Chapter 37 SUSPECTED IRON OVERLOAD OR HIGH SERUM FERRITIN
INTRODUCTION
It is important to note that serum ferritin is influenced by liver injury and inflammation, so an elevated serum ferritin does not necessarily indicate increased body iron stores.
IRON METABOLISM
Serum iron studies
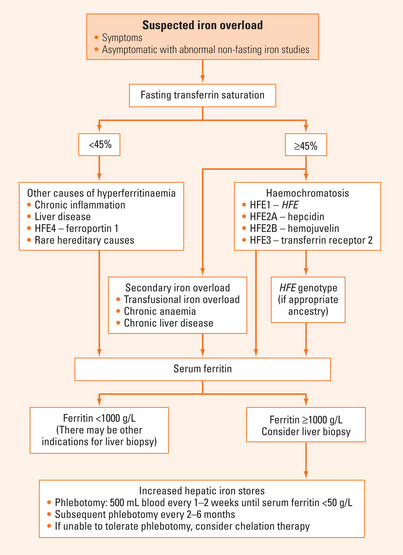
Serum iron is included on some routine blood tests of electrolytes and liver enzymes. It is affected by dietary intake, shows diurnal variation, and is not a reliable indicator of iron stores. Transferrin is the major iron transporting protein in the body. Transferrin saturation reflects iron stores and is usually elevated (>50%) before the serum ferritin increases. Transferrin is calculated from the serum iron and total iron binding capacity, which depends on serum transferrin concentration. Measuring fasting transferrin saturations decreases the effects of diet and diurnal variation, and a value of >45% is suggestive of iron overload.
Causes of high serum ferritin
Serum ferritin is increased in iron overload, liver injury and in inflammatory states. Iron overload can occur with inherited abnormalities of iron metabolism, particularly hereditary haemochromatosis (HFE), repeated blood transfusion and dietary iron overload (including hazardous alcohol consumption). The most common cause of iron overload in Western countries is haemochromatosis. There are a number of different types of haemochromatosis. HFE1 is the most common type of haemochromatosis and is an autosomal recessive condition caused by mutation of the HFE gene, in particular a cysteine to tyrosine mutation at amino acid 282, designated Cys282Tyr or C282Y. This mutation interferes with the regulated movement of iron from enterocytes into the body, so that iron accumulation can occur despite adequate iron stores. This depends on factors like dietary iron intake, and iron depletion through blood loss or pregnancy. The C282Y mutation appears confined to populations with Northern European ancestry and in these groups the prevalence of C282Y homozygotes is about 1 in 200 to 1 in 400. Approximately 50% of C282Y homozygotes will develop significant iron overload, depending on diet, blood loss and other genetic factors. Another HFE mutation that appears to play a role in HFE1 is the H63D mutation, which seems to only be associated with iron overload in combination with C282Y. Other genes implicated in haemochromatosis include transferrin receptor 2, ferritin heavy chain, ferroportin 1, hepcidin and hemojuvelin.
ASSESSMENT
Causes of hyperferritinaemia and iron overload include:
MANAGEMENT OF IRON OVERLOAD
Patients with iron overload who can tolerate phlebotomy should undergo weekly or biweekly venesection of a unit of blood (500 mL) until serum ferritin is <50 μg/L. The haemoglobin should be checked prior to each venesection to ensure it has not fallen by ≥20% from the previous value. Once ‘de-ironing’ has been achieved, the frequency of venesection can be reduced to 3–4 times per year. In patients who are unable to tolerate phlebotomy (including patients with anaemia), de-ironing can be achieved by chelation. A number of chelating agents are available including desferrioxamine at a dose of 40 mg/kg body weight/day. This is expensive and cumbersome to administer, requiring infusion over 8–12 hours. Recently oral chelating agents (deferiprone) have entered clinical practice. Their role in relation to desferrioxamine is being determined.
SUMMARY
Increased body iron stores are seen in hereditary haemochromatosis, a group of diseases caused by mutations in proteins involved in iron regulation. HFE1 is the most prevalent of these disorders in populations with northern European ancestry, affecting 1 in 200–400 people. It is caused by mutations in HFE, almost exclusively homozygosity for the C282Y mutation. Other genes implicated in hereditary haemochromatosis include hepcidin, hemojuvelin, transferrin receptor 2, ferroportin and the ferritin light chain. There are other rare genetic causes of hyperferritinaemia. Secondary iron overload occurs with repeated blood transfusion or iron infusion, chronic anaemia, chronic liver disease and inflammatory states.
Evaluation of suspected iron overload requires history taking, physical examination and appropriate laboratory investigations to rule out chronic inflammation or liver disease and determine if there is secondary iron overload (Figure 37.1). In subjects with an appropriate ancestry, HFE genotyping should be performed if fasting transferrin saturation is ≥45%. When serum ferritin is >1000 μg/L, liver biopsy should be considered.
Aguilar-Martinez P, Schved J-F, Brissot P. The evaluation of hyperferritinemia: an updated strategy based on advances in detecting genetic abnormalities. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005;100:1185-1194.
Andrews NC. Disorders of iron metabolism. N Eng J Med. 1999;341:1986-1995.
Lieu PT, Heiskala M, Peterson PA, et al. The roles of iron in health and disease. Mol Aspects Med. 2001;22:1-87.
Siah CW, Trinder D, Olynyk JK. Iron overload. Clin Chim Acta. 2005;358:24-36.
Tavill AS. Diagnosis and management of hemochromatosis. Hepatology. 2001;33:1321-1328.