Chapter 37 Principles of Cancer Therapy
 Cellular Biology
Cellular Biology
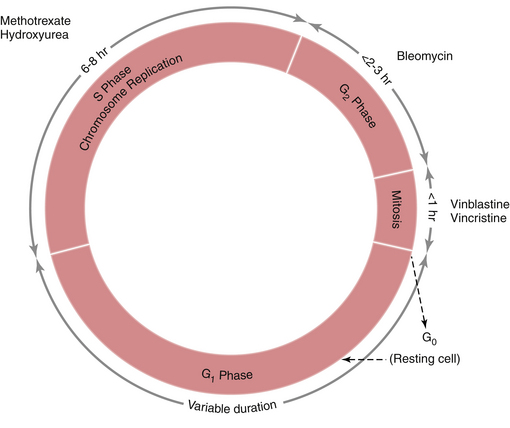
Interphase is subdivided into three separate phases (Figure 37-1). Immediately following mitosis is the G1 phase, which is of variable duration and is characterized by a diploid content of DNA. DNA synthesis is absent, but RNA and protein synthesis occur. During the shorter S phase, the entire DNA content is duplicated. This is followed by the G2 phase, which is characterized by a tetraploid DNA content and by continuing RNA and protein synthesis in preparation for cell division. When mitosis occurs, a duplicate set of chromosomal DNA is inherited by each daughter cell, thus restoring the diploid DNA content. Following mitosis, some cells leave the cycle temporarily or permanently and enter the G0 or resting phase.
 Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
CLASSIFICATION OF CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENTS
CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENTS
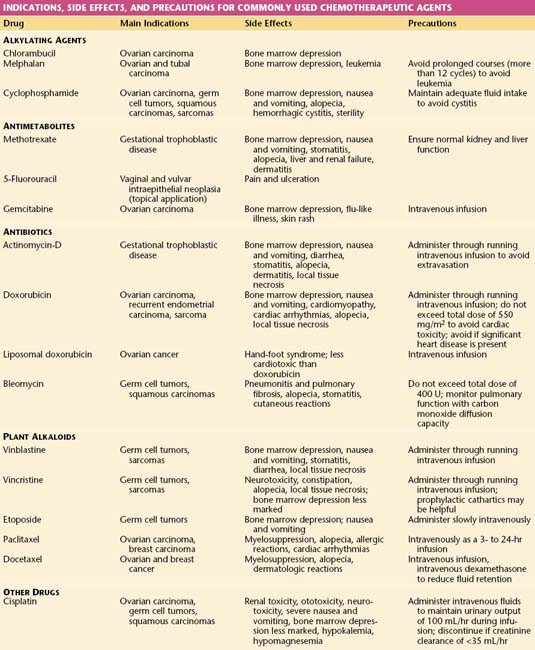
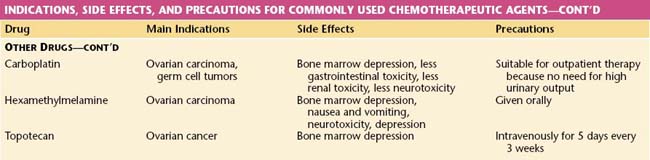
The common agents used in the management of gynecologic malignancies may be classified as shown in Table 37-1. This table also contains a summary of the main indications for and side effects of these drugs.
 Radiation Therapy
Radiation Therapy
Radiation may be defined as the propagation of energy through space or matter.
TYPES OF RADIATION
There are two main types of radiation: electromagnetic and particulate.
UNIT OF RADIATION MEASUREMENT
The Gray (Gy) is equivalent to an absorbed energy of 1 joule per kilogram of absorbing material.
BIOLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS
Time-Dose Fractionation of Radiation
When treating the pelvis with external radiation, each fraction is usually 180 to 200 cGy. In treating the whole abdomen, fractions are decreased to 100 to 120 cGy because the tolerance of normal tissues decreases as the volume irradiated increases. The major factors influencing the outcome of radiation therapy are summarized in Box 37-1.
