21.2 Specific poisons
Common poisons
Paracetamol
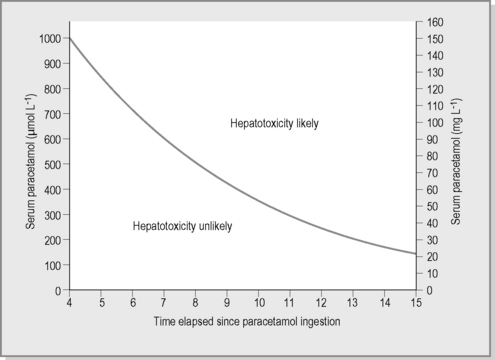
The paracetamol nomogram (Fig. 21.2.1), based on adult toxicity profiles, is extrapolated to children and predicts the potential for significant hepatotoxicity. The nomogram is applicable when a paracetamol level is taken between 4 and 16 hours post-acute ingestion. The nomogram cannot be utilised when the time of ingestion is unknown or in the case of staggered or chronic ingestions. Paracetamol treatment guidelines were reviewed by a representative panel of Clinical Toxicologists to the Australasian Poisons Information Centres and published in 2008. A major shift in management was the amalgamation of the high- and low-risk nomogram treatment lines into a single curve for both adults and children. This current line commences at 1000 μmol L–1 at 4 hours post-ingestion and has a half-life of 4 hours.
Anticholinergics and antihistamines
Other anticholinergic effects include tachycardia, gastrointestinal ileus and urinary retention.
Rare and dangerous poisons
Although most substances are harmless to children in small amounts, a few pharmaceuticals and chemicals are extremely toxic in minute quantities. Table 21.2.1 lists drugs where ‘one pill can kill’ and chemicals where a sip or mouthful is potentially lethal.
Daly F.F.S., Fountain J.S., Murray L., et al. Guidelines for the management of paracetamol poisoning in Australia and New Zealand – explanation and elaboration. Med J Aust. 2008;188:296-301.
Erickson S.J., Duncan A. Clonidine poisoning – an emerging problem: Epidemiology, clinical features, management and preventative strategies. J Paediatr Child Health. 1998;134:280-282.
Kerns W., Kline J., Ford M.D., et al. Beta-blocker and calcium channel blocker toxicity. Emerg Med Clin N Am. 1994;12(2):365-390.
Lifshitz M., Shahak E., Sofer S., et al. Carbamate and organophosphate poisoning in young children. Pediatr Emerg Care. 1999;15:102-103.
Nuutinen M., Uhari M., Karvali T., et al. Consequences of caustic ingestions in children. Acta Paediatr. 1994;83:1200-1205.
Quadrani D.A., Spiller H.A., Widder P. Five-year retrospective evaluation of sulphonylurea ingestion in children. Clin Toxicol. 1996;34:267-270.
Riordan M., Rylance G., Berry K. Poisoning in children 1-5. Arch Dise Child. 2002;87:392-410.
Tibballs J. Clinical effects and management of eucalyptus oil ingestion in infants and young children. Med J Aus. 1995;163:177-180.
Woolf A.D., Wenger T.L., Smith T.W., Lovejoy F.H.Jr, et al. The use of digoxin-specific Fab fragments for severe digitalis intoxication in children. N Engl J Med. 1992;26:1739-1744.