Appendix 1 Landmark Technique Accuracy and Outcome Studies
4. Clinical studies of accurate placement and outcomes between landmark and image guided techniques.
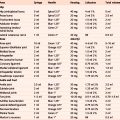
Glenohumeral joint
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints injected) | Clinical outcomes where relevant Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Sethi 18 2006 Cadaver Accuracy |
Anterior approach 80% (16/20) Posterior approach 50% (10/20) |
(X-ray with contrast) |
| Hanchard22 2006 Cadaver Accuracy |
74–91% (worst and best results for different approaches) | Best results with ‘optimized’ technique; 16% dispersal into other structures |
| Esenyel81 2010 Cadaver Accuracy |
Anterior 96% (48/50) | 4% were in surrounding tissues and capsule |
| Sethi19 2005 Clinical Accuracy |
Anterior 27% (11/41) | Insertion just lateral to the coracoid. Most common misplacement either too medial or too superficial in the deltoid muscle (MRI arthrography) |
| Lee57 2009 Clinical Outcome |
Posterior landmark guided (22) vs Ultrasound guided (21) (43 patients with frozen shoulder) |
2 weeks post-injection improvement was significantly greater in the US-guided injection group, but there was no significant difference in the improvement between the 2 groups beyond the 3rd week up to 6 weeks |
| Hegedus2 2010 Clinical Accuracy and Outcome |
Multiple approaches 52% (54/103) | 4 weeks post-injection equal improvement in all regardless of accuracy, despite wide variance in subject duration of symptoms, multiple injectors with varied training, and multiple injection approaches. Accuracy did not appear to depend on the experience of the physician (X-ray fluoroscopy) |
| Eustace17 1997 Clinical Accuracy and Outcome |
42% (10/24) | There were significant differences in outcome between the accurately placed and the inaccurately placed groups (X-ray with contrast) |
Subacromial space
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints injected) | Clinical outcomes where relevant Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Partington21 1998 Cadaver Accuracy |
83% (20/24) | Other structures also infiltrated in 15 shoulders incl. 7 into the cuff |
| Hanchard22 2006 Cadaver Accuracy |
91% | Best results with ‘optimized’ technique; 19% dispersal into other structures |
| Rutten26 2007 Clinical Accuracy |
Ultrasound guided 100% (10/10) vs Landmark guided 100% (10/10) |
(MRI arthrography) |
| Yamakado33 2002 Clinical Accuracy |
70% (39/56) | 12 (21%) were in the deltoid muscle, 2 (4%) were in the glenohumeral joint, 3 (5%) were subcutaneous. Comparison of subacromial bursal with intradeltoid injection showed no immediate significant differences in pain reduction expressed as impingement signs (X-ray with contrast) |
| Kang34 2008 Clinical Accuracy and Outcome |
Anterolateral 70% (14/20) Lateral 70% (14/20) Posterior 70% (14/20) |
At 3 months there was significant clinical improvement that did not correlate with accuracy. Accuracy not related to body mass index (X-ray with contrast) |
| Naredo58 2004 Clinical Accuracy and Outcome |
Landmark guided (20) vs. Ultrasound guided (21) | 6 weeks post-injection, there was significantly greater improvement with US versus LG. Suggest that US guided injections should be indicated, at least, in patients with poor response to previous blind injection to ensure accurate medication placement (ultrasound) |
| Esenyel27 2003 Clinical Accuracy and Outcome |
Anterolateral 87% (42/48) | 2 weeks after treatment, failure of accurate placement was associated with return to pre-treatment values, while significant improvement continued in the other group (X-ray with contrast) |
| Eustace17 1997 Clinical Accuracy and Outcome |
29% (4/14) | There were significant differences in outcome between the accurately placed and the inaccurately placed groups (X-ray with contrast) |
Acromioclavicular joint
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints injected) | Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Partington21 1998 Cadaver Accuracy |
67% (16/24) | Other structures also infiltrated in 8 shoulders |
| Pichler3 2009 Cadaver Accuracy |
57% (33/76) | Skilled specialist and inexperienced resident equally accurate. (Specialist 20/20 accurate with use of an image intensifier) |
| Bisbinas35 2006 Clinical Accuracy |
40% (26/66) | Injections were misplaced laterally in 21 injections (31.8%), medially in 13 (19.8%), anteriorly in 3 (4.5%) and inferiorly in 3 (4.5%) (image intensifier) |
Suprascapular nerve
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Study protocol | Clinical outcomes Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Shanahan59 2004 Clinical Outcome |
Landmark guided vs CT guided (77 shoulders in 67 patients) | 12 weeks post-injection, significant improvements in pain scores and disability with both types of nerve block, no difference in the improvement between the two at any time. No significant adverse effects occurred in either group. Patient satisfaction scores for pain relief high for both |
