Perisplenic hematoma: Located adjacent to spleen and implies disruption or rupture of splenic capsule
• Parenchymal laceration: Irregular linear, branching, or stellate area of nonenhancing low attenuation
• Splenic infarction: Unusual (< 2% of cases) in the setting of trauma, and can be segmental or complete
• Active arterial extravasation: High-attenuation focus isodense with aorta, surrounded by lower attenuation clot or hematoma
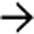 and intraperitoneal blood
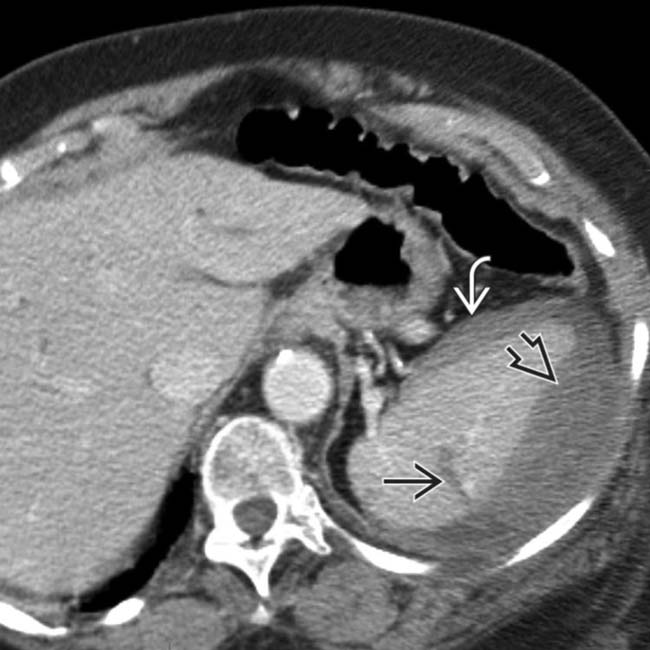
and intraperitoneal blood 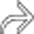 , as well as a lentiform heterogeneous and higher attenuation collection flattening the normal convex lateral splenic contour, representing a subcapsular hematoma
, as well as a lentiform heterogeneous and higher attenuation collection flattening the normal convex lateral splenic contour, representing a subcapsular hematoma  .
.
 in the perisplenic region and large hemoperitoneum
in the perisplenic region and large hemoperitoneum 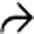 .
.
 , a shattered spleen with intrasplenic high-attenuation pseudoaneurysms
, a shattered spleen with intrasplenic high-attenuation pseudoaneurysms  , and a focus of active arterial extravasation lateral to the spleen within the peritoneal cavity
, and a focus of active arterial extravasation lateral to the spleen within the peritoneal cavity  .
.
 extending into the left paracolic gutter with surrounding hemoperitoneum
extending into the left paracolic gutter with surrounding hemoperitoneum  .
.IMAGING
General Features
CT Findings
• NECT
 High-attenuation hemoperitoneum > 30 HU or perisplenic clot > 45 HU
High-attenuation hemoperitoneum > 30 HU or perisplenic clot > 45 HU
 High-attenuation hemoperitoneum > 30 HU or perisplenic clot > 45 HU
High-attenuation hemoperitoneum > 30 HU or perisplenic clot > 45 HU
• CECT
 Parenchymal laceration: Irregular linear, branching, or stellate area of nonenhancing low attenuation within parenchyma
Parenchymal laceration: Irregular linear, branching, or stellate area of nonenhancing low attenuation within parenchyma
 Active arterial extravasation: High-attenuation focus isodense with aorta, surrounded by lower attenuation clot or hematoma
Active arterial extravasation: High-attenuation focus isodense with aorta, surrounded by lower attenuation clot or hematoma
 Parenchymal laceration: Irregular linear, branching, or stellate area of nonenhancing low attenuation within parenchyma
Parenchymal laceration: Irregular linear, branching, or stellate area of nonenhancing low attenuation within parenchyma
 Active arterial extravasation: High-attenuation focus isodense with aorta, surrounded by lower attenuation clot or hematoma
Active arterial extravasation: High-attenuation focus isodense with aorta, surrounded by lower attenuation clot or hematoma
PATHOLOGY
General Features
Staging, Grading, & Classification
• Grading may be misleading: “Minor” injuries may go on to devastating delayed bleed or delayed rupture
• AAST (American Association for Surgery of Trauma) grading system is based on extent of injury at laparotomy and applied to CT findings
 III: Subcapsular hematoma (> 50% of surface area of spleen), parenchymal hematoma > 5 cm or expanding laceration > 3 cm or involving trabecular vessels, ruptured subcapsular or parenchymal hematoma
