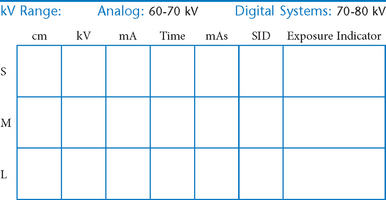
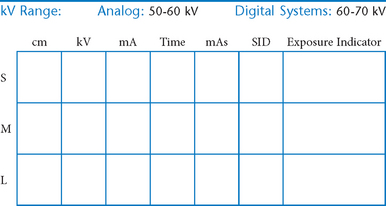
Skull, Facial Bones, and Paranasal Sinuses
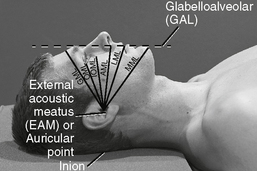
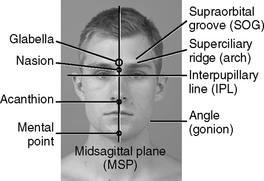
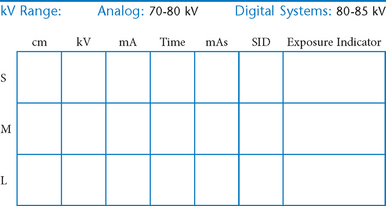
Cranial landmarks and positioning lines used in skull and facial bones positioning.
C Infraorbitomeatal line (IOML) (Reid’s base line, or “base line,” base of cranium)
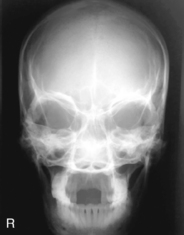
AP (PA) Axial Skull*
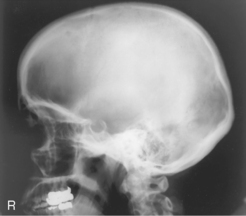
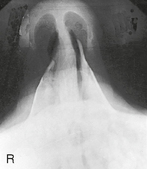
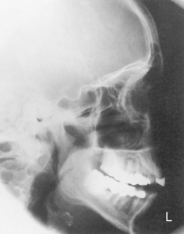
Lateral Skull*
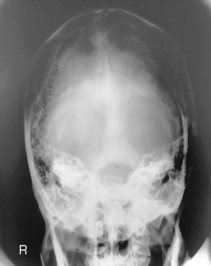
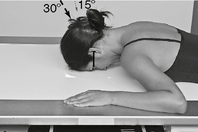
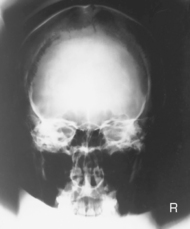
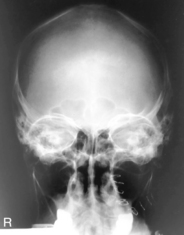
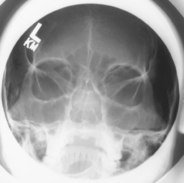
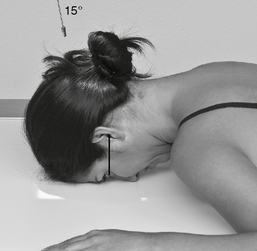
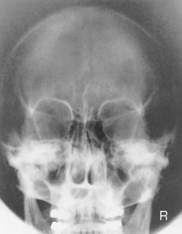
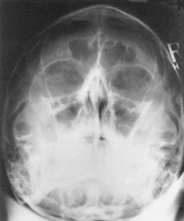
PA (0° and 15°) Caldwell Skull*
PA (0°) and PA Axial Caldwell (15° Caudad)
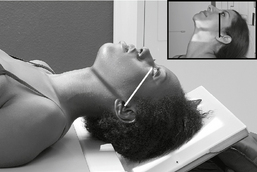
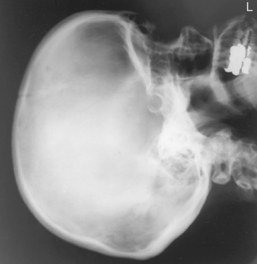
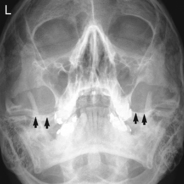
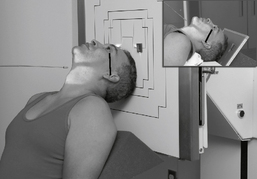
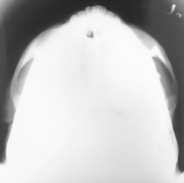
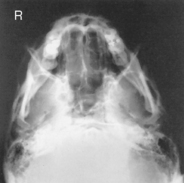
Submentovertex (SMV) Skull*
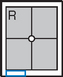
Submentovertex (SMV) Skull
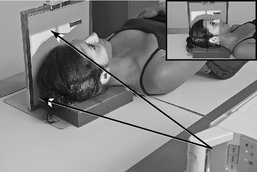
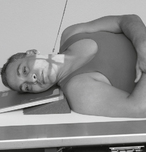
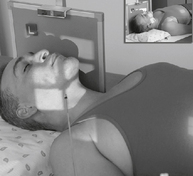
Lateral Trauma Skull*
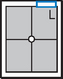
Warning: Do NOT elevate or move patient’s head before cervical spine injuries have been ruled out.
