Test Questions
William R. Grubb and Andrew T. Burr
Questions | Chapter 2: Principles of Ultrasound
2-1. Clinically useful ultrasound imaging waves are:
2-2. True concerning frequency of ultrasound signals include all but:
A Higher frequencies provide better resolution
B Higher frequencies are attenuated
C Higher frequencies are used in the epicardial probes relative to TEE probes
2-4. Which is not a cause of attenuation?
2-5. Which is not true when describing the piezoelectric crystals?
Answers | Chapter 2: Principles of Ultrasound
Questions | Chapter 3: Transducers and Instrumentation
3-1. The use of a damping material is applied to the transducer lens to accomplish all the following except:
A Shorten the length of an ultrasound pulse
B Improve axial resolution for an imaging transducer
C Results in a more homogeneous bandwidth
D Results in a less homogeneous bandwidth for better image acquisition
3-2. All true about axial resolution except:
3-3. True about spatial pulse length is:
A Does not affect axial resolution
B Determined by the number of cycles and the length of each cycle
Answers | Chapter 3: Transducers and Instrumentation
Questions | Chapter 4: Equipment, Infection Control, and Safety
4-1. Acceptable cleaning solutions for the active tip of TEE probe are (multiple answers):
4-2. If the insulation for TEE probe is broken, consequences can be:
4-3. The reason why a probe cannot be removed from a patient’s esophagus:
4-4. It is possible to break TEE probe flexion lock by:
4-5. Which are contraindications for TEE? (multiple answers)
Answers | Chapter 4: Equipment, Infection Control, and Safety
Questions | Chapter 5: Principles of Doppler Ultrasound (True or False)
5-1. Focusing of the transducer beam is accomplished by the use of lenses and electronic phasing
5-2. The intensity of the ultrasound beam decreases in tissue deeper than the focal point of the system
5-3. The near zone length defines the furthest extent of the fresnel zone
5-4. Adding a damping material to a transducer will improve axial resolution because the spatial pulse length decreases
5-5. The duty factor is the percentage of time the transducer is actively putting signal into a tissue
5-6. The bandwidth of the transducer refers to the range of frequencies over which the transducer can respond and is determined by the difference between the highest and lowest usable frequencies
5-7. A shorter pulse duration results in a broader bandwidth
5-8. Modalities that require good axial resolution, such as 2-D, M-mode, and color Doppler, require fewer cycles in a pulse, resulting in a short spatial pulse length
5-9. A 4 MHz transducer transmits a range of frequencies with an average of 4 MHz
5-10. A single pulse from an ultrasound transducer contains a range of frequencies
5-11. Increasing gain (transmit power) increases the voltage going through the piezoelectric crystal producing a better signal to noise ratio
Answers | Chapter 5: Principles of Doppler Ultrasound
Questions | Chapter 6: Quantitative M-Mode and Two-Dimensional Echocardiography
A Is not a form of B-mode echo
B Best for examining the timing of cardiac events
6-2. M-mode echo is useful to detect all the following except:
A The function of the cusps of the mitral valve
B The function of the cusps of the aortic valve
C The thickening of the ventricle walls during systolic
D Speed of passage of red blood cells through the aortic valve as part of the continuity equation
6-3. Color M-mode technology is used to help assess diastolic function in the following manner:
A Measure tissue movement of the mitral annulus
B Measure velocities of mitral inflow patterns
C Create the estimation of velocity of propagation by measuring the movement of a column of blood through the ventricle from the mitral valve to the apex
6-4. M-mode assessment of the aortic valve in patients with aortic insufficiency is notable in that:
A Valve cusps seen in cross section do not approximate in diastoli
B There is no appearance of the “boxcar”-like image
C Valve cusps seen in cross section do not approximate in systoli
6-5. Unique features concerning M-mode echo include all except:
Answers | Chapter 6: Quantitative M-Mode and Two-Dimensional Echocardiography
Questions | Chapter 7: Quantitative Doppler
7-1. Increasing the depth of data acquisition will:
7-2. True concerning PRF except:
A It is the number of times the transducer is excited each second
B It is the reciprocal of the PRP
7-3. Range ambiguity is a feature of:
7-4. The velocity time integral is used in the continuity equation to estimate:
A Length that blood flowed over time in cm
B Area of valves in cm squared
7-5. A cross sectional area multiplied by a VTI (estimated with a Doppler determination of velocities over time) determines a:
Answers | Chapter 7: Quantitative Doppler
Questions | Chapter 8: Doppler Profiles and Assessment of Diastolic Function
8-1. All are true about severe tricuspid regurgitation except:
A Jet area greater than 10 cm squared
B The vena contracta width is greater than 6.5 mm
8-2. A basic concept of the study of diastolic ventricular function and transmitral flow notes that:
A Quicker rises in E-waves are associated with good diastolic function
