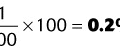CHAPTER 16 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING
PRETEST QUESTIONS
1. What is the minimum percent increase in inspiratory flow following a before-and-after bronchodilator study that indicates significant improvement?
2. In which of the following lung conditions would the FRC be increased?
3. Which of the following pulmonary function tests would best determine the patient’s ability to cough?
4. To evaluate the distribution of ventilation to perfusion with a V/Q scan, instruct the patient to inhale which of the following substances?
5. Following are the results of a patient’s spirometry test before and after bronchodilator therapy.
| Before | After | |
|---|---|---|
| FEV1 | 32% of predicted | 53% of predicted |
| FVC | 38% of predicted | 66% of predicted |
| FEV1/FVC | 50% | 64% |
Which of the following is the correct interpretation of these results?
REVIEW
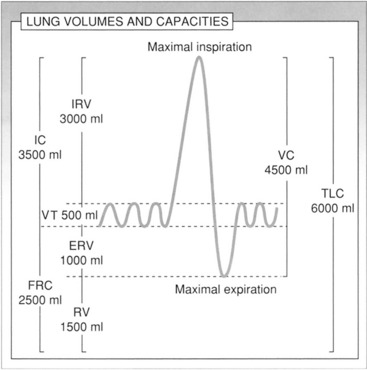
I. LUNG VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IA4, IA7b-c, IB9d-e,m,s, IB10d-e,s, IC5, IIC4, IIIE7a-f
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IA4, IA7b-c, IB9d-e,m,t, IB10d-e,u, IC6, IIC4, IIIE7a-f
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IA4, IA7b-c, IB9d-e,m,s, IB10d-e,s, IC5, IIC4, IIIE7a-f
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IA4, IA7b-c, IB9d-e,m,t, IB10d-e,u, IC6, IIC4, IIIE7a-f
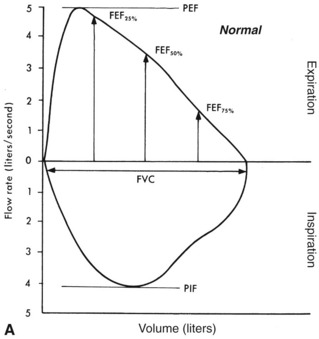
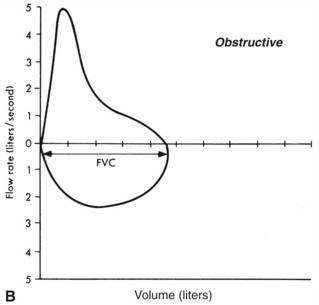
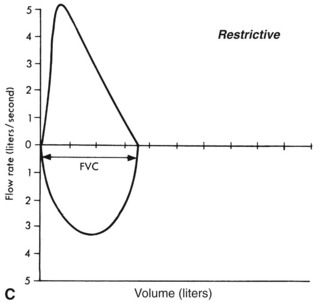
FIGURE 16-2 Comparison of flow volume loops.
From Scanlan C, Spearman C, Sheldon R, Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 5, St Louis, 1990, Mosby, and Wilkins RL, Stoller JK, Kacmarek R, Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 9, St Louis, 2009, Mosby.
III. OBSTRUCTIVE VERSUS RESTRICTIVE LUNG DISEASES
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IA4, IA7b-c, IB9d-e,m,s, IB10d-e,s, IC5, IIC4, IIIE7a-f
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IA4, IA7b-c, IB9d-e,m,t, IB10d-e,u, IC6, IIC4, IIIE7a-f
IV. MISCELLANEOUS PULMONARY FUNCTION STUDIES
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IA4, IB9d-e,m,s, IB10d-e,m,s, IC5, IIIE7a,f
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IA4, IB9d-e,m,t, IB10d-e,m,u, IC6, IIIE7a-f
V. INTERPRETATION OF CHART SUMMARY
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IA4, IB9s, IB10s, IIIE7a-c
RRT Exam Content Matrix: IA4, IB9t, IB10u, IIIE7a-c
| Disease | ||
|---|---|---|
| Function | Obstructive | Restrictive |
| FVC | Decreased | Decreased |
| IC | Decreased or normal | Decreased |
| ERV | Decreased or normal | Decreased |
| VT | Increased | Decreased or normal |
| FRC | Increased | Decreased |
| RV | Increased | Decreased |
| RV/TLC | Increased | Normal |
| FEV1 | Decreased | Normal or decreased |
| FEF200–1200 | Decreased | Normal |
| FEF25%–75% | Decreased | Normal |
| FEV/FVC | Decreased | Normal |
| MVV | Decreased | Decreased |
CRT Exam Content Matrix: IIA16,23
 .
.POSTCHAPTER STUDY QUESTIONS
1. Name a condition that results in an increased RV.
2. What type of lung condition may result in a decreased IC?
3. What device may be used at the patient’s bedside to measure VC?
4. What pulmonary function test is the best indicator for distinguishing an obstructive lung disorder from a restrictive one?
5. List three tests that aid in determining the severity of obstructive airway disease.
6. An FEV1/FVC of less than 75% indicates which type of lung disease?
7. What five values may be measured on a flow volume loop?
8. List five conditions in which DL is decreased.
9. What does a before-and-after bronchodilator test determine?
Hess D, Respiratory care principles and practice, and others, Philadelphia, Saunders, 2002.
Scanlan C, Spearman C, Sheldon R. Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 5. St Louis: Mosby; 1990.
Ruppell G. Manual of pulmonary function testing, ed 9. St Louis: Mosby; 2009.
Wilkins RL, Stoller JK, Kacmarek R. Egan’s fundamentals of respiratory care, ed 9. St Louis: Mosby; 2009.

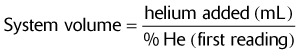
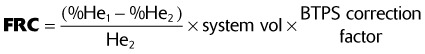



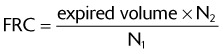
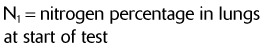
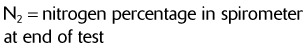
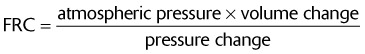
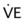 )
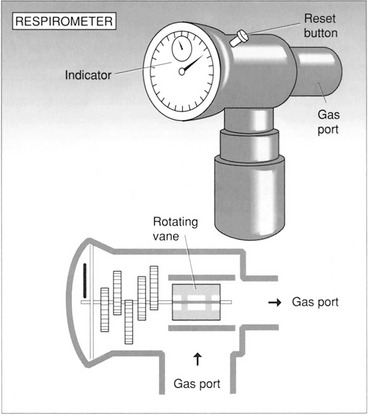
)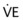 at the bedside, use a respirometer with a mouthpiece. Instruct the patient to breathe normally through the mouthpiece as you time the breathing for 1 min. The reading on the respirometer after 1 min is the
at the bedside, use a respirometer with a mouthpiece. Instruct the patient to breathe normally through the mouthpiece as you time the breathing for 1 min. The reading on the respirometer after 1 min is the 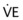 .
.