Retinoschisis
Clinical Presentation:
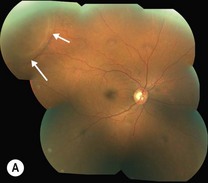
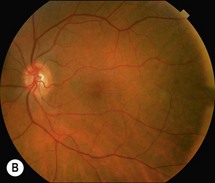
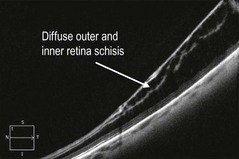
Senile retinoschisis is usually bilateral, with a smooth, domed appearance and most commonly develops inferotemporally (Fig. 25.1.1). There may be non-inflammatory sheathing of retinal blood vessels and retinal ‘snowflakes’ seen over the inner wall of the schisis cavity. An absolute scotoma is seen on visual field testing, in contrast to the relative scotoma seen in acute rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Both inner and outer retinal breaks may be seen, but rarely in conjunction. Unlike a retinal detachment, no demarcation line is seen, unless the schisis progresses into a combined detachment.
OCT Features:
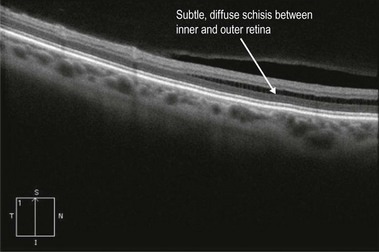
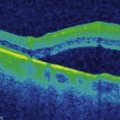
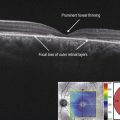
Line scans through the area of retinoschisis show a splitting of the neurosensory retina, with the split between the inner and outer retinal layers, in contrast to a retinal detachment where the separaration is between the retinal pigment epithelium and the neurosensory retina (Fig. 25.1.2 and 25.1.3). Hyporeflective spaces in the nerve fiber layer may represent cystic degeneration.
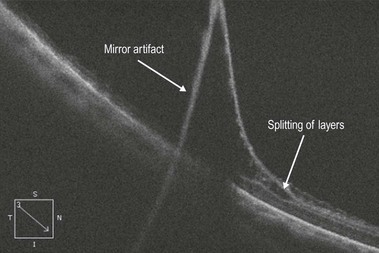
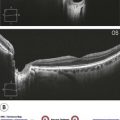
Figure 25.1.2 OCT scan through an area of retinoschisis. Note that the inner and outer retinal layers are separated. Also note the artifactual line seen because the retinoschisis crosses the zero delay line of the OCT scanner.
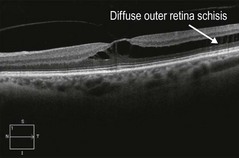
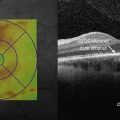
In juvenile retinoschisis, OCT demonstrates foveal cystic alterations primarily in the outer retinal layers, but eventually the inner retina can be involved as well (Fig. 25.1.4). OCT of the peripheral schisis shows cleavage in the retinal tissue, with bridging retinal elements seen traversing the schisis cavity.