Chapter 34 Supportive Devices
34.1 Elastic Supports (Compression Supports)
OVERVIEW.
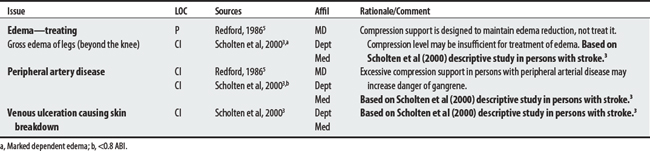
An elastic support is an article of clothing that offers some degree of compression around a body part in order to help prevent DVT (16-18 mm Hg—antiembolism stocking), control scar formation (20-30 mm Hg), control edema in ambulators (30-40 mm Hg),1 or assist in venous circulation return.2 An example of an elastic support is a compression garment.
SUMMARY: CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS.
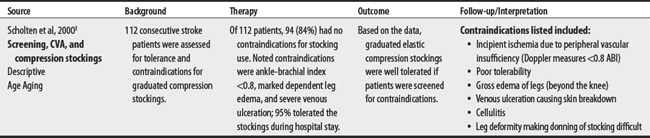
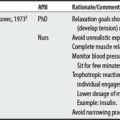
Two sources list seven concerns for compression supports. Concerns ranged from four to six per source; three shared issues included (1) treating edema, (2) peripheral artery disease, and (3) donning difficulties. The concerns of Scholten et al3 are targeted to a stroke population. The FDA4 has received reports of neuropathy and skin blistering as a possible complication of compression support therapy.
1 Cameron MH. Physical agents in rehabilitation: from research to practice. St. Louis: Saunders, 2003.
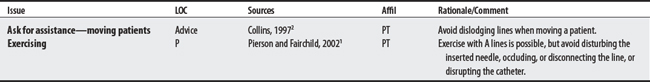
2 Pierson FM, Fairchild SL. Principles and techniques of patient care, ed 3. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2002.
3 Scholten P, Bever A, Turner K, et al. Graduated elastic compression stockings on a stroke unit: a feasibility study. Age Aging. 2000;29(4):357-359.
4 U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Center for Device and Radiological Health. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/cdrh/mdr/. Accessed on November 7, 2005
5 Redford JB. Orthotics etcetera. Baltimore (MD): Williams & Wilkins, 1986.
34.2 Lines
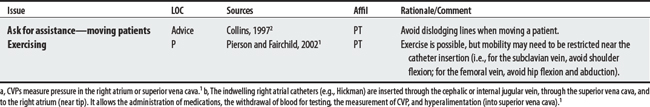
Lines are medical devices that use tubing to infuse fluid, infuse or obtain blood, or monitor hemodynamics. Whereas central lines access a patient’s heart from a peripheral vessel, peripheral lines access the patient’s circulation from a peripheral vessel. Intracranial pressure (ICP) monitors measure the pressure of brain tissue against the skull.1,2 Concerns when treating patients who have these lines are listed below.
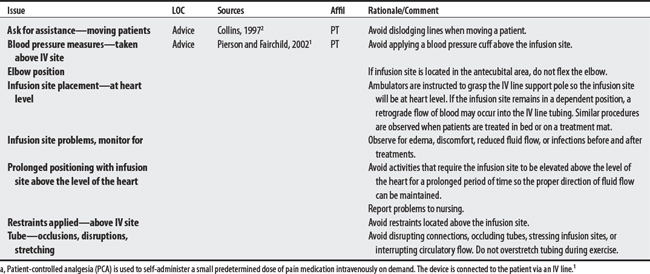
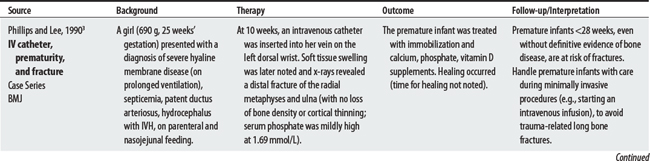
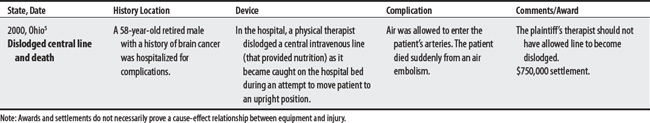
A critical concern when treating patients is the dislodgment of IV lines or catheters because it can lead to a fatal air embolism. See Philips and Lee (1990),3 Zafonte et al (1996),4 and an Ohio lawsuit5 below.
