Chapter 33 Protective Devices
1 Webster’s third new international dictionary. Springfield (MA: Merriam-Webster, 1981.
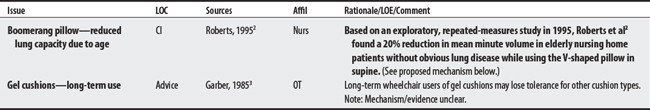
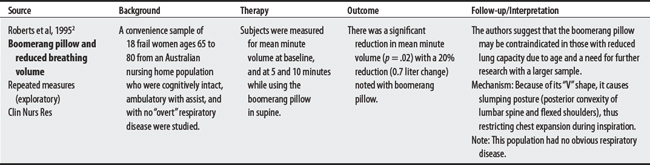
2 Roberts KL, Brittin M, deClifford J. Boomerang pillows and respiratory capacity in frail elderly women. Clin Nurs Res. 1995;4(4):465-471.
3 Garber SL. Wheelchair cushions: a historical review. Am J Occup Ther. 1985;39(7):453-459.
33.2 Restraints
OVERVIEW.
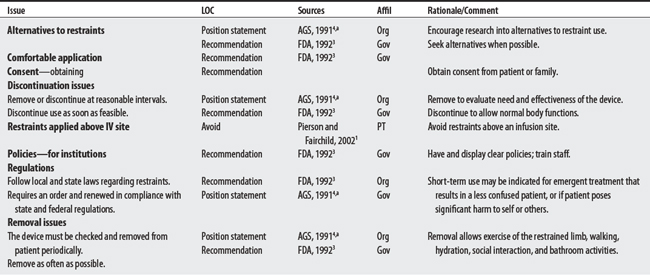
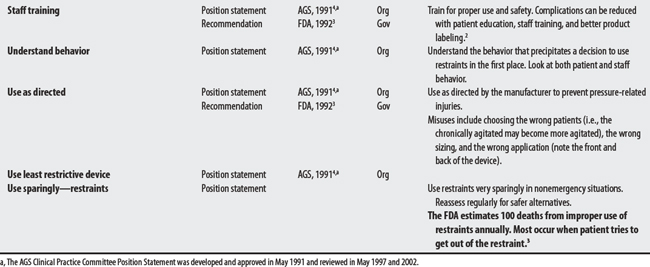
A restraint is a device used to help immobilize a patient. A physical restraint is a manual, physical, or mechanical device that the patient cannot easily remove and that restricts freedom to move. Drug restraints are nonstandard medication treatments, used to control patient behavior and restrict freedom of movement.1 The purpose/rationale of using restraints has been to reduce fall-related injuries from chairs, beds, and during ambulation, to reduce wandering-related injuries, and to implement invasive medical care such as IV lines. Despite these reasons, physical restraint use has led to instances of strangulation, chest compression asphyxiation, escape-related trauma, and skin and nerve injuries.2
SUMMARY: CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS.
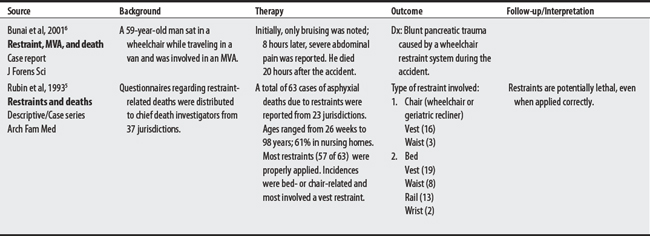
Patient injuries and fatalities are major concerns with restraint use. Recommendations and Position Statements for restraint use on patients are listed from the Food and Drug Administration3 and American Geriatric Society,4 respectively. Thirteen issues are listed; six (about 45%) are shared concerns. Issues include (1) use of alternatives, (2) discontinuation, (3) regulation, (4) removal, (5) staff training, and (6) proper use. Rubin et al,5 in a 1993 descriptive study (case series), noted that restraints used in chairs, wheelchairs, and beds can be lethal, even if applied correctly.
1 Pierson FM, Fairchild SL. Principles and techniques of patient care, ed 3. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2002.
2 Miles SH, Meyers R. Untying the elderly: 1989 to 1993 update. Clin Geriatr Med. 1994;10(3):513-525.
3 Food and Drug Administration. Safe use of physical restraint devices. Rockville (MD): FDA Backgrounder, 1992.
4 American Geriatric Society. Position statement. Restraint use. Available at: http://www.americangeriatrics.org/products/positionpapers/restraintsupdatePF.shtml. Accessed November 9, 2005
5 Rubin BS, Dube AH, Mitchell EK. Asphyxial deaths due to physical restraint. A case series. Arch Fam Med. 1993;2(4):405-408.
6 Bunai Y, Nagai A, Nakamura I, et al. Blunt pancreatic trauma by a wheelchair user restraint system during a traffic accident. J Forens Sci. 2001;46(4):965-967.