III: Subcapsular hematoma (> 50% of surface area of spleen), parenchymal hematoma > 5 cm or expanding laceration > 3 cm or involving trabecular vessels, ruptured subcapsular or parenchymal hematoma
 III: Subcapsular hematoma (> 50% of surface area of spleen), parenchymal hematoma > 5 cm or expanding laceration > 3 cm or involving trabecular vessels, ruptured subcapsular or parenchymal hematoma
III: Subcapsular hematoma (> 50% of surface area of spleen), parenchymal hematoma > 5 cm or expanding laceration > 3 cm or involving trabecular vessels, ruptured subcapsular or parenchymal hematoma• Marmery MDCT-based grading system
 I: Subcapsular hematoma (< 1 cm thick), laceration (< 1 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (< 1 cm in diameter)
I: Subcapsular hematoma (< 1 cm thick), laceration (< 1 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (< 1 cm in diameter)
 II: Subcapsular hematoma (1-3 cm thick), laceration (1-3 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (1-3 cm in diameter)
II: Subcapsular hematoma (1-3 cm thick), laceration (1-3 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (1-3 cm in diameter)
 III: Subcapsular hematoma (> 3 cm thick), laceration (> 3 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (> 3 cm in diameter); splenic capsular rupture
III: Subcapsular hematoma (> 3 cm thick), laceration (> 3 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (> 3 cm in diameter); splenic capsular rupture
 I: Subcapsular hematoma (< 1 cm thick), laceration (< 1 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (< 1 cm in diameter)
I: Subcapsular hematoma (< 1 cm thick), laceration (< 1 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (< 1 cm in diameter) II: Subcapsular hematoma (1-3 cm thick), laceration (1-3 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (1-3 cm in diameter)
II: Subcapsular hematoma (1-3 cm thick), laceration (1-3 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (1-3 cm in diameter) III: Subcapsular hematoma (> 3 cm thick), laceration (> 3 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (> 3 cm in diameter); splenic capsular rupture
III: Subcapsular hematoma (> 3 cm thick), laceration (> 3 cm in depth), or parenchymal hematoma (> 3 cm in diameter); splenic capsular ruptureCLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Treatment
• Hemodynamically unstable patients with splenic injury undergo surgery if focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) scan or diagnostic peritoneal lavage (DPL) are positive.
• Hemodynamically stable patients with AAST grade I-III splenic injury and without other injuries often conservatively (observation or embolization) managed
 Active extravasation, pseudoaneurysm, or hemoperitoneum in hemodynamically stable patients managed with embolization
Active extravasation, pseudoaneurysm, or hemoperitoneum in hemodynamically stable patients managed with embolization
 Active extravasation, pseudoaneurysm, or hemoperitoneum in hemodynamically stable patients managed with embolization
Active extravasation, pseudoaneurysm, or hemoperitoneum in hemodynamically stable patients managed with embolization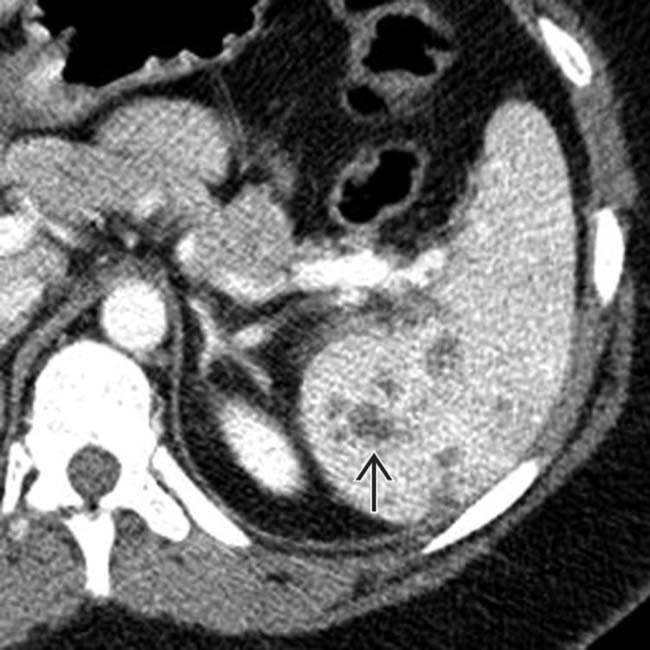
 within the spleen.
