7 Spatial Compound Imaging
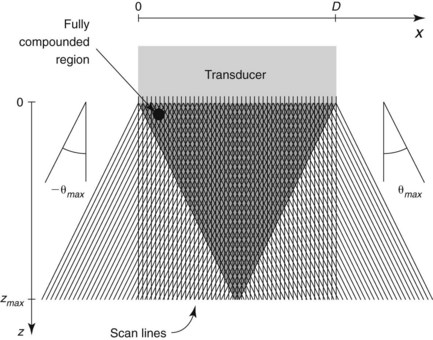
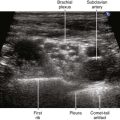
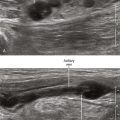
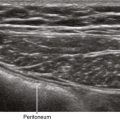
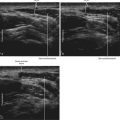
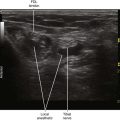
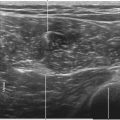
One benefit of the use of spatial compound imaging is the reduction of angle-dependent artifacts (Table 7-1). Speckle is the granular appearance of a sonographic image that results from scattering of the ultrasound beam from small tissue reflectors. This speckle artifact results in the grainy appearance observed on sonograms, representing noise in the image. Improved image quality may be obtained by using spatial compound imaging, which can reduce speckle noise.
Table 7-1 Advantages and Disadvantages of Spatial Compound Imaging
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
Clinical Pearls
• The use of spatial compound imaging can improve imaging of nerve borders and the block needle tip.
• One potential disadvantage of compound imaging is that needle reverberations occur over a broader range of angles and can prevent imaging of deeper structures.
• Compound imaging is being developed for both linear and curved arrays.
• Sliding the transducer along the known course of the nerve is a well-established technique to improve small nerve imaging. However, frame rate reduction that occurs with spatial compound imaging can cause problems with this technique.
• If compound imaging is not an advantage for a particular imaging situation, it can be turned off.