiety.
An often unappreciated major complication of inflammatory bowel disease is substance abuse. As a result of chronic pain, as much as 5% of patients with inflammatory bowel disease are physically addicted to oral narcotics. Many more are psychologically dependent on their pain medication.
Many patients with ulcerative colitis require an ileostomy. The fear of disfigurement, the loss of self-confidence, the potential lack of cleanliness, and the dread of unexpected spillage are common.
Time for listening and an interest in a patient’s problem are important in gaining the patient’s confidence. Listening may reveal and help unravel the emotional problems that may be the source of the exacerbation of the bowel disease. Talking with the patient may be more efficacious than prescribing anti-inflammatory agents or tranquilizers. Careful and thoughtful discussion of the illness strengthens the doctor-patient relationship and produces immeasurable therapeutic benefits.
Physical Examination
The equipment necessary for the examination of the abdomen and rectum consists of a stethoscope, gloves, lubricant, tissues, and occult blood testing card and Hemoccult developer.
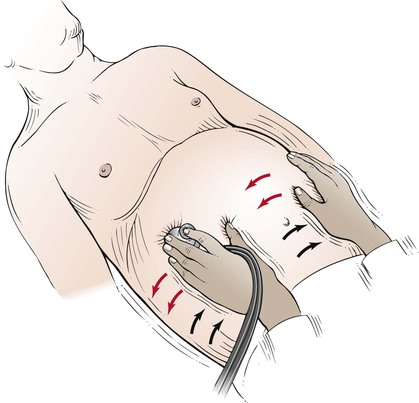
The patient should be lying flat in bed, and the abdomen should be fully exposed from the lower sternum to the knees. The arms should be at the sides, and the legs flat. Frequently, patients tend to place their arms behind their heads, which tightens the abdominal muscles and makes the examination more difficult. Placing a pillow beneath the knees or just bending the knees often aids in relaxation of the abdominal muscles. The examiner should be standing on the patient’s right side. A sheet or towel is placed over the genitalia, as shown in Figure 14-4. A gown covering the chest is appropriate.
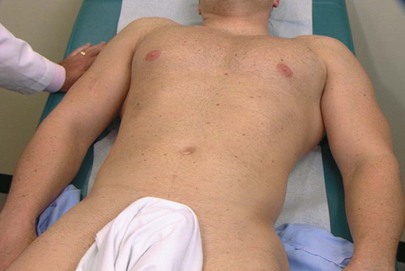
Figure 14–4 Technique for inspecting the abdomen.
If the patient has complained of abdominal pain, examine the area of pain last. If the examiner touches the area of maximal pain, the abdominal muscles tighten, and the examination is more difficult.
The physical examination of the abdomen includes the following:
Inspection
Evaluate General Appearance
The general appearance of the patient often furnishes valuable information as to the nature of the condition. Patients with renal or biliary colic writhe in bed. They squirm constantly and can find no comfortable position. In contrast, patients with peritonitis, who have intense pain on movement, characteristically remain still in bed because any slight motion worsens the pain. They may be lying in bed with their knees drawn up to help relax the abdominal muscles and reduce intra-abdominal pressure. Patients who are pale and sweating may be suffering from the initial shock of pancreatitis or a perforated gastric ulcer.
Determine Respiratory Rate
The respiratory rate is increased in patients with generalized peritonitis, intra-abdominal hemorrhage, or intestinal obstruction.
Inspect the Skin
Inspect the skin and sclera for jaundice. Whenever possible, the patient should be evaluated for jaundice in natural light because incandescent light frequently masks the existence of icterus. Jaundice becomes apparent when the serum bilirubin level exceeds 2.5 mg/dL in adults or 6 mg/dL in neonates. Figure 14-5 shows a patient with jaundice. Notice the scleral icterus and the yellow discoloration of the skin. Hyperbilirubinemia can also result in intense generalized pruritus.
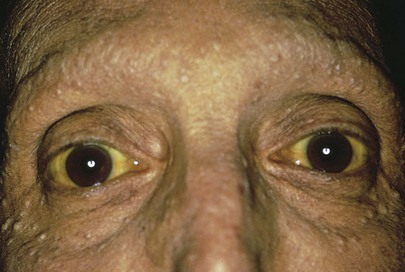
Figure 14–5 Jaundice.
Inspect for spider angiomas. Spider angiomas have a high degree of sensitivity in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis but are nonspecific because they also occur in pregnancy and collagen vascular disorders (see Fig. 5-81).
Figure 14-6 shows the leg of a patient with pyoderma gangrenosum. Notice the necrotic, undermined ulceration with pus. These tender ulcerations, commonly on the lower extremities, are associated with inflammatory bowel disease, especially ulcerative colitis. In general, the clinical course of pyoderma gangrenosum follows the course of the bowel disease. This condition is also seen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, myeloid metaplasia, and chronic myelogenous leukemia.
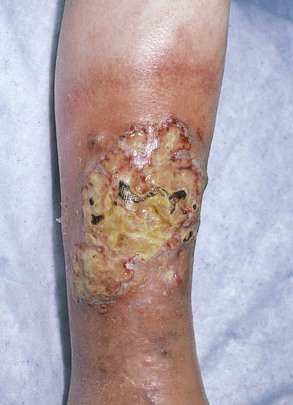
Figure 14–6 Pyoderma gangrenosum.
Inspect the Hands
Is there muscle loss in the small muscles of the hands? This is associated with wasting.
The nails are examined for changes in the nail bed, especially an increase in the size of the lunula. The fingers of a patient with cirrhosis showing “half-and-half” nails are shown in Figure 14-7 (see also Fig. 5-8).
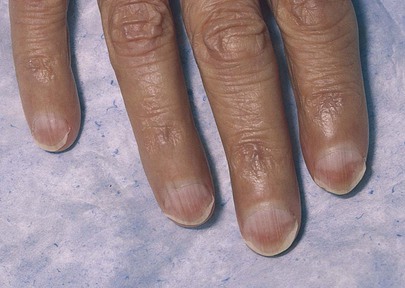
Figure 14–7 Lindsay’s nails.
Inspect the Facies
Are the eyes sunken? Is temporal wasting present? These signs indicate wasting and poor nutrition.
The skin around the mouth and oral mucosa may provide evidence of gastrointestinal disorders. Melanin deposition around and in the oral cavity, especially the buccal mucosa, suggests Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Figure 9-12 shows the lips of a patient with the classic brown pigmentary changes of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. This is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by generalized gastrointestinal, hamartomatous polyposis, and mucocutaneous pigmentation. The benign polyps are most common in the jejunum and only rarely become malignant. The polyps, however, may bleed, cause intussusception, or cause obstruction. Telangiectases of the lips and tongue are suggestive of Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome (see Fig. 9-11), in which multiple telangiectases are present throughout the gastrointestinal tract. These lesions may bleed insidiously, causing anemia. The classic oral lesions on the tongue and lower lip of a patient with Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome are shown in Figure 14-8.
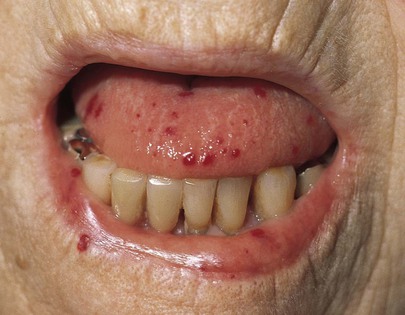
Figure 14–8 Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome.
Hypercortisolism, or Cushing‘s syndrome, has a range of clinical manifestations. The most common are obesity, facial plethora, hirsutism, and hypertension. Obesity occurs in 90% of affected patients. Most patients with hypercortisolism characteristically have round, puffy, red faces called moon facies. They also have prominent fat deposits in the supraclavicular and retrocervical areas (buffalo hump). Figure 14-9 shows a patient with Cushing’s syndrome and the typical moon facies.
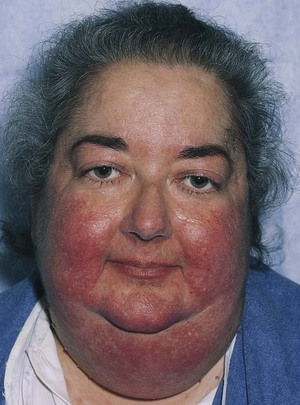
Figure 14–9 Cushing’s syndrome.
Inspect the Contour of the Abdomen and Inspect for Hernias
The contour of the abdomen should be assessed. A scaphoid, or concave, abdomen may be associated with cachexia; a protuberant abdomen may result from gaseous distention of the intestines, ascites, massive splenomegaly, or obesity. When a patient with ascites stands, the fluid sinks into the lower abdomen; when lying supine, the fluid bulges in the flanks. If a patient with ascites lies on the side, the fluid flows to the dependent lower side. A patient with a protuberant abdomen as a result of carcinomatous ascites is shown in Figure 14-10.
