Retinal Light Toxicity (Photochemical)
Clinical Features:
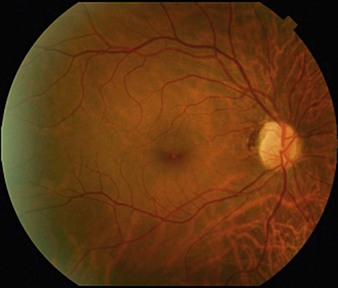
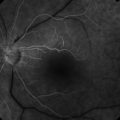
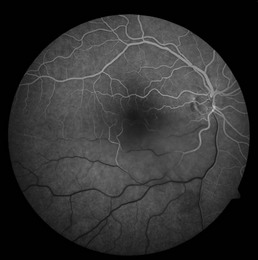
Retinal phototoxicity from the sun or a welding arc appears as small, round, well-circumscribed, yellow acquired vitelliform-like lesions in the fovea (Fig. 20.2.1). Microscope phototoxicity appears as a more broad area that is fairly well-circumscribed either in the inferior or superior macula (dependent on tilt of microscope).
OCT Features:
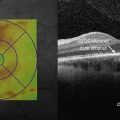
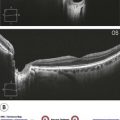
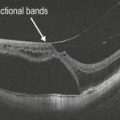
Solar and welding arc injuries appear similar on OCT as a focal loss of the outer retina and IS–OS/ellipsoid layer, leaving a small hyporeflective rectangular cavity or outer retinal hole (Fig. 20.2.2). These can be singular or multifocal. The ELM and RPE are typically spared. Microscope light-induced retinal phototoxicity leads to prominent chorioretinal scarring in the region of the injury.
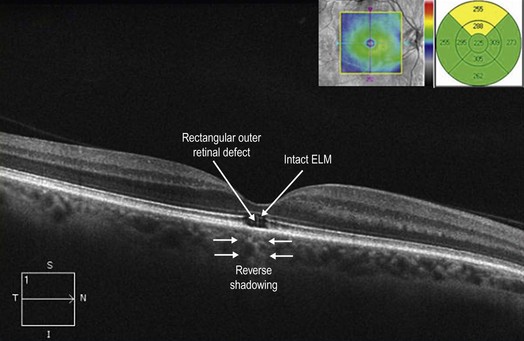
Figure 20.2.2 OCT (corresponding to Figure 20.2.1) shows focal loss of the outer retina including photoreceptors and the IS–OS/ellipsoid layer. In this advanced case, the RPE is also affected, leading to ‘reverse shadowing’ below (between arrowheads). The overall defect is characteristically rectangle-shaped and the overlying ELM is intact.