Trauma AP (0°) and AP Axial (15° Cephalad) Projections
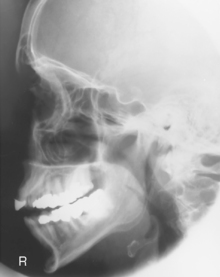
Facial Bones—Lateral*
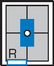
Lateral Facial Bones
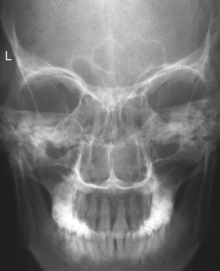
Parietoacanthial and Modified Parietoacanthial
Facial Bones—PA Axial (Caldwell)*

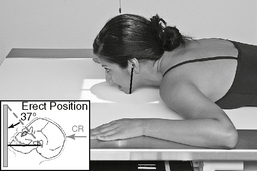
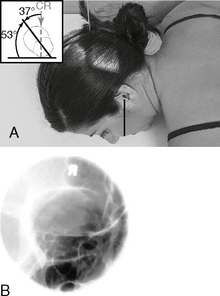
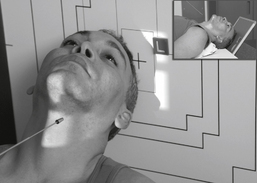
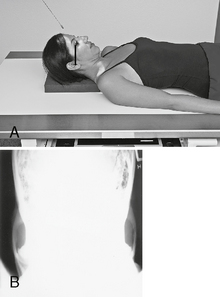
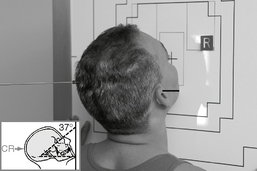
Optic Foramina—Parieto-orbital Oblique*
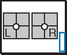
Position
• Seated erect or prone on table
• As a starting reference, adjust the head so the nose, cheek, and chin are touching the tabletop.
• Adjust the head so the AML is perpendicular to the IR, and the midsagittal plane is 53° to the IR (use angle indicator).
Zygomatic Arches—Bilateral*
Zygomatic Arches—Tangential*
(Oblique Inferosuperior Projection)
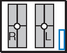
Bilateral Zygomatic Arches—AP Axial*
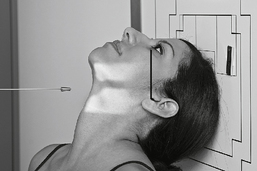
Nasal Bones—Lateral*
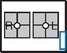
Nasal Bones*
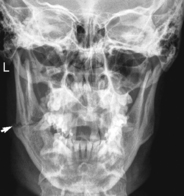
Mandible—PA and PA Axial*
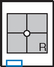
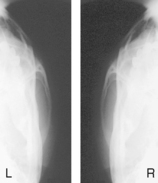
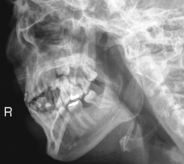
Mandible—Axiolateral Obliques*
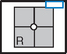
R and L sides generally taken for comparison unless contraindicated.
Mandible—Trauma Axiolateral Oblique*
AP Axial Mandible*
Temporomandibular Joints*
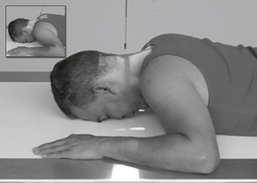
Axiolateral Oblique (Modified Law Method)
R and L sides for comparison in both open and closed mouth positions.
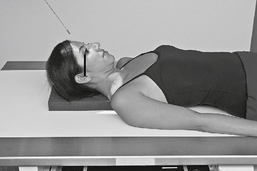
Position
• Seated erect or semiprone on table, affected side down
• Adjust chin to place IOML parallel to top edge of IR.
• Anterior head (midsagittal plane) rotated 15° toward IR, no tilt, IPL remains perpendicular to IR
• Portion of IR being exposed centered to projected CR
• Second exposure in same position except with mouth fully open
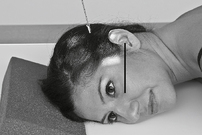
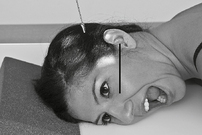
Temporomandibular Joints*
R and L sides for comparison in both open and closed mouth positions.