De quervain’s
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of tendon sheaths injected) | Clinical outcomes where relevant Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Zingas30 1998 Clinical Accuracy |
Accuracy of first dorsal compartment injection 84% (16/19) | Symptom relief in 58% (11/19) (X-ray with contrast in tendon sheath) |
Carpal tunnel syndrome
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Safety (proportion of times needle pierced median nerve [MN]) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| MacLennan82 2009 Cadaver Accuracy |
Both injections given at 30°angle at the wrist crease |
Method 2. Needle mean distance from MN 4.79 mm ±3.96 mm
Method 1. Needle mean distance from palmar cutaneous branch 9.47 mm ± 4.11 mm
Method 2. Needle mean distance from palmar cutaneous branch 1.74 mm ±1.59 mm
Cadaver Accuracy
1 and 2 given at 45° angle 1 cm proximal to the wrist crease
Method 2. Highest accuracy rate, and safest injection site*
* Injection through FCR tendon also recommended by Dubert & Racasan 200684 based on endoscopic survey of the anatomy of the carpal tunnel during 124 release operations
Trapeziometacarpal joint
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints injected) | Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Helm36 2003 Clinical Accuracy |
58% (35/60) | (X-ray fluoroscopy) |
| Pollard29 2007 Clinical Accuracy |
82% (18/22) | Soft-tissue extravasation in 25% (X-ray fluoroscopy) |
Fingers
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints/tendon sheaths injected) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Pichler20 2008 Cadaver Accuracy |
Skilled specialist 85% Inexperienced resident 77% (300 DIPs/PIPs) Dorsal approach (150) Dorsolateral approach (150) |
The failure rate was significantly higher than the average with the joints of the little finger and the DIP joints of each phalanx |
| Kamhin10 1983 Clinical Accuracy |
Patients scheduled for surgical release of trigger fingers had an injection of the involved tendon sheath prior to surgery. 61% (22/36) methylene blue injected proximal-distal direction 37% (13/34) methylene blue injected distal-proximal direction |
There was no significant statistical difference with regard to age, but duration of the disorder and mode of injection regarding the different fingers did have statistical significance |
| Taras66 1998 Clinical Accuracy and Outcome |
95 patients with 107 trigger digits, 52 attempted intra-sheath injections; of these: |
Group 2 had 50% good response
Group 3 had 70% good response. The results of this study suggest that true intra-sheath injection offers no apparent advantage over subcutaneous injection in the treatment of trigger digits (X-ray with contrast)
Hip
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints injected) | Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Leopold85 2001 Cadaver Accuracy |
Anterior 60% (9/15) Lateral 80% (12/15) |
Anterior significantly riskier to the femoral artery/nerve than lateral |
| Kurup16 2010 Clinical Accuracy |
Anterolateral 65% (28/43) | Obesity, severe grade 4 arthritis with no joint space, and flexion deformity accounted for the majority of failed cases (needle position using image intensifier) |
| Ziv15 2009 Clinical Accuracy |
Lateral 78% (31/40) | In all 9 unsuccessful injections, the dye was located distal to the joint, along the more lateral aspect of the femoral neck (dye injection) |
| Diraçoğlu9 2009 Clinical Accuracy | 51% (29/57) | ‘Backflow’ technique did not correlate with accurate placement (fluoroscopy and X-ray with contrast) |
Trochanteric bursitis
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of bursae injected) | Clinical outcomes where relevant Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Cohen60 2005 Clinical Accuracy |
45% (18/40) | Senior doctors 53% Junior doctors 36% (X-ray with contrast) |
| Cohen37 2009 Clinical Outcome |
Landmark guided 33 vs Fluoroscopic guided 32 | No differences in outcomes 3 months post-injection, 15 (47%) patients in LG and 13 (41%) in the FG continued to have a positive outcome |
Knee
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints injected) | Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Essenyel 86 2007 Cadaver Accuracy |
Anterolateral 85% (39) Anteromedial No stat. diff.(39) Lateral midpatellar No stat diff. (39) Medial midpatellar 56% (39) |
Anterolateral lower incidence of soft tissue infiltration. AL results not statistically significant compared to AM and LMP portals. |
| Jackson4 2002 Clinical accuracy |
Anterolateral 71% (57/80) Anteromedial 75% (60/80) Lateral midpatellar 93% (74/80) (240 ‘dry’ knees) |
Hyaluronan study (X-ray fluoroscopy) |
| Luc8 2006 Clinical Accuracy |