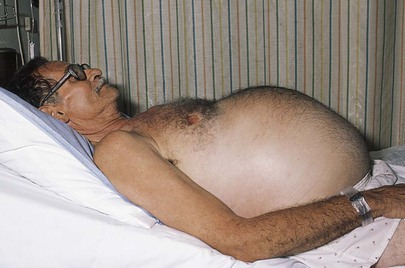
Figure 14–10 Ascites.
The examiner should focus attention on the abdomen to describe adequately the presence of any asymmetry, distention, masses, or visible peristaltic waves. The examiner should then observe the abdomen from above, looking for the same signs. Inspection of the abdomen for striae and scars may provide valuable data. Silver striae are stretch marks consistent with weight loss. Pinkish-purple striae are classic signs of adrenocortical excess. Figure 14-11 shows the characteristic purplish striae in a patient with Cushing’s syndrome.
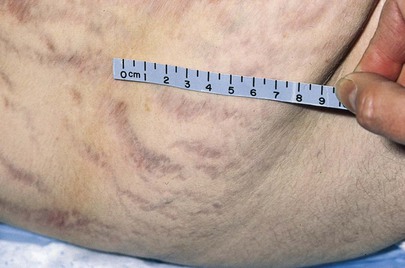
Figure 14–11 Abdominal striae.
Is the umbilicus everted? An everted umbilicus is often a sign of increased abdominal pressure, usually from ascites or a large mass. An umbilical hernia may also cause an umbilicus to become everted.
Are there ecchymoses on the abdomen or on the flanks? Massive ecchymoses may occur in these areas as a result of hemorrhagic pancreatitis or strangulated bowel. This is Grey Turner‘s sign.
Cullen‘s sign is a bluish discoloration of the umbilicus resulting from hemoperitoneum of any cause.
Recognition of classic surgical scars may be helpful. Figure 14-12 shows the locations of some common surgical scars.
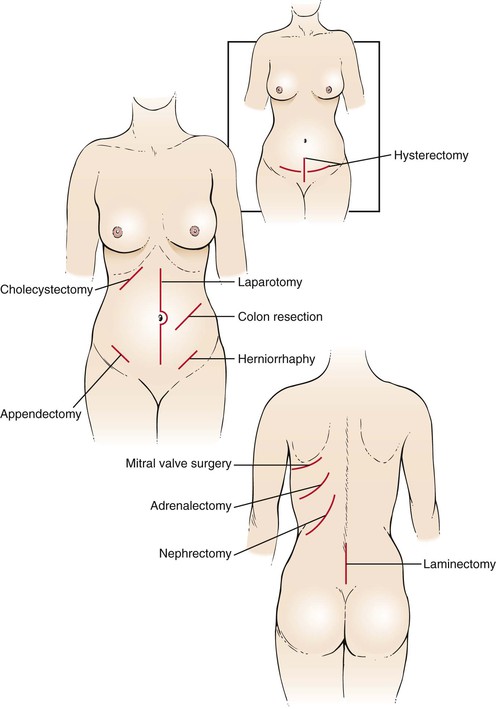
Figure 14–12 Locations of common surgical scars.
The patient lying in bed should be asked to cough while the examiner inspects the inguinal, umbilical, and femoral areas. This maneuver, by increasing intra-abdominal pressure, may produce a sudden bulging in these areas, which may be related to a hernia. If the patient has had surgery, coughing may reveal a bulging along the abdominal scar from the previous incision. In addition, coughing may elicit pain localized to a specific area. This technique enables the examiner to identify the area of maximal tenderness and to perform most of the abdominal examination without too much discomfort to the patient. Ascites secondary to metastatic breast carcinoma and an umbilical hernia are shown in Figure 14-13.
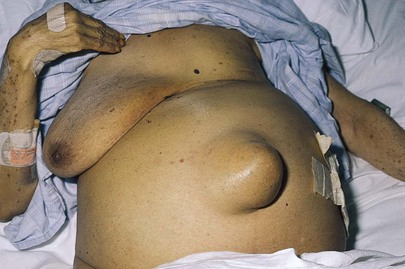
Figure 14–13 Ascites with umbilical hernia.
Inspect the Superficial Veins
The venous pattern of the abdomen is usually barely perceptible. If it is visible in the normal individual, the drainage of the lower two thirds of the abdomen is downward. In the presence of vena caval obstruction, superficial veins may dilate, and the veins drain cephalad (toward the head). In patients with portal hypertension, the dilated veins appear to radiate from the umbilicus. This is caused by backflow through the collateral veins within the falciform ligament, and this pattern is called caput medusae.
If the superficial veins are distended, evaluate the direction of drainage by the following technique: Place the tips of your index fingers on a vein that is oriented cephalad-caudad, not transverse, and compress it. Using continuous pressure, slide your index fingers apart for approximately 3 to 4 inches (7.5 to 10 cm). Remove one finger and observe the refilling in the direction of flow. Repeat this procedure, but this time remove your other finger and observe the direction of flow. Figure 14-14 shows the abdomen of a patient with intrahepatic portal hypertension. Notice the engorged paraumbilical veins; the flow was away from the umbilicus toward the caval system.
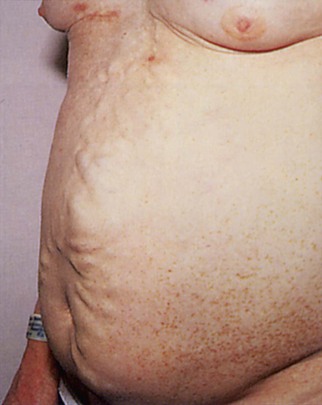
Figure 14–14 Abdominal venous pattern.
Auscultation
Auscultation of bowel sounds can provide information about the motion of air and liquid in the gastrointestinal tract. Always perform auscultation of the abdomen before percussion or palpation, in contrast to the usual order. It is believed that percussion or palpation may change the intestinal motility; therefore, auscultation should be performed first to produce a more accurate assessment of the existing bowel sounds.
Evaluate Bowel Sounds
The patient is placed in a supine position. To perform auscultation of the abdomen, the examiner places the diaphragm of the stethoscope over the midabdomen and listens for bowel sounds. This technique is pictured in Figure 14-15.
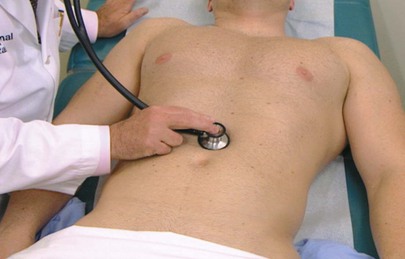
Figure 14–15 Technique for evaluating bowel sounds.
Normal bowel sounds occur approximately every 5 to 10 seconds and have a high-pitched sound. If after 2 minutes no bowel sounds are heard, “absent bowel sounds” may be noted. The absence of bowel sounds suggests a paralytic ileus that results from diffuse peritoneal irritation, peritonitis. Should one palpate before auscultation, one might stimulate the bowel, and the important sign of “absent bowel sounds” might be lost.
There may be rushes of low-pitched rumbling sounds, termed borborygmi, which are associated with hyperperistalsis. These sounds are similar to the sound of the word “borborygmi” itself. They are common in early acute intestinal obstruction.
Rule Out Obstructed Viscus
A succussion splash may be detected in a distended abdomen as a result of the presence of gas and fluid in an obstructed organ. The examiner applies the stethoscope over the patient’s abdomen while shaking the patient’s abdomen from side to side. The presence of a sloshing sound usually indicates distention of the stomach or colon. This technique is illustrated in Figure 14-16.
Rule Out Abdominal Bruits
Auscultation is also useful for determining the presence of bruits. Each quadrant should be evaluated for their presence. Bruits may result from stenosis of the renal artery or of the abdominal aorta. (See discussion of abdominal bruits in Chapter 12, The Peripheral Vascular System.)
Rule Out Peritoneal Rubs
A peritoneal friction rub, like a pleural or pericardial rub, is a rough, grating sound that indicates peritoneal inflammation as the two layers of the peritoneum (parietal and visceral) rub against each other. During respiratory motion, a peritoneal friction rub may be heard in the right or left upper quadrants in the presence of hepatic or splenic inflammation.
Percussion
Percussion is used to demonstrate the presence of gaseous distention and fluid or solid masses. In the normal examination, usually only the size and location of the liver and spleen can be determined. Some examiners prefer to palpate before percussion, especially if the patient complains of abdominal pain; either approach is correct. The technique of percussion is discussed in Chapter 10, The Chest.