within the spleen.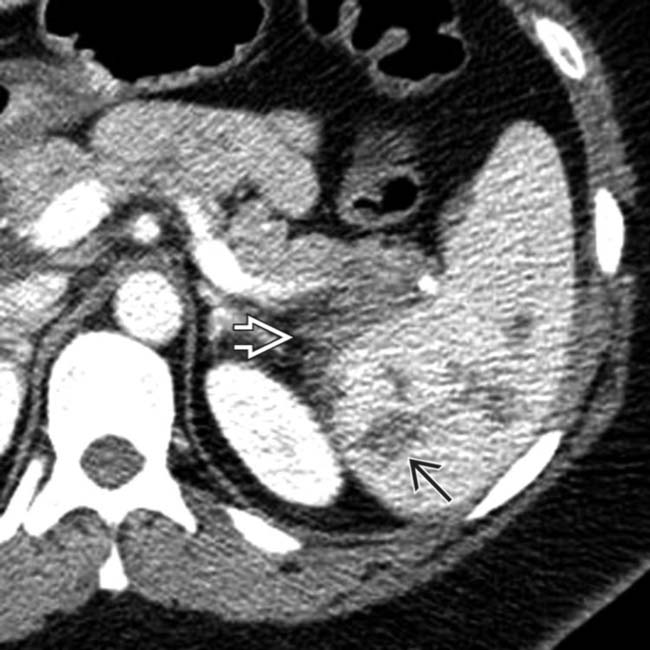
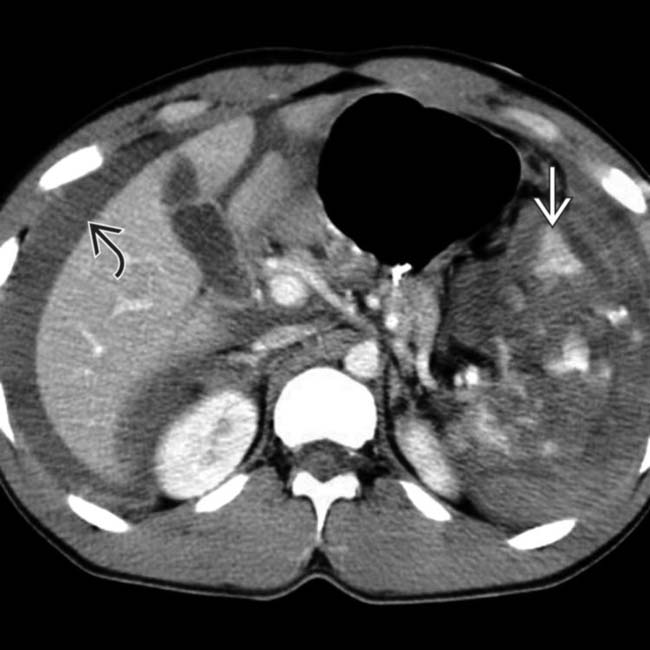
 , as well as a small perisplenic hematoma
, as well as a small perisplenic hematoma  in this typical case of splenic laceration.
