22
Pregnancy Dermatoses
There are several dermatoses that occur during pregnancy or immediately postpartum, in particular polymorphic eruption of pregnancy, pemphigoid gestationis, and atopic eruption of pregnancy. Pruritus due to intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy leads to nonspecific skin lesions, including excoriations due to scratching. Impetigo herpetiformis simply represents pustular psoriasis occurring during pregnancy, and this may be related to the relative hypocalcemia of pregnancy. Lastly, there are physiologic changes that occur during pregnancy.
Polymorphic Eruption of Pregnancy (PEP; Pruritic Urticarial Papules and Plaques of Pregnancy [PUPPP])
• Pruritic edematous papules and plaques, whose color varies from pink to red-brown depending on skin phototype, that often involve the abdominal striae but spare the umbilicus (Fig. 22.1); polymorphic presentation includes patches of erythema, targetoid lesions, tiny vesicles, and eczematous plaques (Fig. 22.2).
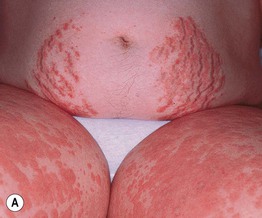
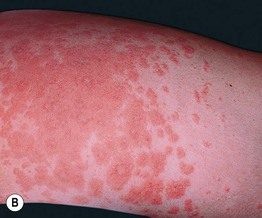
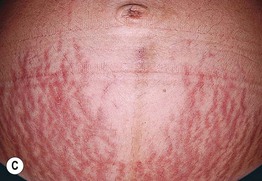
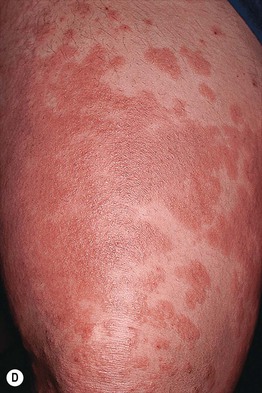
Fig. 22.1 Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy. The edematous urticarial lesions favor the striae (A, C) and the upper thighs (B, D) and spare the umbilicus. Note the pink color in a woman with skin phototype II versus the red-brown color in a more darkly pigmented patient.
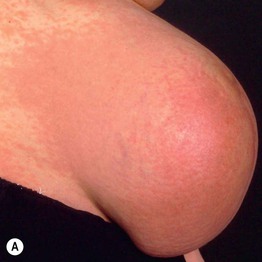
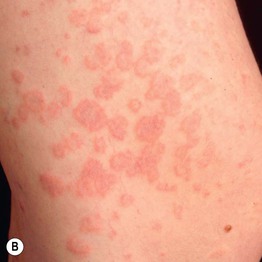
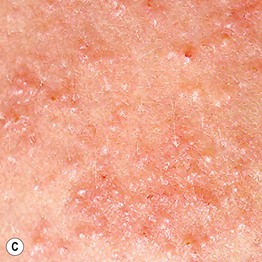
Fig. 22.2 Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy. The clinical spectrum includes: (A) macular erythema, which can be widespread; (B) targetoid lesions; and (C) tiny vesicles due to marked epidermal spongiosis or dermal edema. Courtesy, Christina M. Ambros-Rudolph, MD.
• Rx: topical CS and oral antihistamines usually suffice (see Appendix); occasionally, severe cases require oral CS (prednisolone preferred during pregnancy because of significant inactivation by placenta, leading to a mother : fetus ratio of 10 : 1).
Pemphigoid Gestationis (PG; Gestational Pemphigoid)
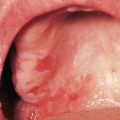
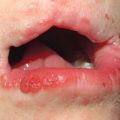
• Unusual pruritic vesiculobullous disorder with significant clinical and histologic overlap with bullous pemphigoid (see Chapter 24).
• Lesions often begin on the abdomen, including around and within the umbilicus, but then become more widespread on the trunk as well as the extremities; in addition to vesicles and bullae, edematous urticarial plaques are seen (Fig. 22.3).
