Proteins and enzymes
Plasma proteins
Albumin
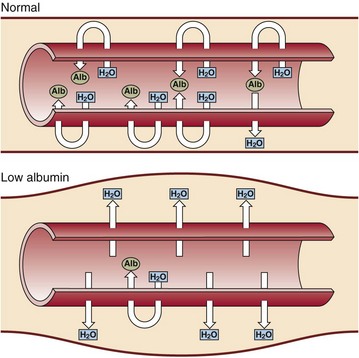
Albumin is the major plasma protein and is synthesized and secreted by the liver. It has a biological half-life in plasma of about 20 days and it accounts for about 50% of the total hepatic protein production. Albumin makes the biggest contribution to the plasma oncotic pressure. If the albumin concentration falls very low, oedema is the result (Fig 25.1). There are four main reasons for the occurrence of a low plasma albumin concentration:
 Abnormal distribution. Albumin can move into the interstitial space as a result of increased capillary permeability in the acute phase response.
Abnormal distribution. Albumin can move into the interstitial space as a result of increased capillary permeability in the acute phase response.
 Decreased synthesis. Due to malnutrition, malabsorption or advanced chronic liver disease.
Decreased synthesis. Due to malnutrition, malabsorption or advanced chronic liver disease.
 Dilution. Hypoalbuminaemia can be induced by overhydration.
Dilution. Hypoalbuminaemia can be induced by overhydration.
 Abnormal excretion or degradation. The causes include the nephrotic syndrome, protein-losing enteropathies, burns, haemorrhage and catabolic states.
Abnormal excretion or degradation. The causes include the nephrotic syndrome, protein-losing enteropathies, burns, haemorrhage and catabolic states.
Specific proteins
Measurement of a number of specific proteins gives useful information in the diagnosis and management of disease (Table 25.1). Characteristic changes in the concentration of certain plasma proteins are seen following surgery or trauma, or during infection or tumour growth. The proteins involved are called acute phase reactants (pp. 110–111). These acute phase proteins may be used to monitor progress of the condition or its treatment.
Table 25.1
Specific proteins that are measured in serum
| Protein name | Function | Reason for assay |
| α1-antitrypsin | Protease inhibitor | Reduced in α1-antitrypsin deficiency |
| β2-microglobulin | A subunit of the HLA antigen | Raised in renal tubular dysfunction on all cell membranes |
| Caeruloplasmin | Oxidizing enzyme | Reduced in Wilson’s disease |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) | Involved in immune response | Increased in acute illness, especially infection |
| Ferritin | Binds iron in tissues | Gives an indication of body iron stores |
| Haptoglobin | Binds haemoglobin | Reduced in haemolytic conditions |
| Thyroid-binding globulin (TBG) | Thyroid hormone binding | Investigation of thyroid disease |
| Sex hormone binding globulin | Binds testosterone and oestradiol | Investigation of androgen excess and/or insulin resistance |
| Transferrin | Iron transport | Assessment of iron status and/or response to nutritional support |
Enzymes
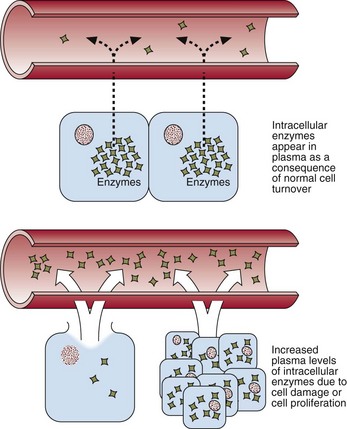
Enzymes may be classified in two groups. Some, such as the enzymes of the coagulation cascade, have a defined function in blood. Others appear in the blood incidentally and their measurement is of value in diagnosis. Damage to the tissues of origin, or proliferation of the cells from which these enzymes arise, will lead to an increase in the activity of these enzymes in plasma (Fig 25.2). It should be noted that increases in serum enzyme activity are only roughly proportional to the extent of tissue damage.
Enzymes that have been shown to have a diagnostic value are:
 Alanine aminotransferase (ALT): an indicator of hepatocellular damage.
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT): an indicator of hepatocellular damage.
 Alkaline phosphatase: increases in cholestatic liver disease and a marker of osteoblast activity in bone disease.
Alkaline phosphatase: increases in cholestatic liver disease and a marker of osteoblast activity in bone disease.
 Amylase: an indicator of cell damage in acute pancreatitis.
Amylase: an indicator of cell damage in acute pancreatitis.
 Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): an indicator of hepatocellular damage, or a marker of muscle damage.
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): an indicator of hepatocellular damage, or a marker of muscle damage.
 Creatine kinase: a marker of muscle damage and acute MI.
Creatine kinase: a marker of muscle damage and acute MI.
 γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase: a sensitive but non-specific marker of liver disease.
γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase: a sensitive but non-specific marker of liver disease.