in this typical case of splenic laceration.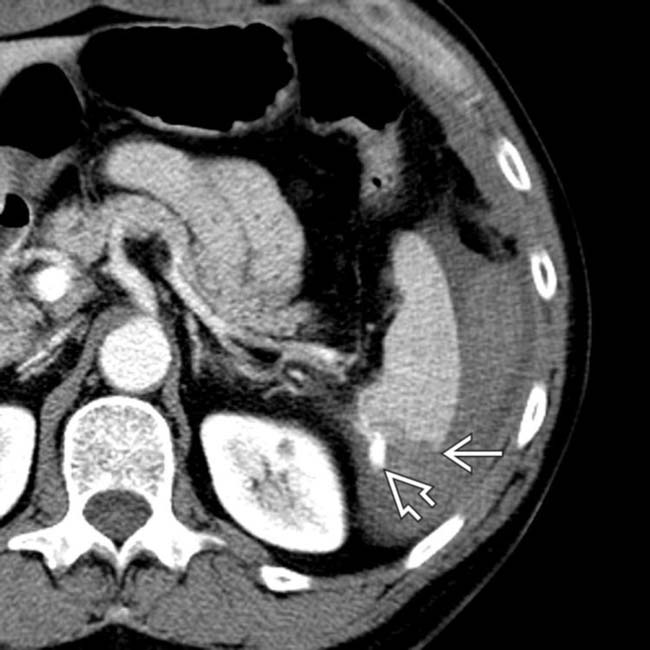
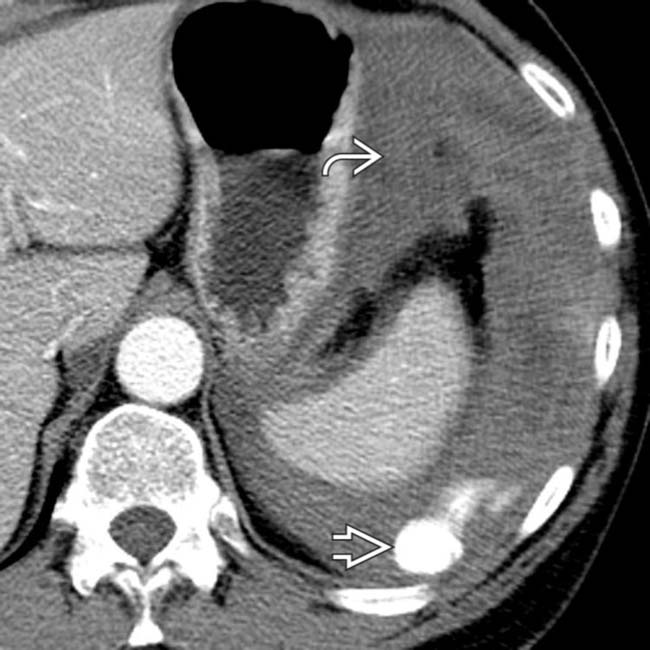
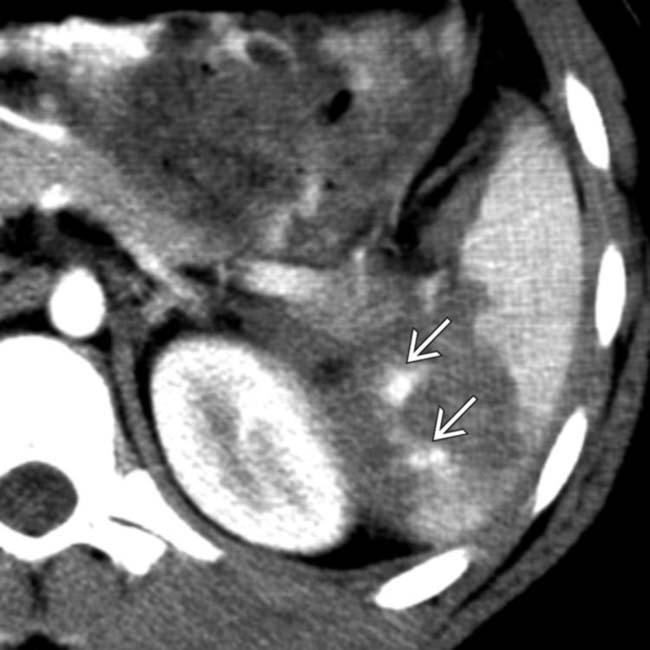
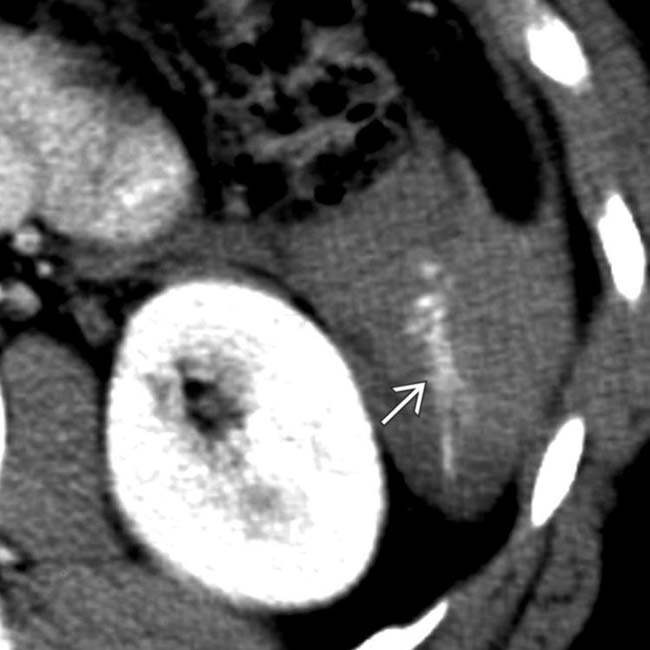
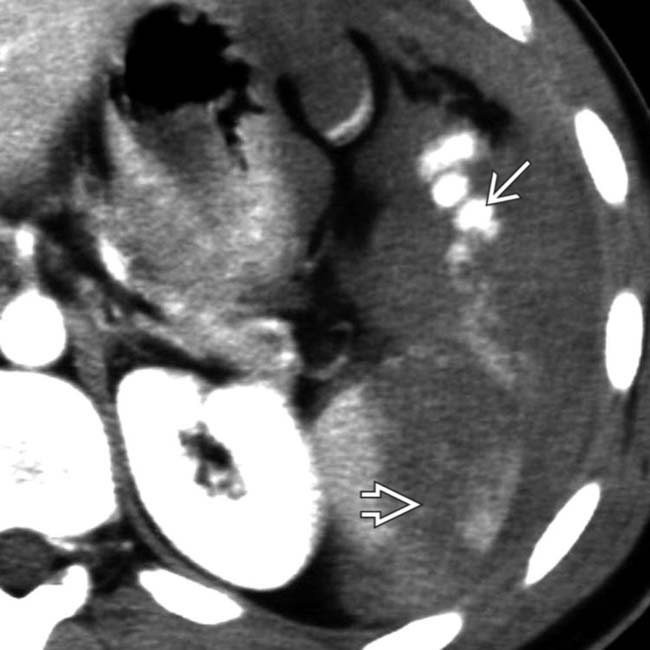
