2 Sexually Transmitted Infections
HIV/AIDS
What are the likely diagnoses and the immediate management?
• Examination of the chest can yield few signs other than tachypnoea and tachycardia. Fine inspiratory crackles might be heard.
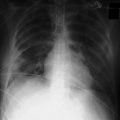
• The CXR is often normal or shows little, although bilateral perihilar interstitial shadowing with a bat-wing appearance is the characteristic abnormality.
• High-resolution CT of the lungs shows a characteristic ground glass appearance even when there is little to see on the plain CXR.
• Oxygen saturation characteristically falls on exercise. Arterial blood gas analysis might show hypoxia with a normal carbon dioxide and pH.
The introduction of highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART) in HIV-infected people has led to a significant decline in pneumocystis and the infection is now most commonly seen in those not previously recognised as HIV infected. Pneumocystis infection occurs most frequently in the context of significant immunosuppression, when the CD4 count is < 200 cells/mm3. There may be clinical markers of poor immune function, such as candidiasis, as in this patient.
What other chest conditions are associated with HIV?
How would you manage an HIV-positive patient with chest problems?
Assessment
• Full history and examination: including details of travel, previous infections, previous or existing HIV-related pathology, current surrogate marker data (if known), current therapy including anti-retroviral drugs and anti-microbial prophylaxis.
• Assess the degree of immunosuppression by looking for clinical signs such as oral candidiasis, hairy oral leukoplakia, and seborrhoeic dermatitis. Look for pathology in all systems, including examination of the mouth and fundi.
• Chest X-ray, exercise oximetry, blood gases, blood cultures, sputum examination for acid-fast bacilli (AFB), and microscopy, culture and sensitivity. Full blood count, liver and renal function.