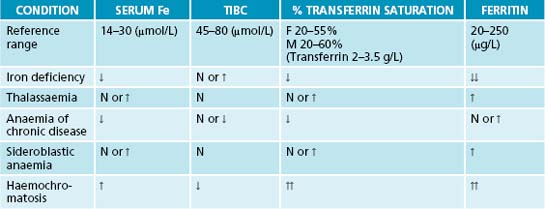
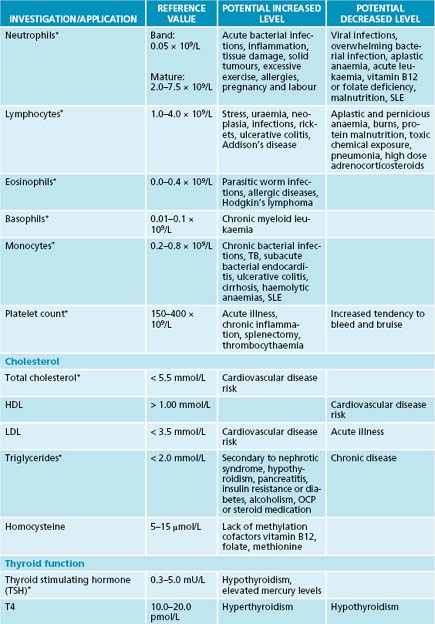
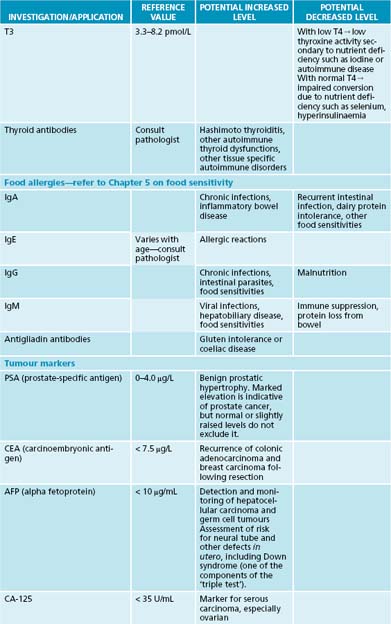
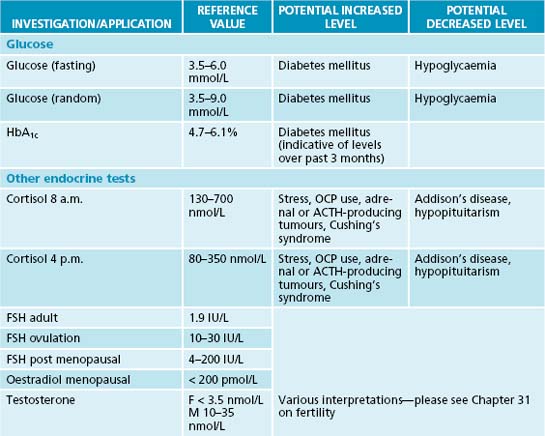
Appendix 4 Laboratory reference values
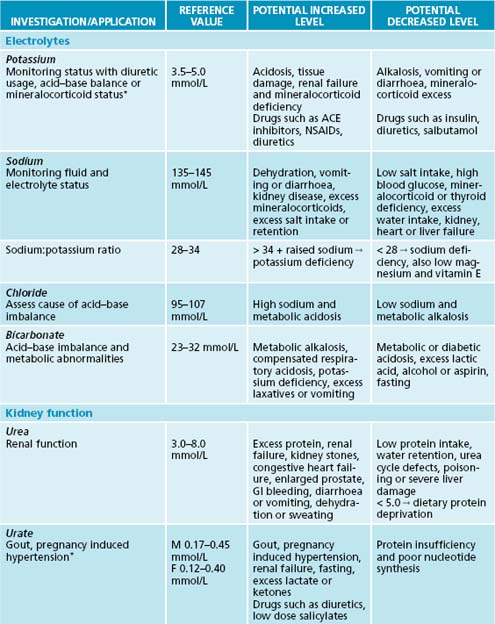
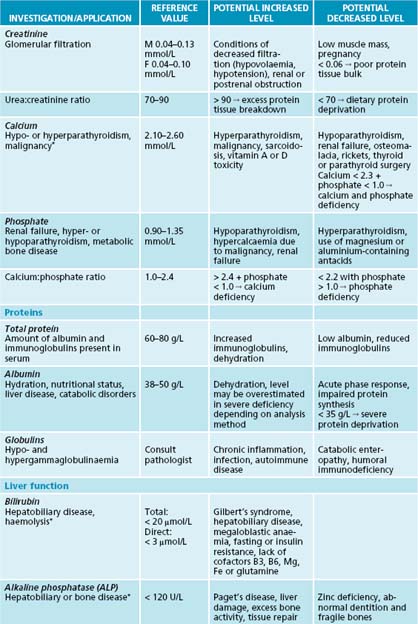
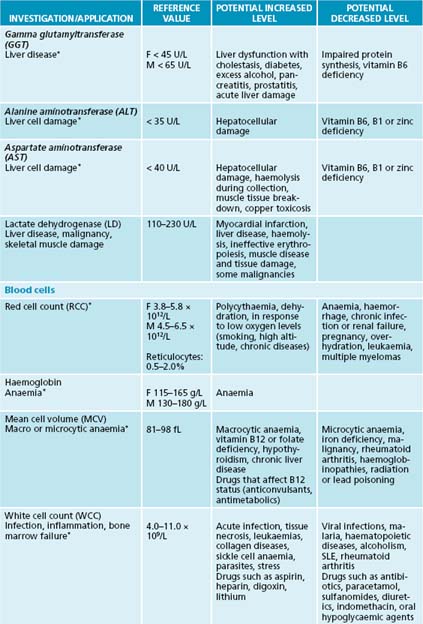
The reference values and ranges for these blood tests are given in the system of international units (SI) and are based on guidelines from the Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia. They may vary from laboratory to laboratory. When paediatric reference ranges may differ from adult ranges they are indicated by an asterisk (∗). Further information and resources can be found at the online manual of the Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia at http://www.rcpamanual.edu.au/.
Markers of inflammation: ESR and CRP
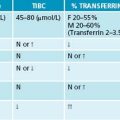
Comparison between ESR and CRP
There is a lag phase of 24–48 hours between the onset of inflammatory stimulation and the production of inflammatory proteins that increase in the ESR. There is also a delay in the fall of the ESR after resolution of the inflammation because the fibrinogen levels can remain elevated for 6 days or so after acute tissue damage—this can take 4–8 weeks to return to normal.
A normal value of < 20 mm/hour generally excludes inflammation. The OCP can push the level to 20–25 mm/hour.
Normal values of ESR—reference interval
| Child | |
| 2–15 mm/hour | |
| Adult male | |
| 17–50 years | 1–10 mm/hour |
| > 50 years | 2–15 mm/hour |
| Adult female | |
| 17–50 years | 3–12 mm/hour |
| > 50 years | 5–20 mm/hour |
C-reactive protein levels (normal value < 10 mg/L)
| MARKED ELEVATION > 40 mg/L | NORMAL TO MILD ELEVATION |
|---|---|