Percuss the Abdomen
The patient lies supine. All four quadrants of the abdomen are evaluated by percussion. Tympany is the most common percussion note in the abdomen. It is caused by the presence of gas in the stomach, small bowel, and colon. The suprapubic area, when percussed, may sound dull if the urinary bladder is distended or, in a woman, if the uterus is enlarged.
Percuss the Liver
The upper border of the liver is percussed in the right midclavicular line, starting in the midchest. As the chest is percussed downward, the resonant note of the chest becomes dull as the liver is reached. As percussion continues still further, this dull note becomes tympanic because the percussion is now over the colon. The upper and lower borders of the liver should be no more than 4 inches (10 cm) apart. The technique is illustrated in Figure 14-17.
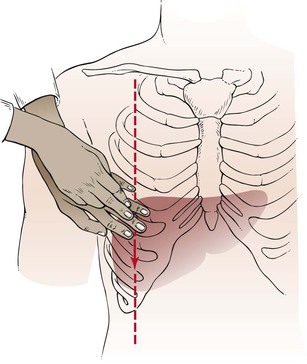
Figure 14–17 Technique for liver percussion.
There are several problems with predicting liver size by percussion. If ascites are present, the examiner can only speculate about the correct size of the liver. A more common cause of overestimating liver size (false-positive measurement) is some form of chronic obstructive lung disease. This makes percussion of the upper border of the liver difficult. Obesity in a patient can cause problems in both percussion and palpation. Distention of the colon may obscure the lower liver dullness. This may result in underestimating the size of the liver (false-negative measurement).
Percuss the Spleen
Although the size of the spleen is often difficult to determine, evaluation of the spleen should begin with percussion of splenic size. In normal individuals, the spleen lies hidden within the rib cage against the posterolateral wall of the abdominal cavity in Traube‘s space. Traube’s space is defined by the sixth rib superiorly, the left anterior axillary line laterally, and the costal margin inferiorly. As the spleen enlarges, it remains close to the abdominal wall, and the tip moves downward and toward the midline. Because the early enlargement is in an anteroposterior direction, considerable enlargement may occur without its becoming palpable below the costal margin. It is thought that dullness to percussion in Traube’s space, the loss of tympany from the air-filled colon and stomach because of the enlarged spleen, is a useful sign for determining splenic enlargement.
Have the patient lie in the supine position. With the patient breathing normally, percuss in the lowest intercostal space in the left anterior axillary line. Normal percussion yields either a resonant or tympanic note. A positive test of splenomegaly is diagnosed when the percussion note is dull. With ultrasonography, the standard imaging technique, splenic percussion has a sensitivity of 62% and a specificity of 72%. In leaner individuals who had not eaten in the previous 2 hours, the sensitivity was 78% and the specificity was 82%.
Rule Out Ascites
On patients in whom ascites are thought to be present, a special percussion test for shifting dullness may be performed. While the patient is lying on the back, the examiner determines the borders of tympany and dullness. The area of tympany is present above the area of dullness and is caused by gas in the bowel that is floating on top of the ascites. The patient is then asked to turn on the side, and the examiner again determines the borders of the percussion notes. If ascites is present, dullness “shifts” to the more dependent position; the area around the umbilicus that was initially tympanic becomes dull. Shifting dullness has a sensitivity of 83% to 88% and a specificity of 56%. The test for shifting dullness is illustrated in Figure 14-18.
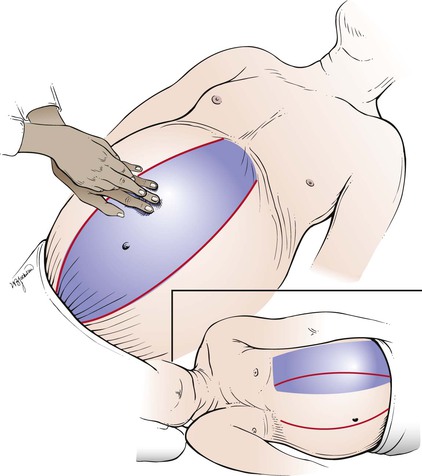
Figure 14–18 Technique for testing for shifting dullness. The shaded areas represent the areas of tympany.
An additional test for ascites is the presence of a fluid wave. Another examiner’s hand or the patient’s own hand is placed in the middle of the patient’s abdomen. Indenting the abdominal wall stops transmission of an impulse by the subcutaneous adipose tissue. The examiner then taps one flank while palpating the other side. The appearance of a fluid wave is suggestive of ascites. This technique is illustrated in Figure 14-19. The presence of a prominent fluid wave is the most specific of all physical diagnostic tests for ascites and has a specificity of 82% to 92%, according to several studies. A false-positive result may be obtained in obese individuals, and a false-negative result may be obtained when the ascites is small to moderate.
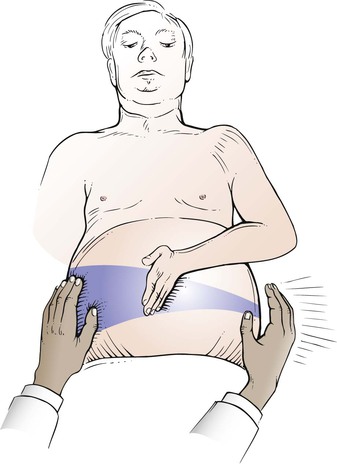
Figure 14–19 Technique for testing a fluid wave.
Another physical finding with ascites is the presence of bulging flanks. This change occurs when the weight of free abdominal fluid is sufficient to push the flanks outward. It has a 93% sensitivity and a 54% specificity for detecting ascites.
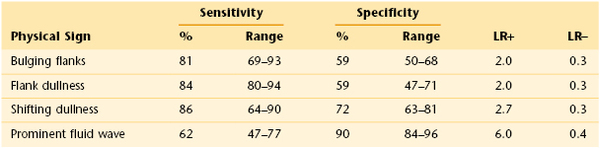
The most sensitive sign for ascites is the presence of shifting dullness, whereas the most specific sign is the presence of a prominent fluid wave. For an individual patient, the examiner must know the prevalence of disease or the pretest probability to apply sensitivity and specificity. Several studies have reviewed the operating characteristics of the physical examination tests for ascites. Their pooled sensitivity, specificity, and likelihood ratios for the presence of ascites are summarized in Table 14-4. The presence of a prominent fluid wave or shifting dullness is associated with the highest likelihood of the presence of ascites; the absence of bulging flanks, flank dullness, or shifting dullness decreases the likelihood.
Table 14–4
Characteristics of Physical Signs (Pooled Data) for Detection of Ascites*
* 95% confidence interval; data pooled from Cummings, et al (1985), Simel, et al (1988), Cattau, et al (1982), and Williams and Simel (1992).
LR+, Positive likelihood ratio; LR−, negative likelihood ratio.
Among the more common historical items perceived by patients, an increase in abdominal girth or recent weight gain has the highest chance of being associated with ascites. An increase in abdominal girth has a positive likelihood ratio (LR+) of 4.16; recent weight gain has an LR+ of 3.20. Conversely, the absence of the subjective increase in abdominal girth has a negative likelihood ratio (LR−) of 0.17; the absence of subjective ankle swelling carries an LR− of 0.10. With regard to the physical examination, the presence of a fluid wave or shifting dullness has the highest LR+ (9.6 or 5.76, respectively). The absence of bulging flanks or edema makes the presence of ascites least likely, with an LR− of 0.12 or 0.17, respectively.
Palpation
Abdominal palpation is commonly divided into the following:
The patient is supine during palpation. Always begin palpation in an area of the abdomen that is farthest from the location of pain.
Light Palpation
Light palpation is used to detect tenderness and areas of muscular spasm or rigidity. The examiner should systematically palpate the entire abdomen by using the flat part of his or her right hand or the pads of the fingers, not the fingertips. The fingers should be together, and sudden jabs are to be avoided. The hand should be lifted from area to area instead of sliding over the abdominal wall. Light palpation is demonstrated in Figure 14-20.
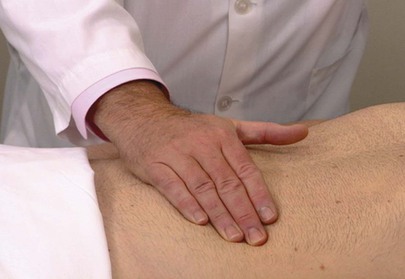
Figure 14–20 Technique for light palpation.
With patients who are ticklish, it may be useful to sandwich their hand between the examiner’s hands, as demonstrated in Figure 14-21.
