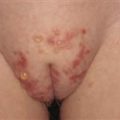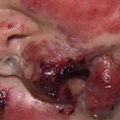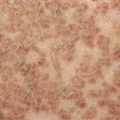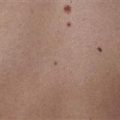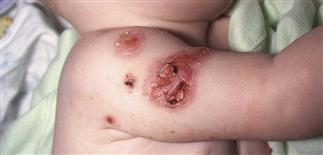
Multiple ulcerated lesions following attempted surgical debridement of pyoderma gangrenosum lesion (pathergy).
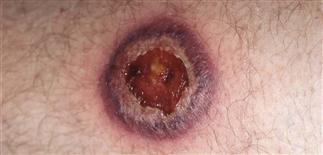
Pyoderma gangrenosum. Ulceration with characteristic loosely attached epidermis and purple border.
CLINICAL FEATURES
Pyoderma gangrenosum begins as a 3−8-mm red papule that progresses within hours to a pustule, then ulcerates with a surrounding loosely attached epidermis and an outer lilac colored border. The ulcer relentlessly enlarges to 2 cm or more.
Skin lesions appear at sites of trauma (pathergy). Sheets of activated neutrophils undermine the skin.
Surgical debridement results in expansion of lesions because of pathergy.
TREATMENT
Long-term (years) immunosuppressive therapy is required and adjunctive therapy such as dapsone or colchine or topical tacrolimus may help maintain improvement.