10 Rheumatology and bone disease
Questions
In a patient who has sustained an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) knee injury and whose pain and swelling have subsided on conservative treatment, what are the chances of complications (e.g. osteoarthritis, fibrosis) from the torn ligament. Will the patient be able to lead a normal life?
In what percentage of patients with psoriatic arthritis does the arthritis precede the onset of skin or scalp lesions?
Are elevated homocysteine levels an independent risk factor for progression of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)/scleroderma? Kindly suggest some references if possible.
Do pulmonary manifestations in Behçet’s syndrome present with pulmonary infiltrates in the upper zone of the lung?
How effective is parathyroid hormone in the management of osteoporosis? Please explain the mechanism.
It is reported by the Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine that glucosamine and chondroitin sulphate have failed an NEJM trial for the treatment of osteoarthritis? Is there still a valid use for these compounds?
Both of these drugs are useful in neuropathic pain. Gabapentin has fewer side-effects and is becoming a first-line drug for nerve injury pain.
With good physiotherapy, patients can lead a normal life but in young athletes ACL repair is a better option. Osteoarthritis can occur in later life.
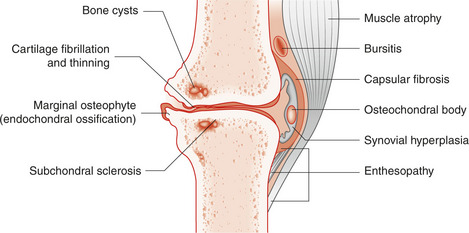
Plain X-ray and skyline views of the patella are necessary. Joint space narrowing, osteophytes, subchondral radiolucencies and sclerosis are the classic signs of OA (Fig. 10.1). Osteophytes are the best predictor of knee pain. Some of these changes will be seen in a patient of advanced age and the significance must be correlated with the symptoms and signs. MRI is commonly used for more precise identification of the damage in osteoarthritis.
‘Active’ rheumatoid arthritis makes people feel unwell so that they don’t eat, and hence lose weight. Control of the disease will allow them to regain appetite. Be careful not to let the patient get overweight.
Do not treat uric acid levels unless they are very high. You treat the symptoms produced by a raised uric acid; that is, gout. Cholesterol levels should be taken in isolation and not related to the uric acid level. The level of 213mg/dL of cholesterol will require treatment in patients who have evidence of cardiovascular disease, usually with a statin.
Many patients with SLE do well with little treatment. Cyclophosphamide is mainly used for lupus nephritis and vasculitis. For lupus nephritis, 0.75g/m2 has been used IV over 60 minutes.
Osteoblasts are rich in alkaline phosphatase, so that in any bone condition with increased activity of osteoblasts, e.g. in the growing child or in Paget’s disease, there will be an increase in the serum alkaline phosphatase.
Alkaline phosphatase is also found in the placenta so that the serum level is raised in pregnancy.
Arch supports and wider shoes often help, and NSAIDs are useful for pain and inflammation. Steroid injection into the tendon is also effective; surgery is the last resort.