B A stiff ventricle that does not relax results in changes in atrial filling and the patterns of the pulmonary vein flows
C Changes in the E-wave and A-wave peaks parallel each other
D The area of the E-wave provides an assessment of diastolic dysfunction
8-3. True concerning E/A ratios in diastolic dysfunction:
A Differences in E/A ratios can distinguish normal from pseudonormal function
B A reduction in preload will help distinguish normal from pseudonormal ventricles with similar E/A ratios
8-4. A patient has an E/A ratio greater than 1, diastolic function can be further distinguished by all the following except:
8-5. In severe forms of ventricular diastolic dysfunction:
A S:D ratios are <1, the A wave reversal speeds are greater than 35 cm/sec and the tissue Doppler E prime velocities are less than 8
B S:D ratios are >1, the A wave reversal speeds are greater than 35 cm/sec and the tissue Doppler E-wave velocities are less than 12
C S:D ratios are <1, the A wave reversal speeds are greater than 35 cm/sec and the tissue Doppler E-wave velocities are less than 12
D S:D ratios are <1, the A wave reversal ratios are greater than 35 and the speeds of the diastolic relaxation are very fast
Answers | Chapter 8: Doppler Profiles and Assessment of Diastolic Function
Questions | Chapter 9: Cardiac Anatomy
9-1. The ME 4 chamber view of the perfusion to the ventricular myocardium on the right side of the screen (the anterolateral wall) is:
9-2. In the ME 4 chamber view, the perfusion to the middle of the ventricular display (the anteroseptal wall) is:
9-3. In the ME LAX135 degree view, the perfusion to the ventricular wall on the right side immediately below the LVOT (the anteroseptal wall) is:
9-4. In the ME 2 chamber view (90 degrees), the perfusion to the wall on the left side of the display (the inferior wall) is:
9-5. In the ME TG SAX view, the perfusion to the myocardium at the top of the screen (the inferior wall) is:
Answers | Chapter 9: Cardiac Anatomy
Questions | Chapter 10: Pericardium and Extra-Cardiac Structures: Anatomy and Pathology
10-1. The pulmonary veins are best imaged:
A In the upper third of esophagus
B In the deep transgastric window
10-2. True concerning pericardial tamponade as seen with TEE:
A Fluid appears echogenic and blood does not appear at all
B Fluid appears echolucent (dark), but clotted blood appears like tissue
10-4. True concerning normal pericardium includes all except:
A During spontaneous inspiration, a decrease in left-sided filling resulting in a decrease in blood pressure
B During spontaneous expiration, a decrease in blood pressure
C During spontaneous inspiration, a decrease in left-sided filling resulting in a decrease in blood pressure greater than 10 mmHg
D During spontaneous expiration, a decrease in blood pressure of greater than 10 mmHg
Answers | Chapter 10: Pericardium and Extra-Cardiac Structures: Anatomy and Pathology
Questions | Chapter 11: Pathology of the Cardiac Valves
11-1. True concerning normal aortic valve:
A Peak velocity <1 m/sec and area 3–5 cm squared
B Peak velocity <1.4 m/sec and area >5 cm squared
11-2. The most common cause of aortic stenosis in >55 yrs:
11-3. All true about the continuity equation except:
A At an instant in time, the VTI × area on each side of a stenotic valve is equal
B It is limited by estimation of the LVOT area
C It is used to estimate aortic valve areas
D Utilizes a pulse wave determination of velocity in the aorta and a continuous wave velocity measurement in the LVOT
11-4. Mitral inflow patterns consist of:
A Early A wave consistent with passive diastolic filling
B Early E wave consistent with active diastolic filling
11-5. All are true concerning the pressure half time determination of the mitral valve except:
Answers | Chapter 11: Pathology of the Cardiac Valves
Questions | Chapter 12: Intra-Cardiac Masses and Devices
12-1. All the following structures are seen in the right atrium except:
12-2. All are true about myxomas, except:
A Has a heterogeneous appearance as it often contains cysts
B Most common pediatric intercardiac tumor
C Often associated with the fossa ovalis portion of the interatrial septum in the left atrium
12-3. All are true about intercardiac lipoma except:
A Can be found in the left ventricle or the right atrium
B Second most common benign primary cardiac mass
C Usually sessile, homogeneous and hyperechoic
D A small vegetation on the downstream side of a aortic valve
12-4. The most common intercardiac mass in the left ventricle is:
Answers | Chapter 12: Intra-Cardiac Masses and Devices
Questions | Chapter 13: Left Ventricular Systolic Function
13-1. All true concerning HOCM, except:
A Inherited autosomal dominant trait
B Always includes SAM of the mitral valve
C Diastolic function is impaired
D Continuous wave Doppler ventricular contraction profiles are characterized by late peaking “dagger-like” appearance
13-2. Treatments for HOCM include all the following except:
13-3. Causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy include all the following except:
Answers | Chapter 13: Left Ventricular Systolic Function
Questions | Chapter 14: Segmental Left Ventricular Systolic Function
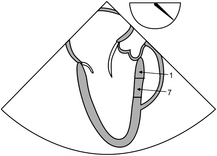
14-1. LAD feeds what walls of the heart?
