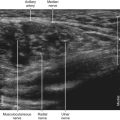
35 Radial Nerve Block
The radial nerve is a branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It provides motor innervation to the extensor-supinator group of muscles. Of the three nerves that surround the axillary artery in the axilla (median, radial, and ulnar), the radial nerve is the most difficult to visualize and access with the block needle.1
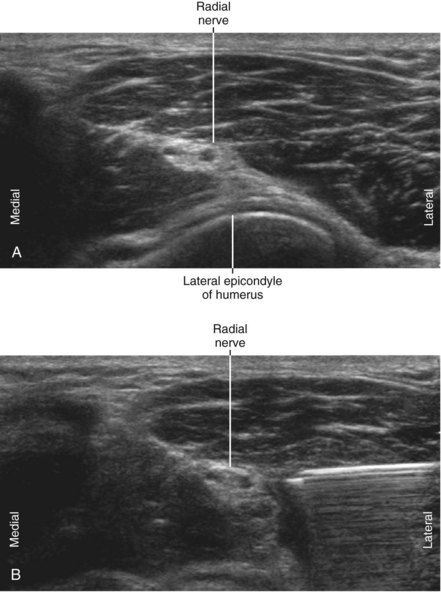
The posterior cutaneous branch of the forearm diverges from the radial nerve about 16 cm proximal to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.2 This branch provides sensation to both the elbow joint and posterior forearm.
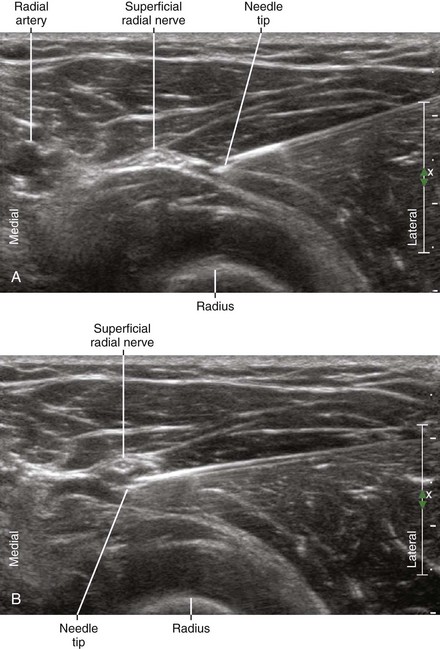
The superficial radial nerve joins the lateral side of the radial artery in the middle third of the forearm. The superficial radial nerve travels the lateral forearm just deep to the brachioradialis muscle. Most patients have radial dominance of sensation of the dorsal aspect of the hand, as primarily supplied by the superficial branch of the radial nerve.3
Suggested Technique
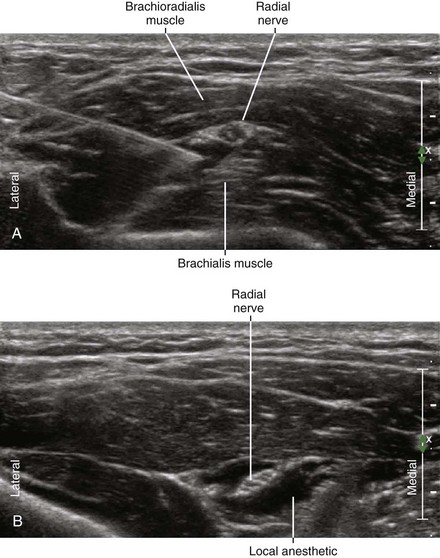
The superficial radial nerve can be blocked in the proximal third of the forearm before it joins the lateral side of the radial artery and divides into smaller branches.4,5 In this location the superficial radial nerve is covered by the brachioradialis as it travels over the supinator muscle. An in-plane approach from the lateral side of the forearm works well with the block needle tip placed under the nerve. The arm is pronated to facilitate placement of the needle. Similarly, the radial nerve can be blocked slightly more proximally in the antecubital fossa before the nerve divides into superficial (sensory) and deep (motor) branches.
Neurologic Assessment
Key Points
| Superficial Radial Nerve Block | The Essentials |
|---|---|
| Anatomy | The brachioradialis muscle covers the SRN in the forearm. |
| Image orientation | The SRN lies lateral to the RA. |
| Positioning | Arm pronated |
| Operator | Standing on the lateral (cephalad) side of the armboard |
| Display | Across the armboard |
| Transducer | High-frequency linear, 23- to 38-mm footprint |
| Initial depth setting | 25 mm |
| Needle | 25 gauge, 38 mm in length |
| Anatomic location | Proximal third of the forearm |
| Approach | SAX view of SRN, in-plane from lateral to medial |
| Place the needle tip through BR adjacent to the SRN. | |
| Local anesthetic should layer under the BR and around the SRN. | |
| Sonographic assessment | The injection should track along the SRN. |
| Anatomic variation | Proximal branching of SRN is possible. |
BR, Brachioradialis muscle; RA, radial artery; SAX, short axis; SRN, superficial radial nerve.
1 Chan VW, Perlas A, McCartney CJ, et al. Ultrasound guidance improves success rate of axillary brachial plexus block. Can J Anaesth. 2007;54:176–182.
2 MacAvoy MC, Rust SS, Green DP. Anatomy of the posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve: practical information for the surgeon operating on the lateral aspect of the elbow. J Hand Surg (Am). 2006;31:908–911.
3 Auerbach DM, Collins ED, Kunkle KL, et al. The radial sensory nerve. An anatomic study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;308:241–249.
4 Ikiz ZA, Ucerler H. Anatomic characteristics and clinical importance of the superficial branch of the radial nerve. Surg Radiol Anat. 2004;26:453–458.
5 Visser LH. High-resolution sonography of the superficial radial nerve with two case reports. Muscle Nerve. 2009;39(3):392–395.