11 Renal disease
Questions
What is the probability that a patient on a moderate daily dose of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs; ibuprofen 800mg once daily for tension headache) will develop analgesic nephropathy?
How does sodium valproate decrease serum urea concentration and GI bleed increases it? Renal disease
In a 69-year-old patient with a 2-cm hard prostatic nodule on digital rectal examination, what is the more appropriate way to make a definitive diagnosis of prostate cancer: prostate biopsy or serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA)?
Expansion of the interstitial compartments (i.e. the peritoneal cavity in ascites) is secondary to the accumulation of sodium in the extracellular compartment. Sodium retention occurs because of increased Na /K – ATPase expression and activity in the cortical collecting duct. Additional factors include elevated tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) levels and an increase in circulating atrial natriuretic protein (ANP) levels, which change capillary permeability.
Aspirin in large doses used over a long time can produce analgesic nephropathy; this was well described in Australia some years ago. In small doses, e.g. 75–150mg a day, aspirin appears very safe and should be used for secondary prevention of further coronary events.
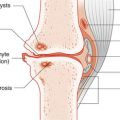
This is a very specialized area and consultation with a paediatric urologist is essential. In general, hydronephrosis is being detected more frequently as routine ultrasonography becomes more common. In most cases, fetal surgery has not been beneficial. The most common cause of hydronephrosis is pelviureteric obstruction, which does not generally impair renal function. Expectant management with follow-up at 2-monthly intervals is the best approach.
CRF can present with polyuria, which is due to failure of tubular reabsorption. When depression of glomerular filtration occurs, Renal disease oliguria tends to replace polyuria. Because tubular dysfunction always accompanies glomerular disease to some extent, the urine output is not a useful guide to renal function. The oedema occurs because of increased sodium tubular reabsorption.
ACE inhibitors reduce intraglomerular pressure and proteinuria as well as blood pressure in chronic renal failure. They slow progression of the renal disease (Box 11.1).
Urinary retention can persist for days, particularly in elderly men with enlarged prostate glands. After 24 hours, catheterization is usually performed. Cholinesterase inhibitors are now not used because of side-effects.