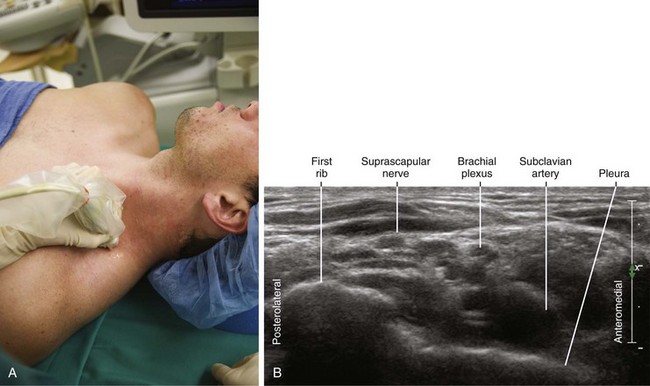
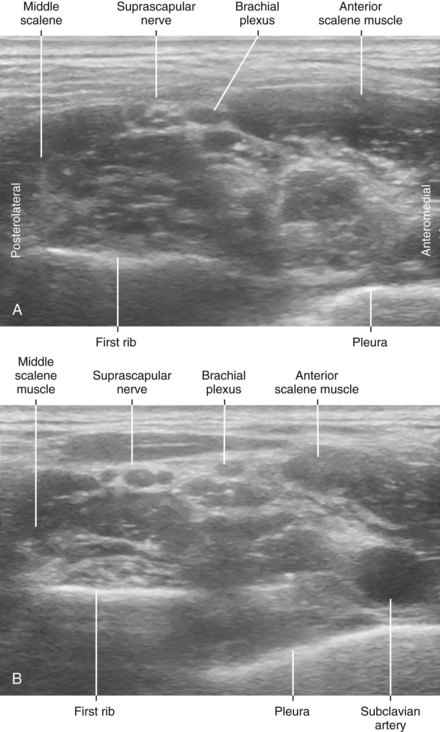
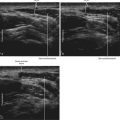
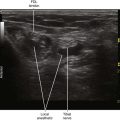
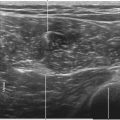
30 Suprascapular Nerve Block
The suprascapular nerve arises from the superior trunk of the brachial plexus, containing contributions from the C5 and C6 ventral rami. The nerve innervates the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles and contains articular branches from the shoulder joint. Cutaneous innervation of the suprascapular nerve is not common, being demonstrated in about 15% of subjects.1,2 When present, the cutaneous distribution is similar to the usual distribution for the axillary nerve.
The suprascapular nerve is about 2 to 3 mm in diameter.3 The suprascapular nerve diverges distally 2 cm from the junction of C5 and C6 into the superior trunk (range, 0-2.5 cm). The distance measured from the origin of the suprascapular nerve to the clavicle is variable (range, 0.5-7.5 cm).4 Recognition of the takeoff of the suprascapular nerve from the brachial plexus is important for complete brachial plexus blocks when performed low in the neck. Suprascapular nerve blocks can provide some analgesia after shoulder surgery, but this effect is small.5 More distal block of the suprascapular nerve near the spinoglenoid notch is potentially more selective, but the nerve and needle imaging for this procedure can be challenging.
Clinical Pearls
• The suprascapular nerve is responsible for most of the sensory innervation to the shoulder joint.6,7
• The suprascapular nerve runs parallel to and under the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle in the posterior triangle of the neck.8 The suprascapular nerve is accompanied by the suprascapular artery along this course.
1 Ajmani ML. The cutaneous branch of the human suprascapular nerve. J Anat. 1994;185:439–442.
2 Yan J, Wu H, Aizawa Y, et al. The human suprascapular nerve belongs to both anterior and posterior divisions of the brachial plexus. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 1999;76:149–155.
3 Aktekin M, Demiryurek D, Bayramoglu A, et al. The significance of the neurovascular structures passing through the spinoglenoid notch. Saudi Med J. 2003;24:933–935.
4 Norkus T, Norkus M, Ramanauskas T. Donor, recipient and nerve grafts in brachial plexus reconstruction: anatomical and technical features for facilitating the exposure. Surg Radiol Anat. 2005;27:524–530.
5 Neal JM, McDonald SB, Larkin KL, et al. Suprascapular nerve block prolongs analgesia after nonarthroscopic shoulder surgery but does not improve outcome. Anesth Analg. 2003;96:982–986.
6 Vorster W, Lange CP, Briët RJ, et al. The sensory branch distribution of the suprascapular nerve: an anatomic study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17:500–502.
7 Horiguchi M. The cutaneous branch of some human suprascapular nerves. J Anat. 1980;130:191–195.
8 Krishnan KG, Pinzer T, Reber F, et al. Endoscopic exploration of the brachial plexus: technique and topographic anatomy. A study in fresh human cadavers. Neurosurgery. 2004;54:401–408.