18 Prostate Diseases
Basic Anatomy
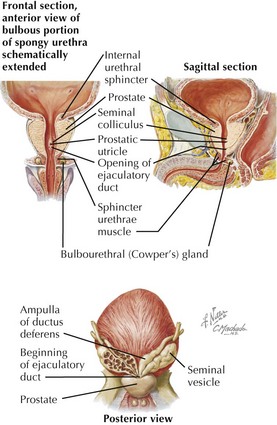
Prostate Proper
• Glandular growth and maturation controlled by testosterone, which is converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by 5-alpha reductase
• Middle lobe: most common site of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), process arising in the periurethral transitional zone
• Anatomical parts: base, apex, four surfaces
• Supported anteriorly by puboprostatic ligaments, central portions of the pubococcygeus, part of the levator ani muscles (anterior pelvic diaphragm)
Prostatic Capsule(s)
• Prostatic (true) capsule: thin, dense, fibrous connective tissue enclosing parenchyma and surrounded by—
Prostatic Ducts and Urethra
• Seminal colliculus (verumontanum) in posterior urethral wall marks location of paired ejaculatory ducts draining ductus deferens and seminal vesicles.
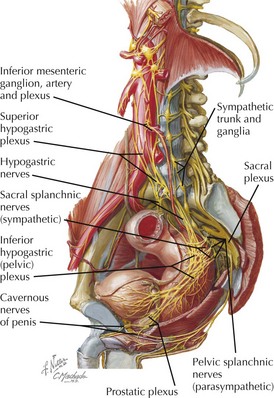
Prostatic Innervation
• Bilateral nerves of the prostate come from sacral (inferior hypogastric) nerve plexus lying between sacrum and rectum.
• Fibers to and from the prostate travel in posterolateral neurovascular bundles with nervi erigentes (responsible for erection-related functions) and prostatic arteries.
• Pelvic parasympathetic efferents travel in pelvic splanchnic fibers (S2-S4, nervi erigentes) through pelvic plexus.
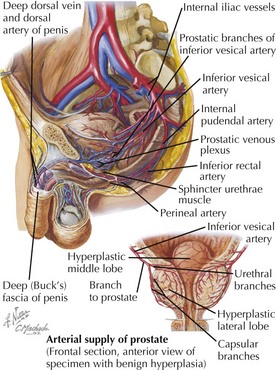
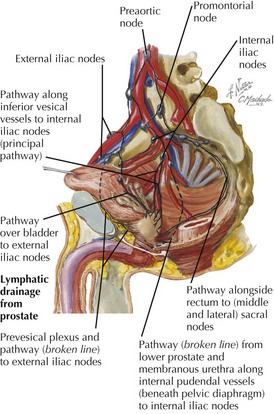
Vessels and Lymphatics
Arterial Supply
Clinical Correlates
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
• PSA increases seen in prostatitis, BPH, prostatic carcinoma, chronic catheterization (nonspecific)
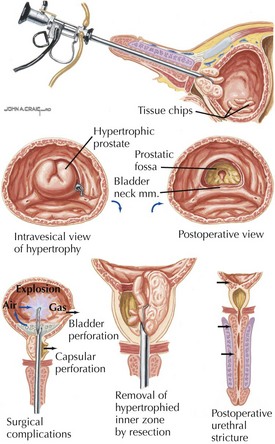
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Diagnosis
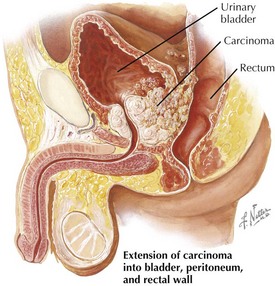
Carcinoma of the Prostate
• Most common male solid organ cancer in the U.S., currently the second most common cause of cancer mortality, with adenocarcinoma the most common type
• Most common site of distal metastasis: bone, with osteoblastic lesions showing increased density on CT and radiograph
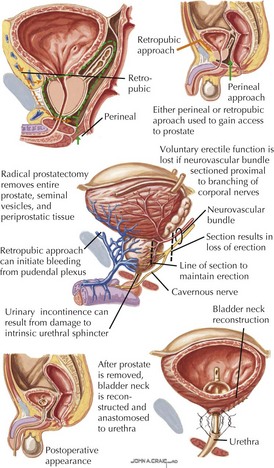
Staging and Treatment
• Gleason scoring system: additional scoring (1-5) from well-differentiated (least aggressive) to poorly differentiated (most aggressive)
• Transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS) can provide an accurate image of the gland and guide needle biopsies.
• Intracapsular tumors, no metastases (on T1 and T2 MRI): irradiation, radical prostatectomy with pelvic lymph node excision, or no treatment depending on age, specifics
• Extracapsular tumors with metastases