17 Pregnancy, birth and the newborn
Introduction
The healthy pregnancy
See Table 17.1 for advice that can be given to women planning pregnancy.
| Advice | Reasoning |
|---|---|
| Folic acid prior to conception | Prevention of neural tube defects |
| Avoid excess alcohol | Prevention of fetal alcohol syndrome |
| Improves maternal health | |
| Stop or decrease smoking | Reduces the risk of premature birth, intrauterine growth retardation (see Chapter 12, p. 147) and respiratory disease in childhood |
| Avoid unpasteurized dairy products | Reduce risk of congenital Listeria |
| Avoid handling cat litter | Reduces risk of toxoplasmosis |
| Rubella immunization if not immune | Avoidance of congenital rubella (see Chapter 16, p. 235) |
Antenatal screening
Pregnant women are screened for a range of maternal and fetal problems:
• Dating scan at ‘booking’ to confirm gestation
• Blood group and antibody screen for potential haemolytic disorders, e.g. rhesus incompatibility (see Chapter 7, p. 60)
• Hepatitis B, syphilis and HIV serology
• Alpha-fetoprotein for neural tube defects
• Triple test for Down syndrome (alpha-fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotrophin, unconjugated oestriol) at 16 weeks’ gestation. Ultrasound scanning to detect increased nuchal translucency (11–14 weeks’ gestation) is being progressively introduced throughout the UK as a more sensitive test for detection of increased risk of Down syndrome and other congenital disorders
• Fetal anomaly scan at 18–20 weeks’ gestation (see Box 17.1).
Box 17.1
Range of abnormalities detectable on fetal anomaly scan
• Neural tube defects (spina bifida, anencephaly, hydrocephalus)
• Cardiovascular (approximately 60%)
• Chest (diaphragmatic hernia)
• Gastrointestinal (cleft lip/palate, see below), duodenal/ileal atresia, exomphalos/gastroschisis, see pp. 259–260)
• Genitourinary (hydronephrosis, renal dysplasia, see Chapter 11, p. 120)
• Skeletal (achondroplasia and other skeletal dysplasias)
• Hydrops fetalis (skin oedema, pleural effusions, ascites)
• Chromosomal (suspicions may be raised by the pattern of anomaly seen)
• Maternal diabetes and other disorders
• Previous child with a genetic abnormality
• Family history of an inherited disorder
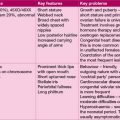
Table 17.2 Medication with recognized teratogenic effects on the fetus
| Maternal medication | Teratogenic effect on fetus |
|---|---|
| Carbamazepine | Neural tube defects |
| Lithium | Congenital heart disease |
| Phenytoin | Fetal hydantoin syndrome |
| Propylthiouracil | Hypothyroidism |
| Tetracycline | Enamel hypoplasia of the teeth |
| Valproate | Neural tube defects valproate embryopathy |
| Warfarin | Microcephaly, nasal hypoplasia |
Birth
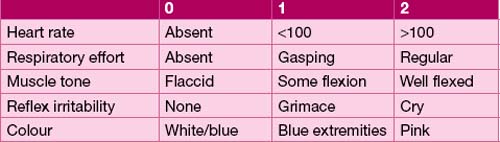
The Apgar score
The Apgar score (named after Virginia Apgar) is calculated at 1 and 5 minutes of life. It gives an indication of the condition of the baby at this time and provides a standard way of documenting the health of the baby in the first few minutes of life. Many parents know about this score. It is sometimes necessary to reassure worried parents that a score of less than 10 at 1 or 5 minutes is not an indicator for a lifetime of under-achievement! (see Table 17.3).
Adaptation to extra-uterine life
The process of delivery, temperature change and the clamping of the umbilical cord results in gasping and the removal of the remaining lung fluid. The pulmonary vascular resistance falls and pulmonary blood flow increases. The increased left atrial filling closes the foramen ovale and oxygenated blood flowing through the ductus arteriosus causes its eventual closure (see also Chapter 9, pp. 91–93).