 featuring a site of high-attenuation arterial extravasation
featuring a site of high-attenuation arterial extravasation  .
.
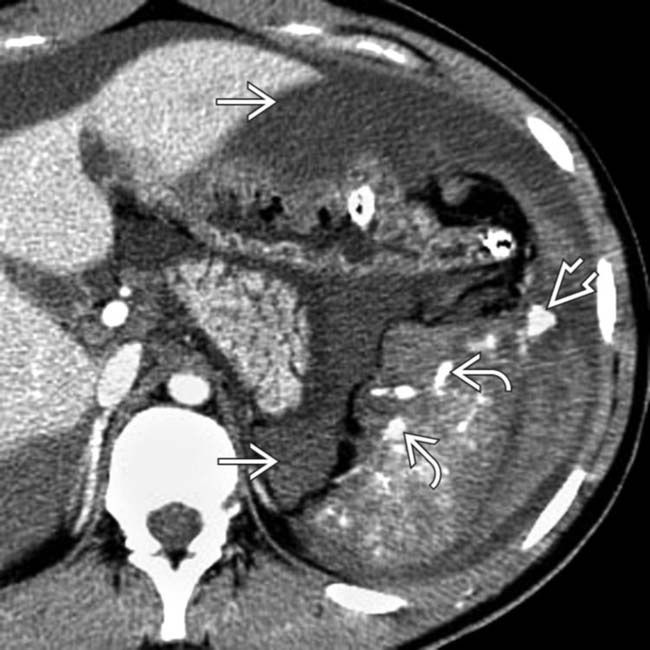
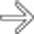
 and extensive arterial extravasation
and extensive arterial extravasation  .