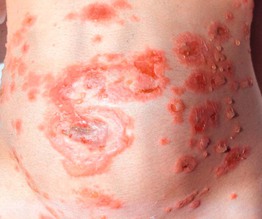
Fig. 22.3 Pemphigoid gestationis. Intact tense bullae arising within areas of edematous erythema as well as erosions due to ruptured bullae. Lesions typically involve the umbilical region. Courtesy, Christina M. Ambros-Rudolph, MD.
• DIF of perilesional skin shows linear deposits of C3 at the BMZ.
• Increased risk of small-for-gestational age and premature neonates and ~10% of newborns have mild skin involvement; often flares at the time of delivery and recurs during subsequent pregnancies.
• DDx: primarily PEP (but in PEP, patients are usually primiparous, large bullae are rare unless there is marked background edema, lesions spare the umbilicus, and DIF of perilesional skin is negative) (Fig. 22.4); urticarial drug eruption, allergic contact dermatitis.
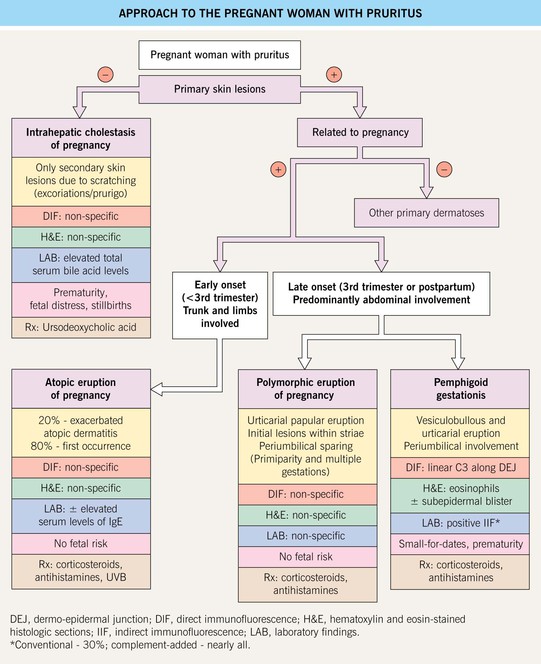
Fig. 22.4 Approach to the pregnant woman with pruritus. Patients with refractory pemphigoid gestationis may benefit from plasmapheresis during pregnancy. Prednisolone is the systemic CS of choice for dermatologic indications during pregnancy as it is largely inactivated in the placenta (mother:fetus ratio = 10 : 1); if use of systemic CS or potent topical CS is long-term during pregnancy, then fetal growth should monitored. During the first trimester, the classic sedating anti-histamines (e.g. chlorpheniramine, clemastine) are preferred and during the second and third trimesters, if a non-sedating agent is requested, loratidine and cetirizine are considered safe. Courtesy, Christina M. Ambros-Rudolph, MD.
• Rx: potent topical or oral CS (prednisolone 0.5 mg/kg/day; see Appendix), depending on severity.
Atopic Eruption of Pregnancy
• Pruritic papules and eczematous plaques that usually develop earlier during pregnancy than other disorders described in this chapter (Fig. 22.5).
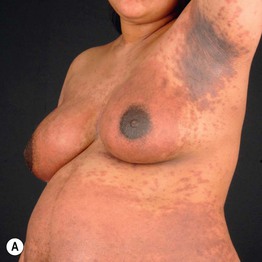
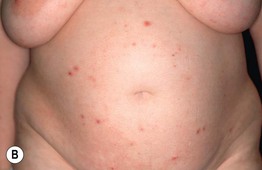
Fig. 22.5 Atopic eruption of pregnancy. A Eczematous lesions involving flexural areas as well as the abdomen and breasts. B Excoriated papules (prurigo lesions) that favored the abdomen and extremities. The former presentation is seen in approximately two-thirds of patients, whereas the latter is seen in approximately one-third. Courtesy, Christina M. Ambros-Rudolph, MD.
• Patients have an atopic diathesis, but the eruption is more likely to have its initial presentation during pregnancy and less often it represents a flare of pre-existing atopic dermatitis.
• May be explained by the predominance of a Th2 immune response during pregnancy.