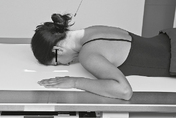
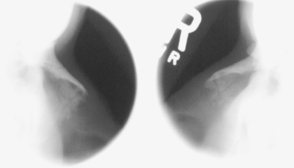
Axiolateral Oblique (Modified Law Method) and Axiolateral (Schuller method) TMJ Projections
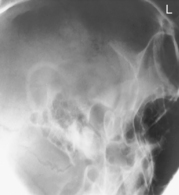
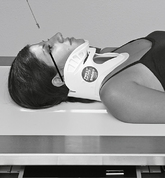
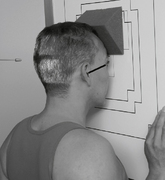
Fig. 8-54 Axiolateral projection—open mouth; TMJ shown with condyle moved to anterior margin of fossa (Schuller).![]()
Lateral Paranasal Sinuses*
Requires an erect position with horizontal CR to demonstrate air-fluid levels.
PA Paranasal Sinuses*
Paranasal Sinuses*
Paranasal Sinuses*
Parietoacanthial (Waters Method) Sinuses and Submentovertex (SMV)
Evaluation Criteria
Position:
• Waters: Petrous ridges just inferior to floor of maxillary sinuses. No rotation; equal distance between orbits and lateral skull
• SMV: Mandibular condyles projected anterior to petrous bone. No rotation or tilt; symmetry of petrous pyramids and equal distance between mandibular border and lateral skull
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 411.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 412.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, pp. 413 and 414.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 415.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 594.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 595.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 418.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, pp. 419 and 421.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 420.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 597.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 427.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 424.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 425.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 426.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 422.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 423.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 429.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 428.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, pp. 428 and 598.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 430.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 434.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 435.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 436.
*Bontrager Textbook, 8th ed, p. 437.

 AP axial (Towne method) and PA axial (Haas method) (R)
AP axial (Towne method) and PA axial (Haas method) (R) AP axial critique
AP axial critique Lateral (R)
Lateral (R) Lateral critique
Lateral critique PA (0°) and PA (15° or 23°) Caldwell (R)
PA (0°) and PA (15° or 23°) Caldwell (R) PA Caldwell critique
PA Caldwell critique Submentovertex (SMV) (S)
Submentovertex (SMV) (S) SMV critique
SMV critique Lateral trauma (S)
Lateral trauma (S) AP 0°, AP 15°, and AP axial trauma (S)
AP 0°, AP 15°, and AP axial trauma (S) Lateral trauma critique
Lateral trauma critique AP (0° and 15°) trauma critique
AP (0° and 15°) trauma critique Lateral (R)
Lateral (R) Lateral critique
Lateral critique Parietoacanthial (Waters and modified Waters) (R)
Parietoacanthial (Waters and modified Waters) (R) Parietoacanthial critique
Parietoacanthial critique PA 15° Caldwell (R)
PA 15° Caldwell (R) PA axial 15° Caldwell critique
PA axial 15° Caldwell critique Lateral, acanthioparietal (reverse Waters and modified Waters) (S)
Lateral, acanthioparietal (reverse Waters and modified Waters) (S) Parieto-orbital oblique (Rhese method) (S)
Parieto-orbital oblique (Rhese method) (S) Submentovertex (SMV) (R)
Submentovertex (SMV) (R) Tangential (R)
Tangential (R) SMV and tangential critique
SMV and tangential critique AP axial (modified Towne) (S)
AP axial (modified Towne) (S) Lateral (R)
Lateral (R) Lateral critique
Lateral critique Superoinferior (axial) (S)
Superoinferior (axial) (S) PA and PA axial (R)
PA and PA axial (R) Axiolateral oblique (R)
Axiolateral oblique (R) Trauma axiolateral oblique (S)
Trauma axiolateral oblique (S) PA and axiolateral oblique critique
PA and axiolateral oblique critique AP axial (mandible or TMJ) (R)
AP axial (mandible or TMJ) (R) Axiolateral oblique (Law) (S)
Axiolateral oblique (Law) (S) Axiolateral (Schuller) (S)
Axiolateral (Schuller) (S) Axiolateral (Law and Schuller) critique
Axiolateral (Law and Schuller) critique Lateral (R)
Lateral (R) PA (Caldwell) (R)
PA (Caldwell) (R) Lateral and PA (Caldwell) critique
Lateral and PA (Caldwell) critique Parietoacanthial (Waters) (R)
Parietoacanthial (Waters) (R) Submentovertex (SMV) (S)
Submentovertex (SMV) (S) Waters and SMV critique
Waters and SMV critique