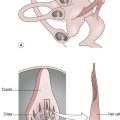
Thalamus and limbic system
Basic anatomy OF THE THALAMUS
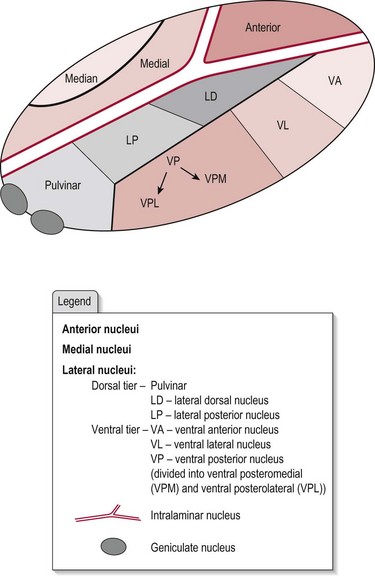
The thalamus is believed to both process and relay sensory information selectively to various parts of the cerebral cortex. The two thalami are prominent bulb-shaped masses about 5.7 cm in length, located on each side of the 3rd ventricle, and form the major part of the diencephalon. The thalamus is composed of a complex system of myelinated neurons separated by distinct clusters of neuron cell bodies, which form specific nuclei. Figure 9.1 shows the anatomical arrangement of the thalamus, with clusters of nuclei being divided into three main parts: anterior, medial and lateral, by the intralaminar nucleus. The lateral part is further sub-divided into dorsal and ventral tiers.
Function of the thalamus
The limbic system
Basic anatomy and function of the expression of emotional behaviour
Our emotional states are various but they all possess common attributes, namely visceral and somatic motor responses and powerful subjective feelings. Figure 9.2 shows a summary of this emotional motor response in terms of the level of control and the response intiated.
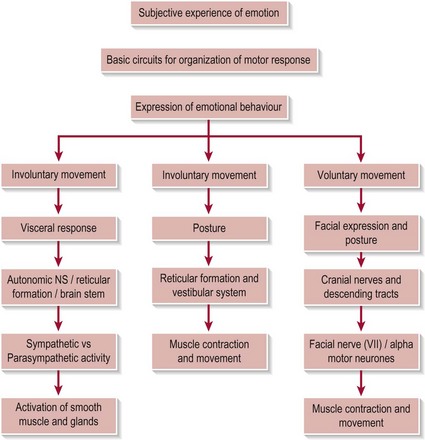
Figure 9.2 Summary of the emotional motor response.
Involuntary movement
Voluntary movement
Basic anatomy and function OF the control of emotional behaviour
The structures involved in control of our emotional behaviour are the:
Mamillary body
Found in the posterior temporal lobe, the mamillary body connects hypothalamus and cingulate cortex.
References and Further Reading
Klit, H, Finnerup, NB, Jensen, TS. Central post-stroke pain: clinical characteristics pathophysiology and management. The Lancet. 2009; 89:857–868.
Purves, D, Augustine, GJ, Fitzpatrick, D, et al. Neuroscience, ed 4. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates; 2008.
Snell, RS. Clinical neuroanatomy, ed 6. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2006.