.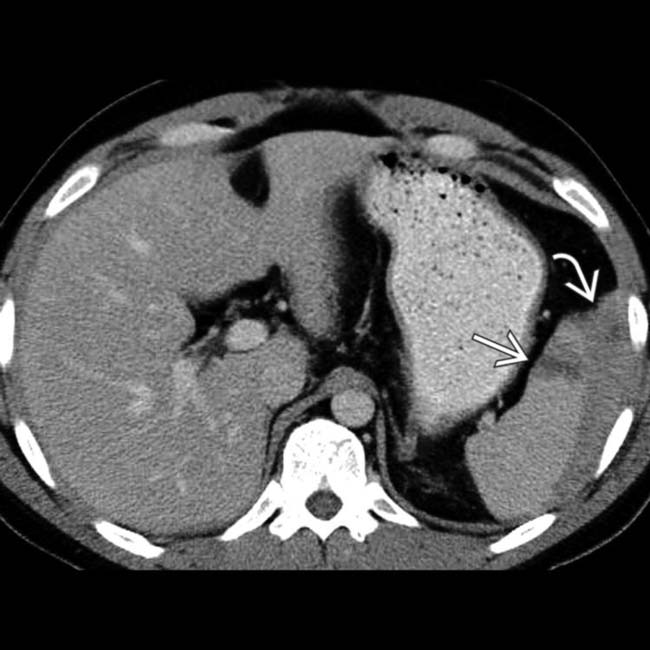
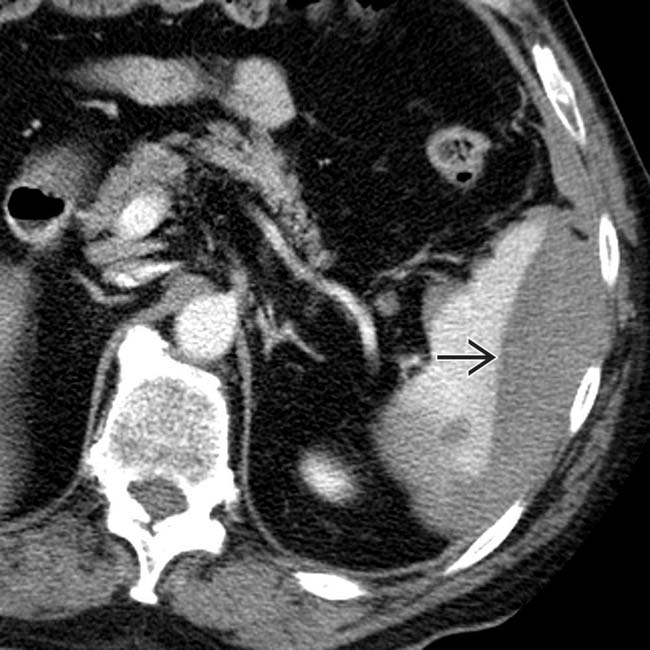
 with a high density clot
with a high density clot  adjacent to the spleen.
adjacent to the spleen.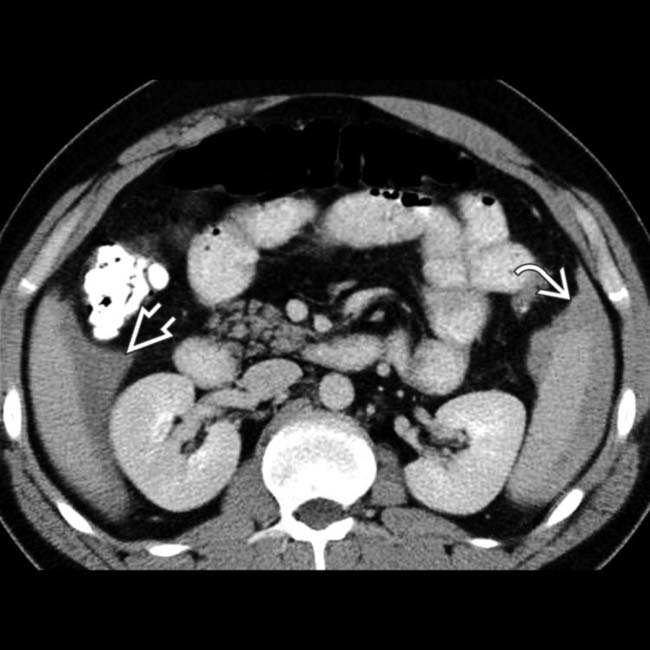
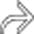 , as well as lower density and more homogeneous blood elsewhere within the peritoneal cavity
, as well as lower density and more homogeneous blood elsewhere within the peritoneal cavity  . This is characteristic of the sentinel clot sign. The injury healed without surgical intervention.