97% (32/33) ‘dry’ knees with OA | Backflow confirmation technique for correct placement using landmarks verified in 32/33 by imaging (X-ray with contrast) |
| Toda28 2008 Clinical Accuracy |
Ankle
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints injected) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Heidari87 2010 Cadaver Accuracy |
Anterolateral 86% (31/36) Anteromedial 78% (31/40) |
Overall 82% accuracy, no statistical difference between approaches |
| Wisniewski23 2010 Cadaver Accuracy |
Ultrasound guided 100% (20/20) vs Landmark guided 85% (17/20) |
Subtalar
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints injected) | Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Wisniewski 201023 Cadaver Accuracy |
Ultrasound guided 90% (18/20) vs Landmark guided 35% (7/20) | Sinus tarsi injection |
| Kirk24 2008 Cadaver Accuracy |
97% (58/60) | Injection into posterior subtalar joint Extravasation into the ankle in 14 and into the peroneal sheath in 2 (X-ray fluoroscopy) |
Plantar fasciitis
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Study protocol | Clinical outcomes Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Yucel63 2009 Clinical Outcome |
Palpation guided vs Ultrasound guided vs Scintigraphy guided (35 heels in 27 patients) | 25 months post-injection all 3 groups improved significantly with no statistically significant differences between groups |
| Kane61 2001 Clinical Outcome |
Palpation guided (14) vs Ultrasound guided (10) (24 heels in 23 patients) | Ultrasound findings correlated with bone scintigraphy Ultrasound and palpation guided injection resulted in equally significant mean improvements. |
Multiple joints in RA
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints injected) | Clinical outcomes where relevant Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Cunnington31 2010 Clinical Outcome |
Ultrasound guided 83% vs Landmark guided 66% (total of 184 joints) | Inflammatory arthritis with an inflamed joint (shoulder, elbow, wrist, knee, or ankle) Equal clinical outcomes at 6 weeks (X-ray with contrast) |
| Lopes32 2008 Clinical Outcome |
Shoulder 82% Elbow 100% Wrist 97% MCP joints 97% Knee 100% Ankle 77% (total 232 joints) |
Statistically significant improvement observed for all variables at 4 weeks (X-ray with contrast) |
Multiple joints in multiple conditions
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints injected) | Clinical outcomes where relevant Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Koski25 2006 Clinical Accuracy |
76–82% accuracy At 6/10 sites >80% (133 joints/tendon sheath) |
Used a contrast medium method with a glucocorticoid-air-saline mixture and ultrasound imaging (GAS-graphy). Good reliability of the method; can be used in developing injection techniques and as an alternative for the radiographic contrast medium method in verifying successful injections |
| Jones1 1993 Clinical Accuracy and Outcome |
Intra-articular 52% (56/108) Uncertain 19% (21/108) Extra-articular 29% (31/108) |
A reduction of joint inflammation was associated with accuracy of injection. No effect seen for clinician seniority (X-ray with contrast) |
| Sibbitt39 2009 Clinical Outcome |
Landmark guided vs Ultrasound guided (total of 148 joints) | Utilized novel one-handed reciprocating device. US guidance resulted in reduction in procedural pain, absolute pain scores at 2 week outcome and reduction in significant pain. US also increased detection of effusion by 200% volume of aspirated fluid by 337% |
Caudal epidural
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion entered ‘blind’) | Clinical outcomes where relevant Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Lewis12 1992 Clinical Accuracy |
73% (19/26) | All 19 correctly placed had positive ‘whoosh’ test (no false positives) i.e. sound heard with stethoscope over sacrum as small amount of air injected (correct needle placement determined by epidurograph) |
Aspiration studies
| Lead author Year Subject Study type |
Accuracy % (proportion of joints aspirated) | Clinical outcomes where relevant Comments (imaging assessment) |
|---|---|---|
| Raza51 2003 Clinical Accuracy and Outcome |
Landmark guided 32% (10/32) vs. Ultrasound guided 96% (30/31) End-point was successful aspiration from small joints |
Ultrasound guidance allows needle placement within a small joint with significantly greater accuracy than a palpation-guided approach. When followed by lavage synovial fluid cells and diluted synovial fluid can be obtained from the majority of small joints. This has important research implications |
| Balint52 2002 Clinical Accuracy and Outcome |
Landmark guided 59% (10/17) vs. Ultrasound guided 97% (51/53) End-point was successful aspiration |
Following US examination, aspiration was performed by a second rheumatologist based on the US localization of fluid or under direct US guidance. The mean volume of fluid obtained from successful aspirations was similar in both groups |