The newborn
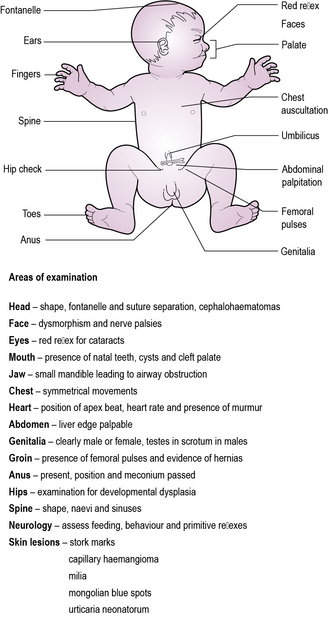
Examination of the newborn
The objectives of the examination are to identify any congenital anomaly not identified by antenatal screening. The most important of these are structural heart lesions (see Chapter 9, pp. 91–95), congenital cataracts and other eye disease detectable through absence of the ‘red reflex’ (see Chapter 14, p. 210), and developmental dysplasia of the hip (see Chapter 6, p. 49) (see Figure 17.1).
The ill neonate
Neonatal encephalopathy
Aetiology
Before birth:
• Inadequate oxygenation of maternal blood (anaesthesia, cyanotic heart disease, respiratory failure)
• Low maternal blood pressure (spinal anaesthesia, inferior vena cava compression)
• Inadequate contraction of the uterus (oxytocin)
• Premature separation of the placenta
Respiratory distress
The signs of respiratory distress include:
Management is directed at identifying the cause and providing appropriate supportive and other treatment. Causes are detailed in Table 17.4.
| Pulmonary | Transient tachypnoea of the newborn Pneumothorax Pneumonia Meconium aspiration Persistent pulmonary hypertension |
| Non-pulmonary | Congenital heart disease Perinatal hypoxia Severe anaemia Metabolic acidosis |
| Rare | Diaphragmatic hernia Tracheo-oesophageal fistula Respiratory distress syndrome Pulmonary hypoplasia |
Jaundice
Most newborn infants become jaundiced. Reasons for this include:
• Increased rate of turnover of red blood cells (red cell lifespan is 70 days in babies compared with 120 days older children and in adults)
• More bilirubin produced due to increased red cell turnover
• Immaturity of the liver, leading to reduced ability to excrete bilirubin in bile.
Investigation of neonatal jaundice
Neonatal jaundice may be a sign of excessive haemolysis (see Chapter 7, p. 60), infection or a metabolic disorder. Conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia suggests serious liver disease (see Chapter 13, p. 175) (see Table 17.5).
| Timing of onset | Cause |
|---|---|
| <24 hours of age | Rhesus incompatability ABO incompatability Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency Spherocytosis Congenital infection |
| 24 hours to 2 weeks | Physiological Breast milk jaundice Infection (e.g. urinary tract infection) Haemolysis (haemolysis/G6PD deficiency) Bruising Polycythaemia |
| >2 weeks | Physiological Breast milk jaundice Hypothyroidism Haemolysis Neonatal hepatitis Biliary atresia |
Harmful jaundice
High levels of unconjugated bilirubin are potentially harmful as unconjugated bilirubin is neurotoxic at high concentrations as it can cross the blood–brain barrier. The cells of the basal ganglia are particularly sensitive. The neurotoxicity manifests as bilirubin encephalopathy or kernicterus, with initial lethargy and poor feeding progressing to irritability, increased muscle tone, rigidity and seizures. Kernicterus has a high fatality rate. Infants who survive often have permanent neurological damage in the form of choreoathetoid cerebral palsy and deafness (see Chapter 14, p. 200).
Hypoglycaemia
Symptoms of hypoglycaemia include:
Blood sugars should be checked in all babies who exhibit these symptoms.
Congenital infection
Important congenital infections include:
• Group B Streptococcus infection (see below) – pneumonia, meningitis, septicaemia
• ToRCH – Toxoplasmosis, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus (CMV) and Herpes simplex virus (HSV). Toxoplasmosis is associated with macrocephaly/hydrocephalus and developmental delay, rubella infection in the first trimester with congenital rubella syndrome, CMV with microcephaly and developmental delay, and HSV with disseminated herpes infection in the newborn period
• Varicella zoster – varicella infection in late pregnancy exposes the newborn infant to a severe disseminated infection
• Parvovirus B19 (hydrops) – fetal anaemia results in high-output heart failure with hydrops fetalis – severe oedema of the fetus, which may be fatal
• Listeriosis – transplacentally acquired infection may present with preterm birth, commonly with meconium staining of the amniotic fluid, otherwise rare in preterm delivery, manifesting as meningitis and/or septicaemia
• Syphilis – although formerly rare in the UK, syphilis is increasing and results in stillbirth, premature delivery and congenital infection.