PERIPHERAL LINES
Arterial Lines (A Line)
Arterial lines are peripheral lines, inserted into the artery (e.g., radial, dorsal, pedal, axillary, brachial, or femoral) to continuously measure blood pressure or obtain blood samples.2
Intravenous (IV) Infusion Lines
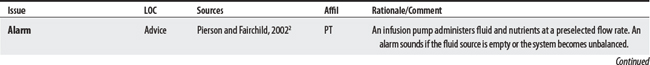
Intravenous (IV) infusion lines are peripheral lines used to obtain venous blood samples, to infuse fluids, nutrients, electrolytes, or medication, or to insert catheters into the central circulatory system to monitor physiologic conditions.1 IV line precautions also apply to patient-controlled analgesia (PCA).1a
CENTRAL LINES
Swan-Ganz Catheter (Pulmonary Artery Catheter)
A Swan-Ganz catheter is an IV tube that is inserted into the internal jugular or femoral vein and is passed into the pulmonary artery to provide accurate continuous measurement of pulmonary artery (PA) pressure.1 Swan-Ganz catheter precautions also apply to central venous pressure catheters (CVPs)a and indwelling right atrial catheters (e.g., Hickman).1,b
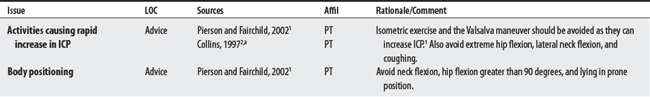
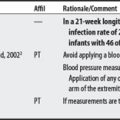
INTRACRANIAL MONITORING
Intracranial pressure (ICP) monitors measure pressure against the skull by brain tissue blood or cerebral spinal fluid (CSF); some monitors can also be used to withdraw CSF fluid. Individuals with closed head injuries, cerebral hemorrhages, brain tumors, and overproduction of CSF are monitored (normal pressure is 4-15 mm Hg). Fluctuations up to 20 mm occur during a variety of routine activities.1
1 Pierson FM, Fairchild SL. Principles and techniques of patient care, ed 3. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2002.
2 Collins SM. Peripheral and central lines and intracranial pressure monitoring IV-A. In: Paz JC, Panik M, editors. Acute care handbook for physical therapists. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1997.
3 Phillips RR, Lee SH. Fractures of long bones occurring in neonatal intensive therapy units. BMJ. 1990;301(6745):225-226.
4 Zafonte RD, Hammond FD, Rahimi R. Air embolism in the agitated brain injury patient: an unusual complication. Brain Inj. 1996;10(10):759-762.
5 Medical malpractice verdict settlement, and experts, November 2000, p 51, loc 1.
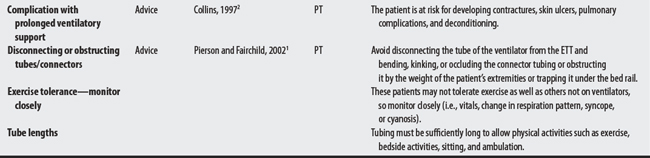
34.3 Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation uses positive pressure to move air into and inflate the patient’s lungs. Concerns center around familiarity with the equipment, communicating with patients, and anticipating patient complications associated with long-term support.1,2
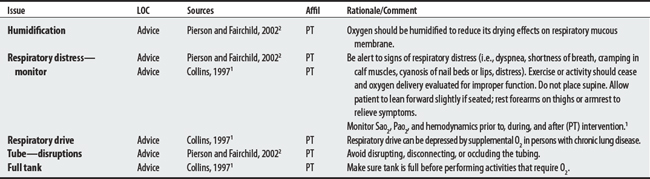
34.4 Supplemental Oxygen Delivery Systems
Supplemental oxygen is provided to patients who experience tissue hypoxia (i.e., Pao2 [partial pressure of arterial oxygen] is <60 mm Hg) or when arterial saturation (Sao2) is less than 90%.1 (Also see O2 tanks in power wheelchairs mobility.)
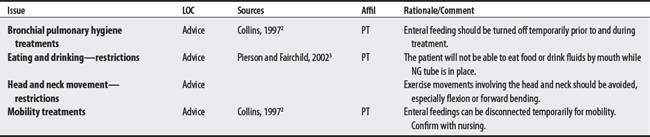
34.5 Tubes
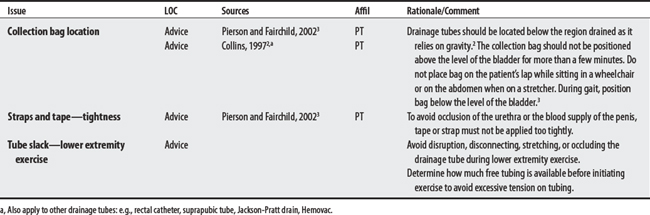
Tubes are medical devices with hollow elongated channels used in feeding systems, to drain a body system (genitourinary or gastrointestinal), or to drain a body space (i.e., edema after surgery).1 Examples include nasogastric, gastrostomy, and jejunostomy tubes.2 Concerns for treating patients who have feeding tubes, drainage tubes, ostomy devices, and chest drainage tubes are listed below.
FEEDING TUBES
1 Webster’s third new international dictionary. Springfield (MA: Merriam-Webster, 1981.
2 Collins SM. Supplemental Oxygen Delivery Systems III-A. In: Paz JC, Panik M, editors. Acute care handbook for physical therapists. Boston (MA): Butterworth-Heinemann, 1997.
3 Pierson FM, Fairchild SL. Principles and techniques of patient care, ed 3. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2002.
4 United Ostomy Association, Inc. Home page. Available at: http://www.uoa.org/ostomy_main.htm. Accessed November 9, 2005
5 Panik M. Chest tubes. In: Paz JC, Panik M, editors. Acute care handbook for physical therapists. Boston (MA): Butterworth-Heinemann, 1997.
a Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) is used to self-administer a small predetermined dose of pain medication intravenously on demand. The device is connected to the patient via an IV line.1
a CVPs measure pressure in the right atrium or superior vena cava.1
b The indwelling right atrial catheters (e.g., Hickman) are inserted through the cephalic or internal jugular vein, through the superior vena cava, and to the right atrium (near tip). It allows the administration of medications, the withdrawal of blood for testing, the measurement of CVP, and hyperalimentation (into superior vena cava).1