• No maternal or fetal risks, but recurrence during subsequent pregnancies common.
• Rx: topical CS, oral antihistamines, and other routine therapies for atopic dermatitis (e.g. emollients; oral antibiotics such as cephalexin if secondary bacterial infection; see Chapter 10); NBUVB phototherapy or oral CS for more severe cases.
Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy
• Cholestasis leads to elevated serum levels of bile acids and this leads to intense pruritus.
• Cutaneous lesions are nonspecific and vary from excoriations to prurigo nodularis (Fig. 22.6); jaundice occurs in a small minority of patients.
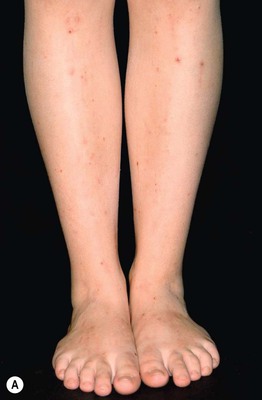
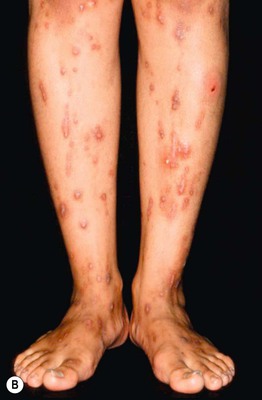
Fig. 22.6 Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Marked pruritus leads to secondary skin lesions that vary based on disease duration, from subtle linear excoriations and prurigo simplex early on (A) to pronounced prurigo nodularis when the pruritus is longstanding (B). From Ambros-Rudolph CM, Glatz M, Trauner M, Kerl H, Müllegger RR. The importance of serum bile acid level analysis and treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: A case series from central Europe. Arch. Dermatol. 2007;143:757–762. © (2006) American Medical Association. All rights reserved.
• DDx: other causes of cholestasis (e.g. primary biliary cirrhosis) and hepatitis (e.g. hepatitis B, hepatitis C), especially if pruritus does not resolve within days of delivery; scabies, atopic eruption of pregnancy other causes of primary pruritus (see Fig. 4.1).
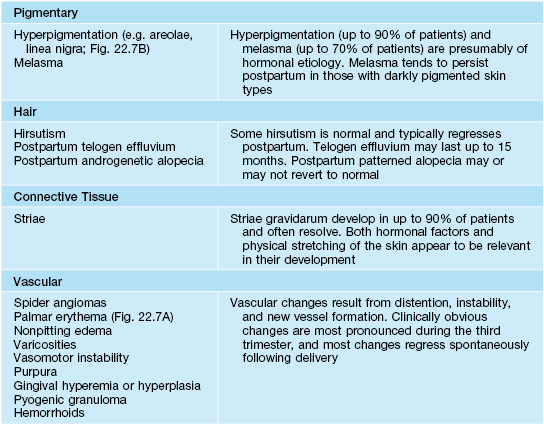
Physiological Changes During Pregnancy
These are outlined in Table 22.1.
Table 22.1
Physiologic changes during pregnancy.
Nail changes are nonspecific and include subungual hyperkeratosis, distal onycholysis, transverse grooving, and brittleness.
Adapted from Kroumpouzos G, Cohen LM. Dermatoses of pregnancy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001;45:1–19.
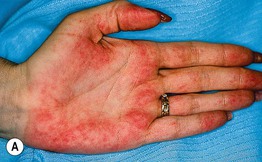
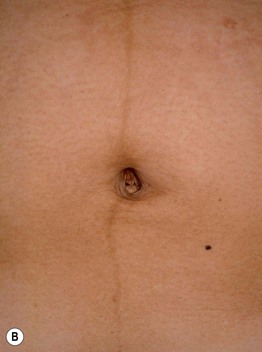
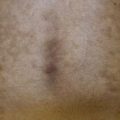
Fig. 22.7 Physiologic changes during pregnancy. Palmar erythema of pregnancy (A) and linea nigra (B). B, Courtesy, Jean L. Bolognia, MD.
For further information see Ch. 27. From Dermatology, Third Edition.