14-2. Normal movement of a LV segment during systole is:
14-3. Blood supply to the area highlighted in the figure below is:
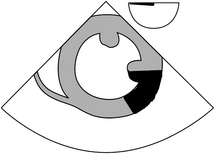
14-4. Immediately post sternal closure the patient’s blood pressure drops; arrhythmia ensues and TEE shows RWMA. The most probable explanation is:
Answers | Chapter 14: Segmental Left Ventricular Systolic Function
Questions | Chapter 15: The 17 Segment Model
15-1. In the 17 segment model, the anterior wall of the left ventricle depicted in the figure below is composed of segments:
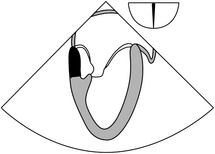
15-2. The segments (2 basal, 8 middle, 13 apical) in the above figure are perfused by:
15-3. In the 17 segment model as depicted in the figure below the inferior wall of the left ventricle is composed of segments:
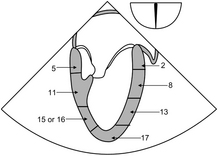
A 5 basal, 11 middle, 15 apical or portions of 16
B 5 basal, 11 middle, 17 apical
15-4. The segments (5 basal, 11 middle) in the above figure (question 15-3) are perfused by:
15-5. The segments numbered 1,7 and seen in figure below in the 17 segment model, are perfused by:
Answers | Chapter 15: The 17 Segment Model
Questions | Chapter 16: Assessment of Perioperative Events and Problems
16-1. TEE assessment during CPB is performed to:
A Visualize aortic cannulation site
B Determine function of prosthetic valves
C Assess venous cannulation sites
D Determine that the left ventricle is not distending during administration of cardioplegia into the aortic root
A Drains into the right atrium and is associated with the thesbian valve
16-3. The best method for determining dissection at the site of aortic cannulation is
16-4. The landmark arterial vessel for assessment of IABP placement is
Answers | Chapter 16: Assessment of Perioperative Events and Problems
Questions | Chapter 17: Congenital Heart Disease
17-1. Tetrology of Fallot consists of the following features except:
17-2. Persistent left superior vena cava includes all the following except:
A Congenital anomaly with large coronary sinus
B Venous injection of agitated saline appears first in the coronary sinus and then in the right ventricle
C Venous injection of agitated saline appears first in the left atrium
D Difficulty in establishing retrograde coronary cardioplegia flow
17-3. All true concerning coronary fistulas except:
A Commonly involve the right coronary artery
B Drain to the PA, coronary sinus, or superior vena cava
Answers | Chapter 17: Congenital Heart Disease
Questions | Chapter 18: Artifacts and Pitfalls
18-1. Side lobes are created when ultrasound interacts with:
A The propagation speed of two mediums is the same
B The incident angle is less than 90 degrees
18-3. Reverberation artifact is caused when
A The ultrasound interacts with a strong reflector or bounces between the transducer surface and a structure
C Ultrasound beam is absorbed by calcium in a structure
D The probe orientation is changed through many different angles
A The same in all elements of the body
D Assigned a speed of 1540 m/sec in most soft tissues for ease of calculating
18-5. When the ultrasound beam encounters the interface between two mediums with different propagation speeds at an oblique angle:
Answers | Chapter 18: Artifacts and Pitfalls
Questions | Chapter 19: Related Diagnostic Modalities
19-1. Advantages of epicardial echo include all the following except:
A Ability to visualize the ascending aorta and pulmonic valve
B Ability to detect plaque in the aorta
C Can be used in patients with esophageal pathology when TEE is contraindicated
19-2. Best epicardial imaging of planar view of the aortic valve
19-3. Best epicardial view for determination of velocity of flow with Doppler
19-4. Best longitudinal epicardial view for determination of inferior wall function:
19-5. This epicardial transverse view shows the posterior papillary muscle in the 9 o’clock position:
Answers | Chapter 19: Related Diagnostic Modalities
Questions | Chapter 20: Intraoperative 3-D Echocardiography
20-1. Benefits of 3D TEE include all except:
A Facilitates the assessment of complex cardiac pathology
B Uses volumetric technique to display chambers such as the right ventricle
A Dispersion is the technique when data are converted to Cartesian coordinates
B Extrapolation is the technique used to fill in data between the coordinates
C Data acquisition takes place, followed by RAM storage, conversion, and interpolation
20-4. In 3-D imaging techniques, the poorest temporal resolution is associated with:
Answers | Chapter 20: Intraoperative 3-D Echocardiography
Questions | Chapter 21: The Structured TEE Examination
21-1. In the ME 2 chamber view; the following walls of the left ventricle are seen:
21-2. The ME commissural view of the mitral valve (60 degrees) is most notable in that:
A Only the a2 leaflet of the mitral valve is seen
B P3 of the posterior, a2 of the anterior, and p1 of the posterior are the most frequently seen cusps
21-3. The view used to create the most parallel and precise continuous wave assessment of velocity of blood flow in the ascending aorta is:
21-4. The best view for simultaneous assessment of the tricuspid valve and pulmonic valve is:
21-5. The best view for identifying coronary sinus, IVC, SVC, and the foramen ovale is:
Answers | Chapter 21: The Structured TEE Examination
Questions | Chapter 22: Sonographic Formulas
Answers | Chapter 22: Sonographic Formulas