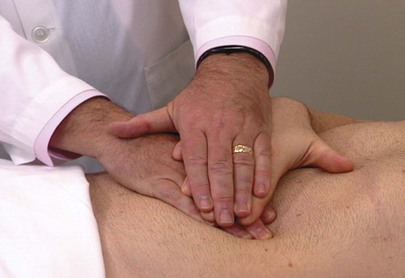
Figure 14–21 Technique used for ticklish patients. The patient’s hand is sandwiched between the examiner’s hands.
During expiration, the rectus muscles usually relax and soften. If there is little change, rigidity is said to be present. Rigidity is involuntary spasm of the abdominal muscles and is indicative of peritoneal irritation. Rigidity may be diffuse, as in diffuse peritonitis, or localized, as over an inflamed appendix or gallbladder. In patients with generalized peritonitis, the abdomen is described as “boardlike.”
In patients who complain of abdominal pain, palpation should be performed gently. Lightly stroking the abdomen with a pin may reveal an area of increased sensation that is caused by inflammation of the visceral or parietal peritoneum. This sensation is hyperesthesia. The patient is asked to determine whether the pin feels sharper on one side of the abdomen than on the corresponding area on the other side. Although useful, the presence or absence of this finding must be considered in view of all other findings.
Deep Palpation
Deep palpation is used to determine organ size, as well as the presence of abnormal abdominal masses. In deep palpation, the examiner places the flat portion of his or her right hand on the patient’s abdomen, and his or her left hand is placed over the right hand. The fingertips of the left hand exert the pressure, while the right hand should appreciate any tactile stimulation. Pressure should be applied to the abdomen gently but steadily. The technique of deep palpation is demonstrated in Figure 14-22.
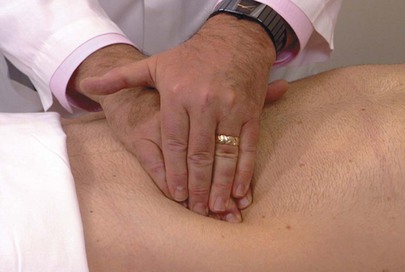
Figure 14–22 Technique for deep palpation.
During deep palpation, the patient should be instructed to breathe quietly through the mouth and to keep arms at the sides. Asking the patient to open the mouth when breathing seems to aid in generalized muscular relaxation. The palpating hands should be warm, because cold hands may produce voluntary muscular spasm called guarding. Engaging the patient in conversation often aids in relaxing the patient’s abdominal musculature. Patients with well-developed rectus muscles should be instructed to flex their knees to relax the abdominal muscles. Any tender areas must be identified.
Rule Out Rebound Tenderness
In a patient with abdominal pain, it should be determined whether rebound tenderness is present. Rebound tenderness is a sign of peritoneal irritation and can be elicited by palpating deeply and slowly in an abdominal area away from the suspected area of local inflammation. The palpating hand is then quickly removed. The sensation of pain on the side of the inflammation that occurs on release of pressure is rebound tenderness. If generalized peritonitis is present, pain is felt in the area of palpation. The patient should be asked, “Which hurts more, now (while pressing) or now (during release)?” This is a useful test, but because generalized pain is elicited in the patient with peritonitis, the maneuver should be performed near the conclusion of the abdominal examination.
Liver Palpation
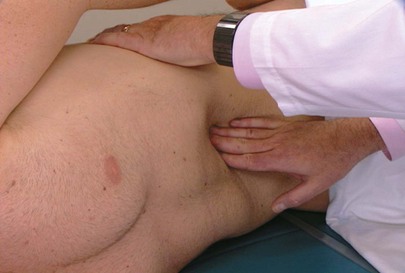
To perform palpation of the liver, place your left hand posteriorly between the patient’s right twelfth rib and the iliac crest, lateral to the paraspinal muscles. Place your right hand in the patient’s right upper quadrant parallel and lateral to the rectus muscles and below the area of liver dullness. The patient is instructed to take a deep breath as you press inward and upward with your right hand and pull upward with your left hand. You may feel the liver edge slipping over the fingertips of your right hand as the patient breathes. Start as low as the pelvic brim and gradually work upward. If the examination does not start low, a markedly enlarged liver edge may be missed. The technique of liver palpation is demonstrated in Figure 14-23.
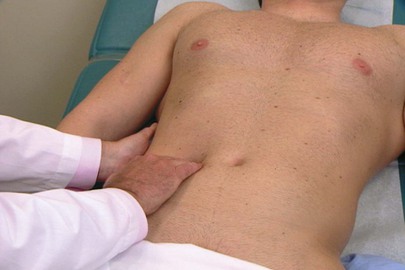
Figure 14–23 Technique for liver palpation.
The normal liver edge has a firm, regular ridge, with a smooth surface. If the liver edge is not felt, repeat the maneuver after readjusting your right hand closer to the costal margin. Enlargement of the liver results from vascular congestion, hepatitis, neoplasm, or cirrhosis.
Another technique for liver palpation is the “hooking” method. The examiner stands near the patient’s head and places both hands together below the right costal margin and the area of dullness. The examiner presses inward and upward and “hooks” around the liver edge while the patient inhales deeply. The technique of hooking the liver is shown in Figure 14-24.
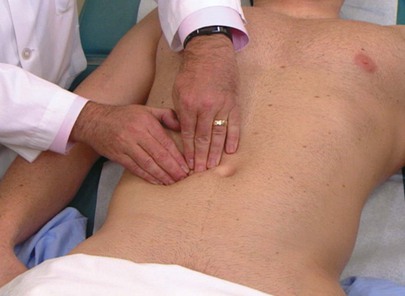
Figure 14–24 Technique for “hooking” the liver.
On occasion, the liver appears to be enlarged, but the actual border is difficult to determine. The scratch test may be helpful in ascertaining the liver’s edge. The examiner holds the diaphragm of the stethoscope with the left hand and places it below the patient’s right costal margin over the liver. While the examiner listens through the stethoscope, his or her right index finger “scratches” the abdominal wall at points in a semicircle equidistant from the stethoscope. As the finger scratches over the liver’s edge, there is a marked increase in the intensity of the sound. This technique is illustrated in Figure 14-25.
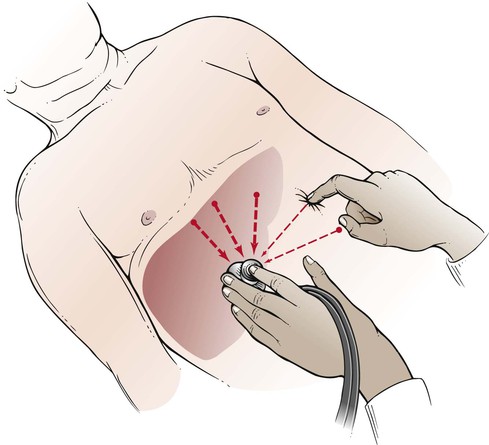
Figure 14–25 The scratch test for determining liver size.
A palpable liver is not necessarily enlarged or diseased; however, its being palpable does increase the possibility of hepatomegaly. Being nonpalpable does not rule out hepatomegaly, but it does reduce the likelihood that the liver is enlarged. The LR+ for hepatomegaly, if the liver is palpable, is 2.5; if the liver is not palpable or if enlargement of the liver is detected by scintigraphic scanning, the LR− is 0.45.
Rule Out Hepatic Tenderness
To elicit hepatic tenderness, place the palm of your left hand over the patient’s right upper quadrant and gently hit it with the ulnar surface of the fist of your right hand. Inflammatory processes involving the liver or gallbladder produce tenderness on fist palpation. Figure 14-26 demonstrates this technique.
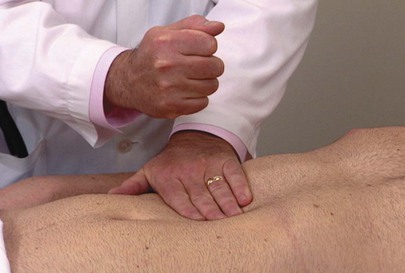
Figure 14–26 Liver tap technique for assessing liver tenderness.
On occasion during liver palpation, pain is elicited in the left upper quadrant during inspiration, and the patient suddenly stops inspiratory efforts. This is called Murphy‘s sign and is suggestive of acute cholecystitis. On inspiration, the lungs expand, pushing the diaphragm, liver, and inflamed gallbladder down into the abdominal cavity. As the inflamed gallbladder descends against the palpating hand, pain is produced, and there is sudden inspiratory arrest.