MODALITIES OF RADIATION THERAPY
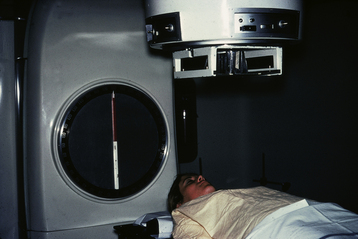
The modalities used to deliver radiation therapy are listed in Box 37-2. In general, there are two radiation techniques: teletherapy and brachytherapy. In teletherapy, a device quite removed from the patient is used, as with external-beam techniques. Figure 37-2 is a linear accelerator used to deliver external-beam pelvic radiation. In brachytherapy, the radiation source is placed either within or close to the target tissue, as with intracavitary and interstitial techniques. In contrast to external-beam therapy, intracavitary and interstitial techniques allow a high dose of radiation to be delivered to the tumor, whereas dosages to surrounding normal tissues are considerably lower and are determined by the inverse square law.
Teletherapy
EXTERNAL-BEAM THERAPY
Orthovoltage machines are no longer used except to treat skin cancers. Cobalt machines, developed in the early 1950s, have also been largely replaced by linear accelerators, which have a higher range of energies. The advantages of megavoltage therapy over the earlier orthovoltage machines are listed in Box 37-3.
Brachytherapy
INTRACAVITARY RADIATION
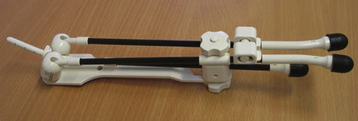
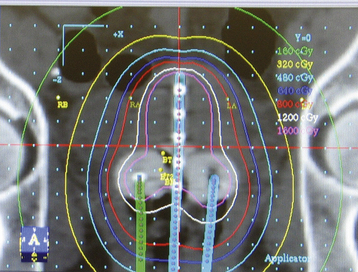
Intracavitary therapy is used particularly in the treatment of cervical and vaginal cancer. All applicators now in use should be afterloaded, which means that they are placed in the patient and their position checked by radiography before the radioactive substance is loaded into the applicator. Traditionally, brachytherapy has been given at a low dose rate using radioactive substances such as cesium-137 (137Cs). Applicators for the management of cervical cancer are placed under general anesthesia. For low–dose-rate therapy, the applicators are left in situ for 48 to 72 hours. Remote afterloading devices, such as the Selectron, allow the radioactive sources to be removed from the applicators when medical or nursing personnel enter the room, thereby significantly limiting staff exposure to radiation. More recently, high–dose-rate brachytherapy has been given, using radioactive sources such as iridium (192Ir) (Figures 37-3 and 37-4). Treatment is given as an outpatient, which is much more acceptable for patients.
COMPLICATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH RADIATION
Radiation Enteropathy
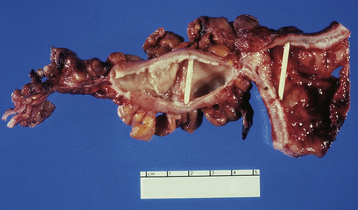
Large bowel injuries, which are best diagnosed by sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, may include proctosigmoiditis, manifested by pelvic pain, tenesmus, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding; ulceration, manifested by rectal bleeding and tenesmus; rectal or sigmoid stenosis, manifested by progressive large bowel obstruction; and rectovaginal fistula, manifested by passage of stool through the vagina. Figure 37-5 shows a radiation-induced stricture of the sigmoid colon.
Eifel P.J. Radiation therapy. In: Berek J.S., Hacker N.F., editors. Practical Gynecologic Oncology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005:119-162.
Hortobagyi G.N., Theriault R.L., Lipton A., et al. Long-term prevention of skeletal complications of metastatic breast cancer with pamidronate. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:2038-2044.
Lickiss J.N., Philip J.A.M. Palliative care and pain management. In: Berek J.S., Hacker N.F., editors. Practical Gynecologic Oncology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005:835-862.
Markman M. Chemotherapy. In: Berek J.S., Hacker N.F., editors. Practical Gynecologic Oncology. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005:89-118.
Singer P.A., Martin D.K., Kelner M. Quality end-of-life care: Patient’s perspectives. JAMA. 1999;281:163-168.

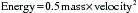
 Hormonal Therapy
Hormonal Therapy Pain Management
Pain Management End-of-Life Issues
End-of-Life Issues