Chapter 61 Sports Injuries
EPIDEMIOLOGY
1 Which sports are associated with the highest injury rates in children? What are the most common types of injuries seen?
Patel DR, Nelson TL: Sports injuries in adolescents. Med Clin North Am 84:983–1007, 2000.
Taylor BL, Attia MW: Sports-related injuries in children. Acad Emerg Med 7:1376–1382, 2000.
OVERUSE INJURIES
5 Why is the early identification of “gymnast’s wrist” important?
Patel DR, Nelson TL: Sports injuries in adolescents. Med Clin North Am 84:983–1007, 2000.
6 Name the two types of apophysitis syndromes that occur surrounding the patellar tendon
 Osgood-Schlatter disease: An apophysitis at the anterior tibial tubercle due to traction by the inferior aspect of the patellar tendon.
Osgood-Schlatter disease: An apophysitis at the anterior tibial tubercle due to traction by the inferior aspect of the patellar tendon.
 Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome: An apophysitis of the inferior pole of the patella due to traction by the superior aspect of the patellar tendon. Treatment is analogous to that for Osgood-Schlatter disease. Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome is differentiated from “jumper’s knee” in that the latter is not an apophysitis but rather an inflammation within the proximal patellar tendon itself.
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome: An apophysitis of the inferior pole of the patella due to traction by the superior aspect of the patellar tendon. Treatment is analogous to that for Osgood-Schlatter disease. Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome is differentiated from “jumper’s knee” in that the latter is not an apophysitis but rather an inflammation within the proximal patellar tendon itself.
7 Which is the most common overuse injury in the young athlete?
Adirim TA, Cheng TL: Overview of injuries in the young athlete. Sports Med 33:75–81, 2003.
9 List the most common locations for stress fractures in pediatric athletes
Coady CM, Micheli LJ: Stress fractures in the pediatric athlete. Clin Sports Med 16:225–238, 1997.
10 In which sports are participants most likely to sustain stress fractures?
1 They are the most common sports injuries seen in adolescents.
2 They are due to repetitive stress or trauma to an area that has had inadequate time for recovery between injuries.
3 Rest and proper conditioning regimens are crucial elements in management.
4 Osgood-Schlatter disease is the most common overuse injury in young athletes.
ACUTE INJURIES
12 What is the most dreaded complication of returning to sports too soon following a concussion?
Second impact syndrome. This results from acute brain swelling when a second head trauma is sustained prior to full recovery from an initial concussion. Second impact syndrome is thought to occur because the athlete reinjures the head during a period of disordered cerebral autoregulation following the initial head injury. The American Academy of Neurology guidelines on return to sports (Table 61-1) theoretically allow for this critical time period to pass and for the vascular autoregulatory mechanisms in the brain to heal and regain their normal function. Second impact syndrome, though quite rare, is not treatable and almost universally fatal.
Table 61-1 Summary of Recommendations For Management Of Concussion in Sports
From Quality Standards Subcommittee, American Academy of Neurology. www.aan.com/;professionals/;practice/;guidelines/;concussion_sports
Cantu RC: “Second impact syndrome.” Clin Sports Med 17:37–44, 1998.
13 Does posttraumatic seizure (the occurrence of a seizure directly after head trauma) increase the risk of intracranial injury?
14 What is commotio cordis?
Maron BJ: Sudden death in young athletes. N Engl J Med 349:1064–1075, 2003.
20 What is the difference between a mallet finger and a jersey finger?
| Variable | Mallet Finger | Jersey Finger |
|---|---|---|
| Injury | Extensor digitorum tendon disruption | Flexor digitorum tendon disruption |
| Physical examination | Forced flexion of an extended distal interphalangeal joint | Forced extension of a flexed distal interphalangeal joint |
| Mechanisms | Finger struck on the tip by a ball | Football player grabs another player’s jersey |
| Forcefully tucking in a bedspread | Lifting a latch on a car door | |
| Pushing off a sock with an extended finger |
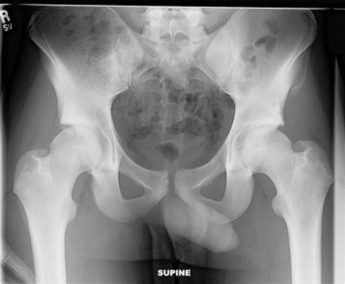
21 How do pelvic avulsion fractures occur?
Avulsion fractures (Fig. 61-1) result from sudden muscular contractions and are usually associated with vigorous running or jumping. These are seen in sports that require rapid acceleration or deceleration, or quick changes of direction.
Kim SS, Thomas M: A football player with thigh pain. Pediatr Emerg Care 17:267–268, 2001.
22 What are the most common locations of pelvic avulsion fractures? What muscle attachment contributes to the fracture?
| Location | Involved Muscle |
|---|---|
| Ischial tuberosity | Hamstrings and adductors |
| Anterior superior iliac spine | Sartorius |
| Anterior inferior iliac spine | Rectus femoris |
| Lesser trochanter of the femur | Iliopsoas |