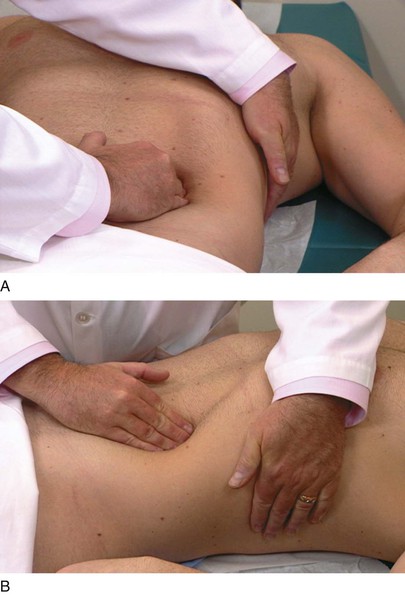
Spleen Palpation
Palpation of the spleen is more difficult than palpation of the liver. The patient lies on the back, with the examiner at the patient’s right side. The examiner places his or her left hand over the patient’s chest and elevates the patient’s left rib cage. The examiner’s right hand is placed flat below the patient’s left costal margin and presses inward and upward toward the anterior axillary line. The left hand exerts an anterior force to displace the spleen anteriorly. Figure 14-27 illustrates the positions of the hands for splenic palpation.
The patient is instructed to take a deep breath as the examiner presses inward with the right hand. The examiner should attempt to feel the tip of the patient’s spleen as it descends during inspiration. The tip of an enlarged spleen will lift the fingers of the right hand upward.
The examination of the spleen is repeated with the patient lying on the right side. This maneuver allows gravity to help bring the spleen anterior and downward into a more favorable position for palpation. The examiner places his or her left hand on the patient’s left costal margin while the right hand palpates in the left upper quadrant. The technique is demonstrated in Figure 14-28.
Because the spleen enlarges diagonally in the abdomen from the left upper quadrant toward the umbilicus, the examiner’s right hand should always palpate near the umbilicus and gradually move toward the left upper quadrant. This is particularly important if the spleen is massively enlarged because starting the palpation too high may cause the examiner to miss the splenic border.
The spleen is not palpable in normal conditions, but both techniques should be used in an attempt to palpate it. Splenic enlargement may result from hyperplasia, congestion, infection, or infiltration by tumor or myeloid elements. Massive splenomegaly in a patient with chronic myelocytic leukemia is pictured in Figure 14-29.
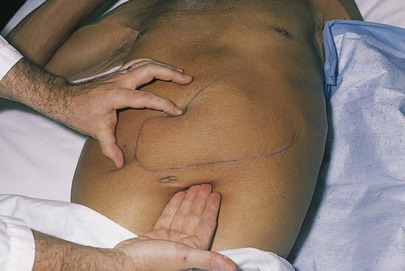
Figure 14–29 Splenomegaly. Note the splenic notch.
Kidney Palpation
More often than not, neither kidney can be palpated in the adult. This is related to the fact that the kidneys are retroperitoneal structures and extremely difficult to evaluate in the adult because of adipose tissue and muscle. The technique, however, is important to know, especially in the evaluation of a newborn.
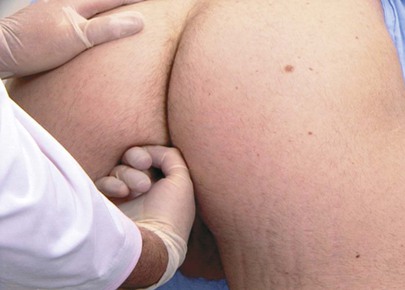
Palpation of the right kidney is performed by deep palpation below the right costal margin. The examiner stands at the patient’s right side and places his or her left hand behind the patient’s right flank, between the costal margin and the iliac crest. The right hand is placed just below the patient’s costal margin with the tips of the fingers pointing to the examiner’s left. The method of kidney palpation is demonstrated in Figure 14-30.
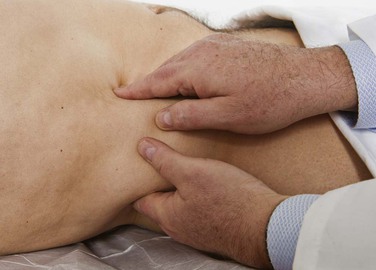
Figure 14–30 Technique for kidney palpation.
Very deep palpation may reveal the lower pole of the right kidney as it descends during inspiration. The lower pole may be felt as a smooth, rounded mass.
The same procedure is used for the left kidney except that the examiner is on the patient’s left side. Because the left kidney is more superior than the right, the lower pole of a normal left kidney is rarely palpable. On occasion, the spleen may be mistaken for an enlarged left kidney. The medial notch of the spleen is helpful in differentiating it from the kidney (see Fig. 14-29).
Rule Out Renal Tenderness
For this part of the examination, the patient should be seated. The examiner should make a fist and gently hit the area overlying the costovertebral angle on each side. Figure 14-31 demonstrates the technique. Patients with pyelonephritis usually have extreme pain even on slight percussion in these areas. If pyelonephritis is suspected, only digital pressure should be used. As is described in Chapter 19, Putting the Examination Together, this portion of the abdominal examination is usually performed when the posterior chest is examined.
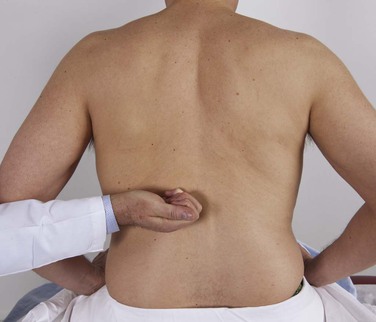
Figure 14–31 Assessing costovertebral angle tenderness.
Rectal Examination
The routine abdominal examination concludes with the digital rectal examination (DRE). Because the anterior rectum has a peritoneal surface, the DRE may reveal tenderness if peritoneal inflammation is present.
The patient should be instructed to empty his bladder and bowels before the examination.
The rectal examination for the male patient is discussed here; for the female patient, it is discussed in Chapter 16, Female Genitalia.
Patient Positioning
The examination of the rectum in the male patient may be performed with the patient lying on his back, lying on the left side, or standing and bent over the examination table. The modified lithotomy position (patient on the back with knees flexed) is used when the patient has difficulty standing or when a detailed examination of the anus is not required. The examiner passes the right hand under the patient’s right thigh. The index finger in the patient’s rectum is used in conjunction with the examiner’s left hand, which is placed on the patient’s abdomen. This bimanual approach is useful and causes minimal disturbance of the sick patient.
The left lateral prone position, called Sims’ position, is used commonly in patients who are weak and confined to bed. In this position, the right upper leg should be flexed while the left lower leg is semiextended. The modified lithotomy and left lateral prone positions are pictured in Figure 14-32.
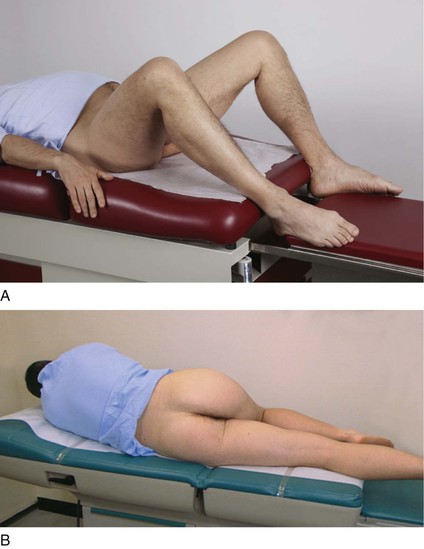
Figure 14–32 Positions for the rectal examination. A, Modified lithotomy position. B, Sims’ position.
The standing position is the one most commonly used for men and allows for thorough inspection of the anus and palpation of the rectum. The patient is instructed to stand bent over, with shoulders and elbows supported on the bed or examination table. The examiner’s gloved right hand is used to examine the anus and the tissue surrounding it while the left hand carefully spreads the buttocks. The examiner should wear gloves on both hands. The anal skin is inspected for signs of inflammation, excoriation, fissures, nodules, fistulas, scars, tumors, and hemorrhoids. Any abnormal areas should be palpated. The patient is asked to strain while the examiner inspects the anus for hemorrhoids or fissures. Figure 14-33 shows prolapsed internal hemorrhoids.
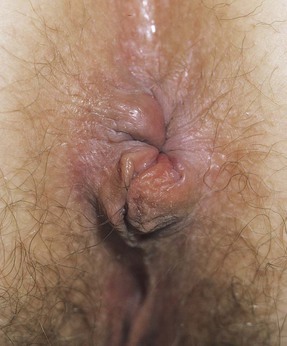
Figure 14–33 Prolapsed internal hemorrhoids.
The Technique
The patient is told that a rectal examination will now be performed. The examiner should tell the patient that a lubricant that will feel cool will be used, and this will be followed by the sensation of having to move the bowels; the patient should be assured that he will not do so. Inspect the anus as shown in Figure 14-34A.