. This is characteristic of the sentinel clot sign. The injury healed without surgical intervention.
 .
.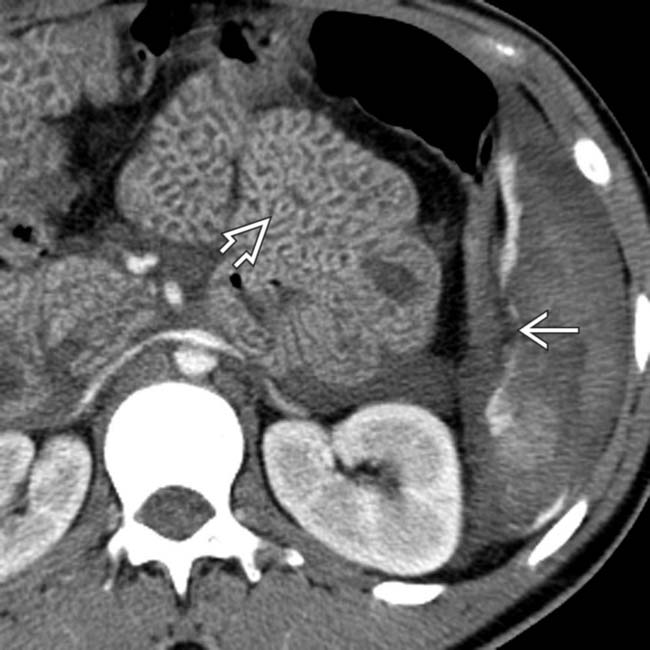
 . Note the thickened small bowel loops
. Note the thickened small bowel loops  and flattened inferior vena cava (IVC) indicating hypoperfusion syndrome.
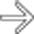
and flattened inferior vena cava (IVC) indicating hypoperfusion syndrome.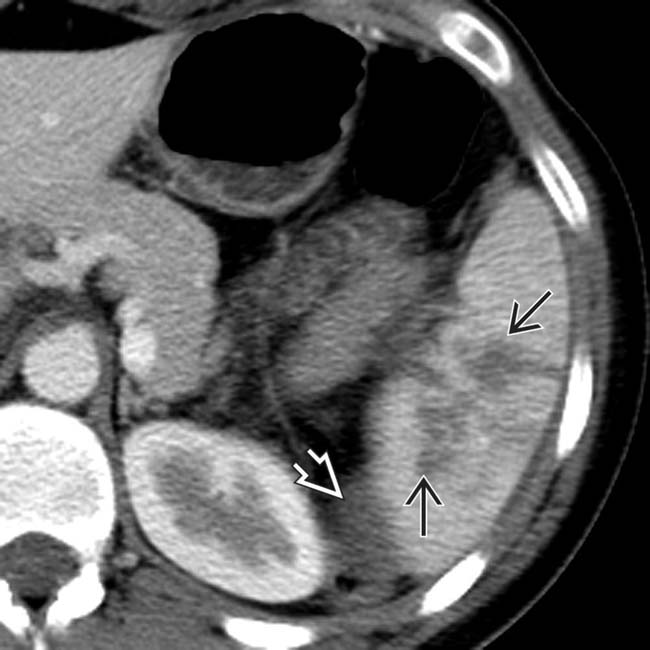
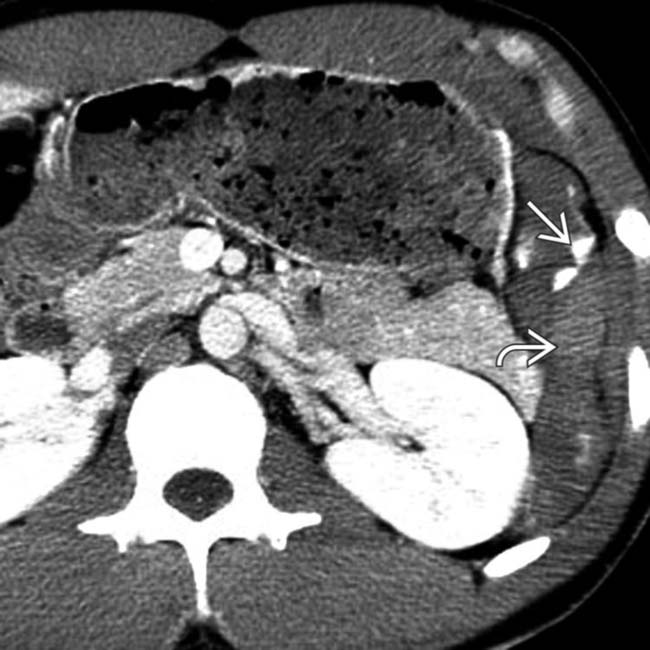
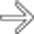
 following blunt trauma. Note the small amount of perisplenic blood
following blunt trauma. Note the small amount of perisplenic blood  .
