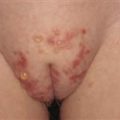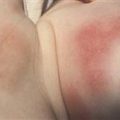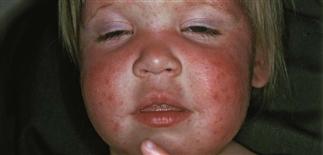
Acute sunburn of face of child.
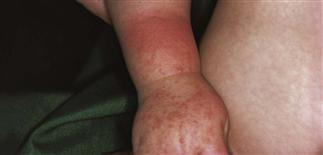
Acute sunburn on arm of child. Note the sharp demarcation due to protective clothing.
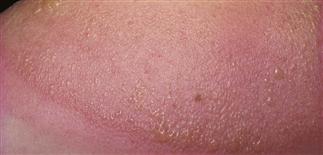
Sunburn with vesiculation on neck of adolescent.
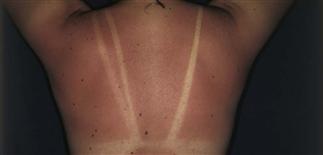
Sunburn on back of adolescent. Note uninvolved skin protected by clothing.
CLINICAL FEATURES
Sunburn occurs readily in fair-skinned children and correlates with the amount of melanin pigment in the epidermis.
Investigation into exposure to medications that may accentuate sunburn including sulfonamides, phenothiazines, ibuprofen, naproxen, tetracyclines, griseofulvin and tretinoin should be instituted. It should be remembered that prolonged sunburn reactions occur in the rare types of xeroderma pigmentosum.
TREATMENT
The pain and redness of acute sunburn can be relieved by wet dressings or cool compresses. If given within 6 hours of exposure, indomethacin or aspirin may modify the sunburn. Topical steroids and anesthetics are not efficacious in sunburn.