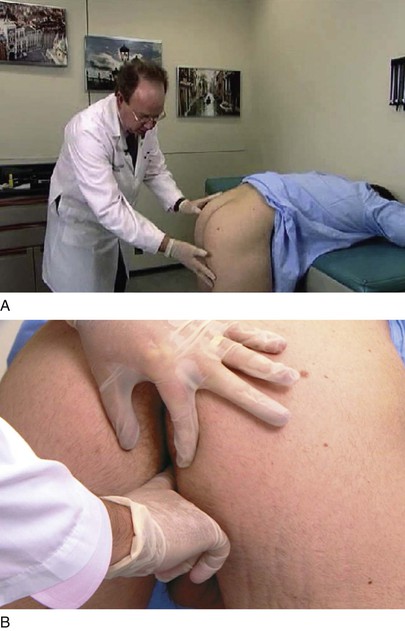
Figure 14–34 Technique of the rectal examination. A, Inspection. B, Palpation. The examiner’s finger is inserted with the palm of the hand facing downward.
The examiner lubricates the right gloved index finger and places the left hand on the patient’s buttocks. As the left hand spreads the patient’s buttocks, the examiner’s right index finger is gently placed on the anal verge. The sphincter should be relaxed by gentle pressure with the palmar surface of the finger. Figure 14-35A illustrates the procedure.
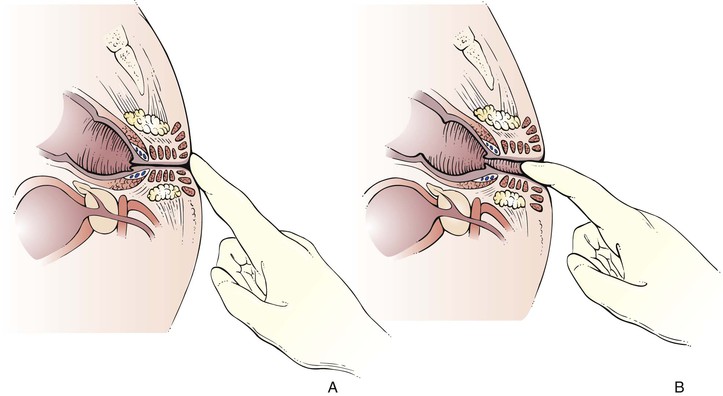
Figure 14–35 Illustration of the rectal examination. A, The sphincter is relaxed by gentle pressure with the palmar surface of the examiner’s finger. B, With the examiner’s left hand spreading the patient’s buttocks, examination is carried out with the examiner’s right index finger.
The patient is instructed to take a deep breath, at which time the examiner’s right index finger is inserted into the anal canal as the anal sphincter relaxes (see Fig. 14-34B). The sphincter should close completely around the examining digit. The sphincter tone should be assessed. This examination is illustrated in Figure 14-35B.
The finger should be inserted as far as possible into the rectum, although 4 inches (approximately 10 cm) is the probable limit of digital exploration. The examiner’s left hand can now be moved to the patient’s left buttock, while the right index finger examines the rectum.
Palpate the Rectal Walls
The lateral, posterior, and anterior walls of the rectum are palpated. To palpate the lateral walls, rotate your digit along the sides of the patient’s rectum, as shown in Figure 14-36. The ischial spines, coccyx, and lower sacrum can be felt easily. Palpate the walls for polyps, which may be sessile (attached by a base) or pedunculated (attached by a stalk). Any irregularities or undue tenderness should be noted. The only way to examine the entire circumference of the rectal wall fully is to turn your back to the patient, which will allow you to hyperpronate your hand. Unless you do so, you will be unable to examine the portion of the rectal wall between the 12 o’clock and 3 o’clock positions. A small lesion in this quadrant may go undetected.
Palpate the Prostate Gland
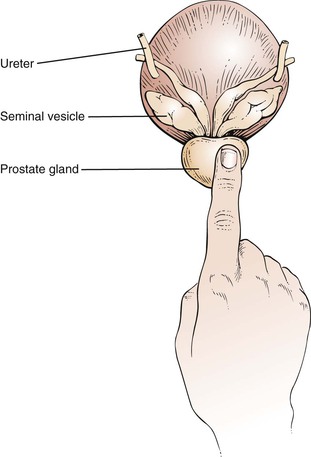
The prostate gland lies anterior to the wall of the rectum. The size, surface, consistency, sensitivity, and shape of the prostate gland should be assessed.
The prostate is a bilobed, heart-shaped structure approximately 1.5 inches (4 cm) in diameter. It is normally smooth and firm and has the consistency of a hard rubber ball. The apex of the heart shape points toward the anus. Identify the median sulcus and the lateral lobes. Note any masses, tenderness, and nodules. Only the lower apex portion of the gland is palpable. The superior margin is usually too high to reach. The examination of the prostate is illustrated in Figure 14-37. The size of the prostate in relation to the examiner’s finger is illustrated in Figure 14-38.
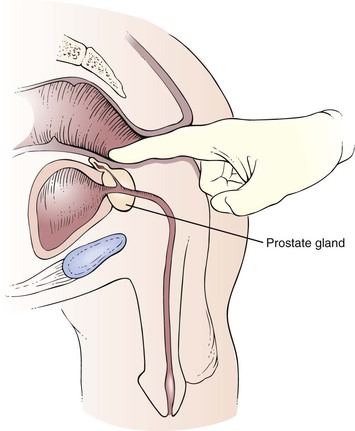
Figure 14–37 Examination of the prostate.
A hard, irregular nodule produces asymmetry of the prostate gland and is suggestive of cancer. Carcinoma of the prostate frequently involves the posterior lobe, which can easily be identified during the DRE. Carcinoma of the prostate is the third leading cause of death in men (9% of all cancer deaths) in the United States. In 2011, there were 240,890 new cases of prostate cancer and 33,720 deaths from the disease in the United States. Early detection is usually limited to detection of an abnormality on DRE.
Benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) produces a symmetrically enlarged, soft gland that protrudes into the rectal lumen. This diffuse enlargement is common among men older than 60 years. A boggy, fluctuant, or tender prostate may indicate acute prostatitis. The seminal vesicles lie superior to the prostate gland and are rarely palpated, unless they are enlarged.
The rectal examination is concluded by informing the patient that you are now going to withdraw your finger. Gently remove the examining finger, and give the patient tissues to wipe himself.
Fecal Occult Blood Test
The examining digit should be inspected. The color of the fecal material should be noted. The fecal material should be placed on the fecal occult blood test (FOBT) card and examined with the Hemoccult developer.
The guaiac or benzidine test detects occult blood. If blood is present, a chemical reaction results in a blue coloration on the card. The reaction is graded by the intensity of the blue color, from light blue (trace blood) to dark blue (4+ positive).
Although the examination for inguinal hernias is part of the abdominal examination, it is discussed in Chapter 15, Male Genitalia and Hernias.
Special Techniques
Intra-abdominal inflammation, such as that which results from an inflamed appendix lying on the psoas muscle, may produce some physical signs. A special test performed when there is suspicion of intra-abdominal inflammation is the iliopsoas test. The patient is asked to lie on the unaffected side and extend the other leg at the hip against the resistance of the examiner’s hand. A positive psoas sign is abdominal pain with this maneuver. Irritation of the right psoas muscle by an acutely inflamed appendix produces a right psoas sign. This test is demonstrated in Figure 14-39.
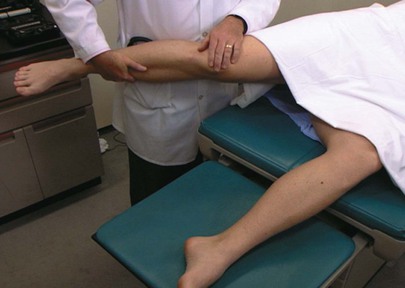
Figure 14–39 The iliopsoas test.
Another useful test for inflammation is the obturator test. While the patient is lying on the back, the examiner flexes the patient’s thigh at the hip, with the patient’s knees bent, and rotates the leg internally and externally at the hip. If there is an inflammatory process adjacent to the obturator muscle, pain is elicited. The obturator test is demonstrated in Figure 14-40.
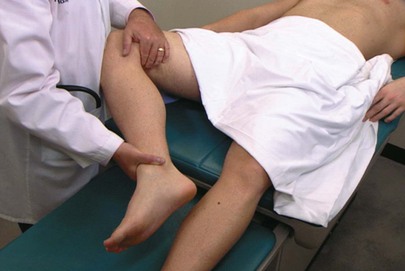
Figure 14–40 The obturator test.
Clinicopathologic Correlations
There is evidence that detecting and removing polyps reduces the incidence of colorectal cancer and that detecting early cancers lowers the mortality rate from colorectal cancer. The American Cancer Society has suggested the following guidelines for the early detection of colorectal cancer in individuals without increased risk. Beginning at age 50 years, men and women should follow one of the following examination schedules:
Tests That Find Polyps and Cancer:
Tests That Primarily Find Cancer:
These schedules may be modified based on a patient’s personal history or family history.