.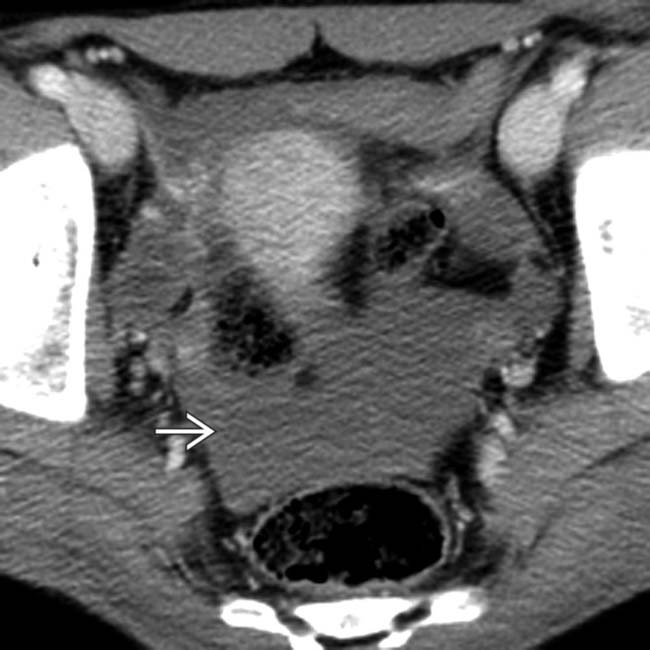
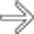 . Despite hemodynamic stability during the scan, this patient had massive delayed bleeding 24 hours later, requiring urgent surgery.
. Despite hemodynamic stability during the scan, this patient had massive delayed bleeding 24 hours later, requiring urgent surgery.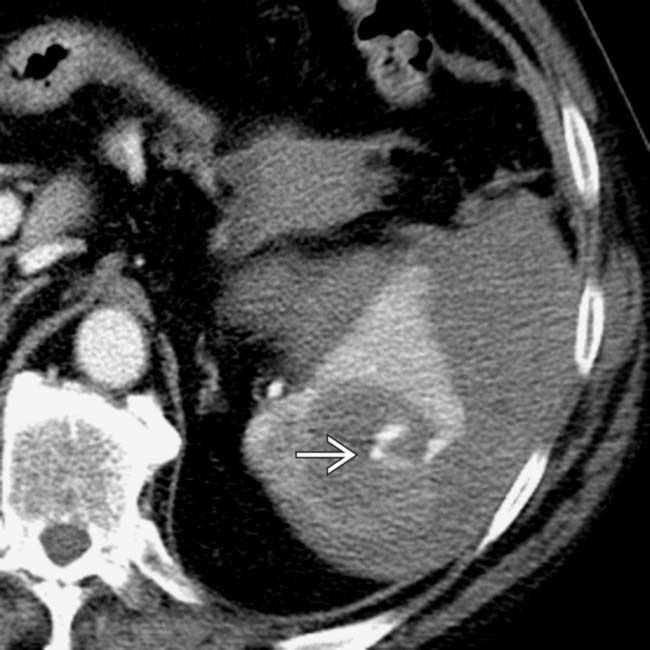
 .
.
 .
.






















































 .
.
 in the left paracolic gutter.
in the left paracolic gutter.
 with adjacent active bleeding
with adjacent active bleeding  .
.
 and high-density active bleeding
and high-density active bleeding  .
.

