Chapter 38 Reproductive hormones
There are several major classes of steroid hormone:
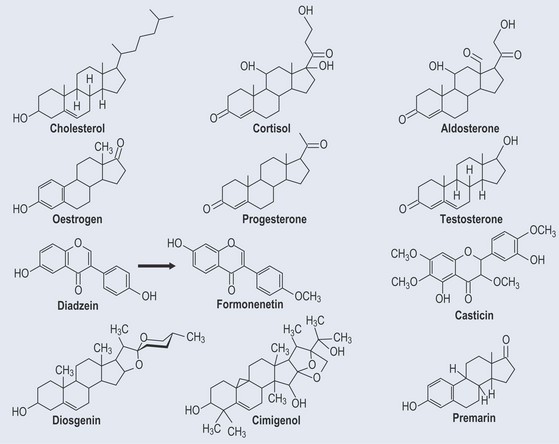
These are all derived from cholesterol. There is an interconversion between male and female hormones, as the structures are very similar (see Figure 38.3, p. 305). This occurs naturally in both males and females, although in females there is a predominance of female hormones and in males a predominance of male hormones.
Female Hormones
The Menstrual Cycle
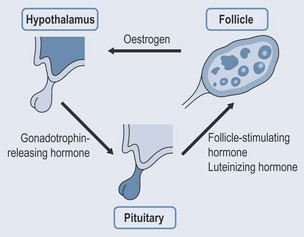
Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulates the pituitary gland, which secretes follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and is responsible for the synthesis and secretion of oestrogen in the ovaries. When oestrogen levels rise to a critical point, production is switched off by shutting off the GnRH release from the hypothalamus (Figure 38.1).
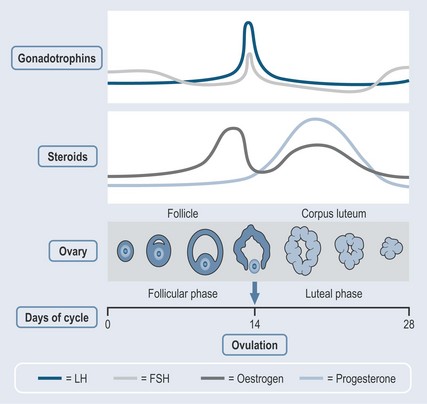
Progesterone production is stimulated by luteinizing hormone (LH), which is produced by the pituitary as a result of stimulation by GnRH. Progesterone levels cannot rise too high, as they are controlled in the same way as oestrogen. A new follicle begins to form in one of the ovaries at this stage and, when menstruation ceases, the follicle continues to develop while at the same time secreting oestrogen (Figure 38.2). The rising oestrogen levels cause the endometrium to thicken and become richly supplied with blood vessels and glands.
Rising levels of LH create a change in the follicle until a sudden surge in LH levels at about 2 weeks triggers ovulation (mid-cycle). The unfertilized egg is then released into the fallopian tube. The presence of LH encourages the empty follicle to develop into a corpus luteum, which then starts to secrete progesterone. This:
Menstruation occurs every 28 days, when the lining of the uterus breaks down and is discharged.
Pregnancy
Birth
Infertility Treatment
Diagnostic Tests
• The Importance of Hormonal Levels in Infertility Blood Tests
Treatment
• Infection
Any infection is identified and treated with antibiotics. Both parties can be treated in this case.
• Infertility Drugs
Generally three classes of drug are used:
Human Menopausal Gonadotrophin
Menopause
With the reduction of oestrogen, the hypothalamus is no longer inhibited and is able to stimulate the pituitary to secrete hormones at a much higher level. The high concentrations of FSH and LH can cause a variety of physical and emotional symptoms.
What are the Natural Alternatives?
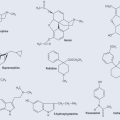
Diadzein
Diadzein is naturally occurring isoflavone (Figure 38.3), which is classed as a phytoestrogen because it possesses oestrogen-like properties. It appears to have both weak oestrogenic and antioestrogenic effects and might also be an antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, antiatherogenic and provide some protection against osteoporosis. It is found as the glycoside diadzein in:
Dioscorea spp. (Shan Yao)
The plant sterol diosgenin (see Figure 38.3) comes from Dioscorea spp. (wild yam). It occurs as a glycoside. Diosgenin can be converted to progesterone via a chemical process called ‘Marker degradation’, which gives access to many important steroids, e.g. testosterone and oestradiol.
Vitex Agnus Castus
Casticin (Figure 38.3), a flavonoid, may be one of the active components, but its activity is far from clear.