The colorectal cancer mortality rate can be reduced 15% to 33% by FOBT and diagnostic evaluation and treatment for positive test results. Annual FOBT screening leads to a greater reduction in the colorectal cancer mortality rate than does biennial screening. Flexible sigmoidoscopy identifies nearly all cancers and polyps greater than 0.4 inch (1 cm) in diameter and 75% to 80% of small polyps that are located in the portion of the bowel examined. Screening with flexible sigmoidoscopy has been shown to result in a 60% to 80% reduction in risk of death from colorectal cancer in the part of the colon examined. There is indirect evidence supporting the use of double-contrast barium enema testing in screening for colorectal cancer. This test can image the entire colon and detect cancers and large polyps. Screening colonoscopy offers the potential both to identify and remove cancers and premalignant lesions throughout the colon and rectum. However, no studies that show a reduction in the mortality rate associated with screening colonoscopy have been completed to date.
Anal cancer is increasing in both men and women worldwide. Men who have sex with men, HIV-positive individuals, transplant recipients, and women with cervical neoplasia have a higher risk for anal cancer than the general population. Men who have sex with men have a 44% greater risk for anal cancer than the general population (Chin-Hong, 2008). Anal cancer, like cervical cancer, is potentially preventable. Anal cytologic findings have been studied and found to be a useful screening test to detect anal cancer. It has been shown that a high proportion of men who have sex with men were infected with anal human papillomavirus (66%).
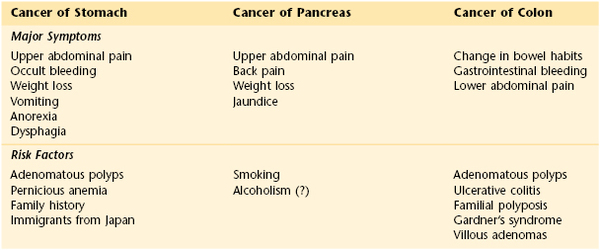
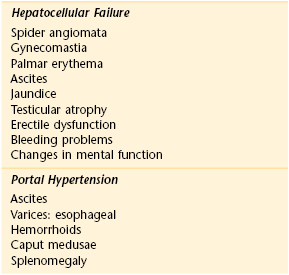
Table 14-2 lists the classic locations of pain referred from abdominal structures. Table 14-3 summarizes the maneuvers for ameliorating abdominal pain. Table 14-4 summarizes the sensitivities and specificities of the various maneuvers used to detect ascites. Table 14-5 is a comparison of the clinical manifestations of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Table 14-6 lists the clinical features of cancer of the stomach, pancreas, and colon. Table 14-7 lists the variation of symptoms in right-sided and left-sided colon cancer and in rectal cancer. Table 14-8 compares the symptoms and signs of cirrhosis, which are numerous, as they relate to hepatocellular failure and portal hypertension.
Table 14–5
Clinical Comparison of Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
| Feature | Ulcerative Colitis | Crohn’s Disease |
| Diarrhea | Present | Present |
| Hematochezia | Common | Rare |
| Extraintestinal manifestations | Common | Common |
| Perirectal disease | Fissures | Fistulas Abscesses |
| Rectal disease | Present | Absent |
| Anal disease | Absent | Present |
Table 14–7
Variation of Symptoms of Cancer of the Right Colon, Left Colon, and Rectum
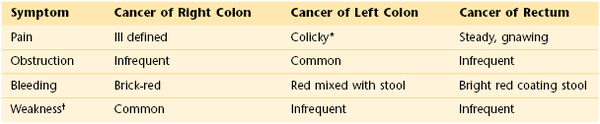
* Worse with ingestion of foods.
† Secondary to anemia.
Prostate cancer is the leading cancer diagnosed among men in the United States, accounting for 33% of all cancers in men. However, racial and ethnic variations in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) study data are striking: The incidence rate among African-American men (180.6 per 100,000) is more than seven times that among Koreans (24.2 per 100,000). Indeed, African Americans in the United States have the highest rates of this cancer in the world. Although the incidence among white persons is quite high, it is distinctly lower than that among African Americans. Asian and Native American men have the lowest rates. The very low rate in Korean men possibly reflects the fact that most of the Koreans in the SEER areas were recent immigrants from Asia, where rates are lower than in the United States.
Nearly 9 per 10 prostate cancers (86%) are diagnosed at a localized stage, when the 5-year survival rate is 100%. The incidence rates for prostate cancer, however, continue to increase, in part because of increased numbers of screening tests. Prostate cancer can often be found early by a DRE and by testing the amount of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in a sample of blood. If a man has routine yearly examinations and either one of these test results becomes abnormal, any cancer that he may have has probably been found at an early, more treatable stage. Since the use of these early detection tests for prostate cancer became relatively common around 1990, the death rate from prostate cancer has dropped.
PSA is a substance made by the normal prostate gland. Although PSA is found mostly in semen, a small amount is also present in the blood. Most men have levels under 4 ng/mL of blood. When prostate cancer develops, the PSA level usually goes above 4 ng/mL. If the level is above 4 ng/mL but less than 10 ng/mL, the man has about a 25% chance of having prostate cancer. If it goes above 10 ng/mL, the chance of having prostate cancer is more than 67% and increases as the PSA level increases.
The PSA level can be affected by many factors and as such has many false positives for cancer. It is increased with noncancerous enlargement of the prostate (i.e., BPH), and with prostatitis. PSA levels also normally rise slowly with aging. Ejaculation can cause a temporary increase in blood PSA levels, so it is often recommended that men abstain from ejaculation for 2 days before testing. A false-positive test result may create anxiety for the man and his family and lead to additional medical procedures, such as a prostate biopsy, that can potentially be harmful: Serious infections, pain, and bleeding can result. False negatives may also occur, giving the man, his family, and his doctor false assurance that he does not have cancer, when he may in fact have a cancer that requires treatment.
Until recently, many doctors and professional organizations encouraged yearly PSA screening for men beginning at age 50. Some organizations recommended that men who are at higher risk of prostate cancer, including African-American men and men whose father or brother had prostate cancer, begin screening at age 40 or 45. However as of 2013, as more has been learned about both the benefits and harms of prostate cancer screening,5 a number of organizations have begun to caution against routine population screening. Although some organizations continue to recommend PSA screening, there is widespread agreement that any man who is considering getting tested should first be informed in detail about the potential harms and benefits.
The “Ask-Tell-Ask” approach derived from motivational interviewing is useful in counseling patients about the benefits and risks of screening. It is a back-and-forth, bidirectional cycle between the patient and the clinician that addresses four essential components: the patient’s perspective, information that needs to be delivered, response to the patient’s emotions, and recommendations by the clinician. Ask the male patient to describe his current understanding of the issue. You might say:
“To make sure we are on the same page, can you tell me what your understanding of your disease is?”
“What have your others been telling you about your illness since the last time we spoke?”
“Have you thought about whether you want to be screened for prostate cancer?”
Tell the patient in straightforward language what you need to communicate: treatment options, bad news, or other information. Stop short of giving a long lecture or huge amounts of detail. Finally, ask the patient if he understood what you just said.6Researchers are now investigating ways to improve the PSA test to better distinguish cancerous from benign lesions and slow-growing cancers from fast-growing, potentially lethal cancers. Some of the methods being studied include:
• PSA density of the transition zone8
• Age-specific PSA reference ranges9
The bibliography for this chapter is available at studentconsult.com.
Bibliography
American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2010. [Available at] http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@epidemiologysurveilance/documents/document/acspc-026238.pdf [Accessed January 30, 2013] .
American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2012. American Cancer Society: Atlanta; 2012.
American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2013. American Cancer Society: Atlanta; 2013.
American Cancer Society. American Cancer Society recommendation for early detection of prostate cancer. [Updated February 27, 2012. Available at] http://www.cancer.org/cancer/prostatecancer/moreinformation/prostatecancerearlydetection/prostate-cancer-early-detection-acs-recommendations [Accessed January 31, 2013] .
American Urological Association. American Urological Association guideline: management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). [Available at] http://www.auanet.org/education/guidelines/benign-prostatic-hyperplasia.cfm [Accessed August 24, 2013] .
American Urological Association. Early detection of prostate cancer: AUA guideline. [Available at] http://www.auanet.org/common/pdf/education/clinical-guidance/Prostate-Cancer-Detection.pdf; April 2013 [Accessed August 24, 2013] .
American Urological Association. PSA testing for the pretreatment staging and posttreatment management of prostate cancer: 2013 revision of 2009 best practice statement. [Available] http://www.auanet.org/education/guidelines/prostate-specific-antigen.cfm [Accessed August 24, 2013] .
Andriole GL, et al. Prostate cancer screening in the randomized Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial: mortality results after 13 years of follow-up. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104(2):125.
Barkun AN, et al. Splenic enlargement and Traube’s space: how useful is percussion? Am J Med. 1989;87:562.
Barkun AN, et al. The bedside assessment of splenic enlargement. Am J Med. 1991;91:512.
Barry MJ. Screening for prostate cancer: a controversy that refused to die (editorial). N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1351.
Bernstein CN, et al. The incidence of fracture among patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2000;133:795.
Carter HB, et al. Detection of life-threatening prostate cancer with prostate-specific antigen velocity during a window of curability. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:1521.
Castell DO. The spleen percussion sign: a useful diagnostic technique. Ann Intern Med. 1967;67:1265.
Cattau EL, et al. The accuracy of the physical examination in the diagnosis of suspected ascites. JAMA. 1982;247:1164.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis A fact sheet. [Available at] http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/A/pdfs/HepAGeneralFactSheet.pdf; June 2010 [Accessed January 31, 2013] .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis B information for health professionals. [Updated May 16, 2012. Available at] http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/HBV/index.htm [Accessed January 31, 2013] .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis C FAQs for health professionals. [Updated August 16, 2012. Available at] http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/HCV/HCVfaq.htm [Accessed January 31, 2013] .
Chin-Hong PV, et al. Comparison of patient- and clinician-collected anal cytology samples to screen for human papillomavirus-associated anal intraepithelial neoplasia in men who have sex with men. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:300.
Cotterchio M, et al. Colorectal screening is associated with reduced colorectal cancer risk: a case-control study within the population-based Ontario Familial Colorectal Cancer Registry. Cancer Causes Control. 2005;16:865.
Cummings S, et al. The predictive value of physical examination for ascites. West J Med. 1985;142:633.
Dienstag JL. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1486.
DuPont HL. Bacterial diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1560.
Edwards JL. Diagnosis and management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Am Fam Phys. 2008;77:1403.
Fowler FJ, et al. The impact of a suspicious prostate biopsy on patients’ psychological, socio-behavioral, and medical care outcomes. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21:715.
Gaster B, et al. Patient-centered discussions about prostate cancer screening: a real-world approach. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153:661.
Ghany MG, et al. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: an update, American Association for the Study of Liver Disease (AASLD) practice guidelines. Hepatology. 2009;49:1335.
Grover SA, Barkun AN, Sackett DL. Does this patient have splenomegaly? JAMA. 1993;270:2218.
Gu Y, Lim HJ, Moser MA. How useful are bowel sounds in assessing the abdomen? Dig Surg. 2010;27:422.
Guptak WB. In the clinic: acute pancreatitis. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153.
Halpern S, et al. Correlation of liver and spleen size: determinations by nuclear medicine studies and physical examination. Arch Intern Med. 1974;134:123.
Harris R, Lohr KN. Screening for prostate cancer: an update of the evidence for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137:917.
Imperiale TF, et al. Fecal DNA versus fecal occult blood for colorectal-cancer screening in an average-risk population. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2704.
Lederle F. In the clinic: abdominal aortic aneurysm. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150.
Leitzmann MF, et al. Ejaculation frequency and subsequent risk of prostate cancer. JAMA. 2004;291:1578.
Levin B, et al. Emerging technologies in screening for colorectal cancer: CT colonography, immunochemical fecal occult blood tests, and stool screening using molecular markers. CA Cancer J Clin. 2003;53:44.
Levin B, et al. Screening and surveillance for the early detection of colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps, 2008: a joint guideline from the American Cancer Society, the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, and the American College of Radiology. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58(3):130.
Lin K, et al. Benefits and harms of prostate-specific antigen screening for prostate cancer: an evidence update from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:192.
Markowitz SD, et al. Focus on colon cancer. Cancer. 2002;1:233.
Mayer EA. Irritable bowel syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1692.
Meidl EJ, Ende J. Evaluation of liver size by physical examination. J Gen Intern Med. 1993;8:635.
Moyer VA. Screening for prostate cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. [on behalf of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force] Ann Intern Med. 2012;157(2):120.
National Cancer Institute. Colorectal cancer prevention. Health professional version. [Updated December 3, 2012. Available at] http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/prevention/colorectal/HealthProfessional [Accessed January 31, 2013] .
National Cancer Institute. Colorectal cancer screening. Health professional version. [Updated December 4, 2012. Available at] http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/screening/colorectal/HealthProfessional/AllPages [Accessed January 31, 2013] .
National Cancer Institute. Prostate cancer screening. Health professional version. [Updated November 28, 2012. Available at] http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/screening/prostate/healthprofessional/allpages [Accessed January 31, 2013] .
National Cancer Institute. Prostatic-specific antigen (PSA) test. [Available at] http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/factsheet/Detection/PSA [Updated July 24, 2012. Accessed February 18, 2013] .
Naylor CD. Physical examination of the liver. JAMA. 1994;271:1859.
Robertson DJ, et al. Colorectal cancer in patients under close colonoscopic surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:34.
Schiller LR. Chronic diarrhea. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:287.
Schröder FH, et al. Prostate-cancer mortality at 11 years of follow-up. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(11):981.
Seeff L, Shapiro J, Nadel M. Are we doing enough to screen for colorectal cancer? Findings from the 1999 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. J Fam Pract. 2003;51:761.
Simel DL, Halvorsen RA, Feussner JR. Quantitating bedside diagnosis: clinical evaluation of ascites. J Gen Intern Med. 1988;3:423.
Smith RA, Cokkinides V, Eyre HJ. American Cancer Society guidelines for the early detection of cancer, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin. 2004;54:41.
Thompson IM, et al. Prevalence of prostate cancer among men with a prostate-specific antigen level < or = 4.0 ng per milliliter. New Engl J Med. 2004;350:2239.
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148:627.
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for prostate cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149:185.
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for prostate cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148:627 [Available at http://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf08/prostate/prostaters.htm. Accessed January 31, 2013] .
Vickers AJ, et al. Prostatic specific antigen concentration at age 60 and death from metastasis from prostate cancer: case-control study. BMJ. 2010;341:c4521.
Weinberg DS. In the clinic: colorectal cancer screening. Ann Intern Med. 2008;148.
Whitcomb DC. Acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2142.
Williams JW, Simel DL. Does this patient have ascites? How to divine fluid in the abdomen. JAMA. 1992;267:2645.
Wilson JE. In the clinic: irritable bowel syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147.
Wilson JE. In the clinic: gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149.
1 Often abbreviated as BRBPR.
2 For example, dermatitis herpetiformis (a blistering disease predominantly on the buttocks, shoulders, elbows, and knees) or lichen planus.
3 If the test is positive, a colonoscopy should be done.
4 The multiple stool take-home test should be used. One test done by the doctor in the office is not adequate for testing. A colonoscopy should be done if the test is positive.
5 Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian (PLCO) Cancer Screening Trial was a trial of 76,693 men, and the European Randomized Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer (ERSPC) trial of 182,000 men. The results of these studies were conflicting. The PLCO trial showed no benefit from screening in reducing mortality. The ERSPC trial showed a 20% reduction in mortality in men ages 55 to 69 years of age but at a cost of overdiagnosis with a 76% false-positive rate on biopsy.
7 The amount of PSA in the blood that is “free” (not bound to other proteins) divided by the total amount of PSA (free plus bound). Some evidence suggests that a lower proportion of free PSA may be associated with more aggressive cancer.
8 The blood level of PSA divided by the volume of the transition zone of the prostate. The transition zone is the interior part of the prostate that surrounds the urethra. Some evidence suggests that this measure may be more accurate at detecting prostate cancer than the standard PSA test.
9 Because a man’s PSA level tends to increase with age, it has been suggested that the use of age-specific PSA reference ranges may increase the accuracy of PSA tests. However, age-specific reference ranges have not been generally favored because their use may delay the detection of prostate cancer in many men.
10 PSA velocity is the rate of change in a man’s PSA level over time, expressed as ng/mL per year. PSA doubling time is the period of time over which a man’s PSA level doubles. Some evidence suggests that the rate of increase in a man’s PSA level may be helpful in predicting whether he has prostate cancer.
11 Pro-PSA refers to several different inactive precursors of PSA. There is some evidence that pro-PSA is more strongly associated with prostate cancer than with BPH. One recently approved test combines measurement of a form of pro-PSA with measurements of PSA and free PSA. The resulting “prostate health index” can be used to help a man with a PSA level of between 4 and 10 ng/mL decide whether he should have a biopsy.