The preterm infant
Principal causes of mortality are respiratory disease (acute or chronic), brain injury from intraventricular haemorrhage, and infection (as in Case 17.1).
See Table 17.6 for complications of prematurity.
| General care | Temperature instability |
|---|---|
| Respiratory | Respiratory distress syndrome Chronic lung disease of prematurity |
| Cardiac | Hypotension Patent ductus arteriosus (see Chapter 9, p. 95) |
| Gastrointestinal | Feed intolerance Necrotizing enterocolitis Hypo- and hyperglycaemia |
| Liver | Jaundice Cholestatic obstructive jaundice (see Chapter 13, p. 175) |
| Renal | Electrolyte abnormalities Acute renal failure |
| Neurological | Periventricular haemorrhage Ischaemic brain injury |
| Vision | Retinopathy of prematurity, cortical blindness |
| Hearing | Sensorineural deafness |
| Haematological | Anaemia of prematurity Impaired leucocyte function |
| Infection | Septicaemia, meningitis Urinary tract infection Fungal and viral infections |
| Social | Parental anxiety and distress Family relationship disruption |
Respiratory distress syndrome
Respiratory distress syndrome is caused by a deficiency in surfactant and is usually associated with prematurity. Surfactant is a mixture of lipoproteins excreted by type II pneumocytes in the alveolar epithelium, lowering surface tension. Surfactant deficiency leads to a higher surface tension, alveolar collapse and inadequate gas exchange. Other causes of surfactant deficiency include sepsis, hypoxia, acidosis and hypothermia. Exogenous surfactant therapy is given to many premature infants but may also be used in term infants in certain conditions where surfactant deficiency is thought to be a contributing factor in a disease process. One major advance in the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome has been to give mothers antenatal steroids to stimulate fetal surfactant production (see Figure 17.2).
Chronic lung disease is defined as oxygen dependency (or other respiratory support) at the equivalent of 36 weeks of gestation. The likelihood of chronic lung disease is greatly increased in growth-retarded infants and those with patent ductus arteriosus (see Chapter 9, p. 95). Chronic lung disease renders the infant very susceptible to respiratory infection, particularly with respiratory syncytial virus and right heart failure (cor pulmonale). Steroids – usually dexamethasone – may improve lung function sufficiently to wean a child from respiratory support, but their use is associated with a high incidence of cerebral palsy (>30%) and does not improve long-term survival.
Periventricular haemorrhage
Haemorrhages are graded according to severity:
• Grade I – haemorrhage within the germinal layer of the ventricle
• Grade II – haemorrhage confined to the ventricle
• Grade III – distension of the ventricle by haemorrhage
• Grade IV – extension of haemorrhage into the surrounding brain.
Grade I and II haemorrhages are not associated with adverse outcomes, but grade III or IV haemorrhages, particularly if bilateral, are associated with a high risk of cerebral palsy (see Chapter 14, p. 197).
Congenital anomalies
Cleft lip and palate
These embryological abnormalities may be diagnosed antenatally. They are common, affecting 1 in 700 infants. Careful examination is necessary to exclude other abnormalities that might suggest a syndrome such as D George syndrome (see Chapter 18, p. 272) or fetal alcohol syndrome. Most concerning is Pierre Robin syndrome, in which there is cleft palate and an underdeveloped jaw, causing the tongue to obstruct the airway.
Congenital gut abnormalities
Lower gastrointestinal obstruction
Lower obstructions, including imperforate anus and Hirschsprung’s disease, may present with bile-stained vomiting, abdominal distension or failure to pass stool. Ninety-five per cent of normal infants pass stool within 24 hours of birth. Contrast studies may help determine the level of obstruction (see also Chapter 13, p. 165).
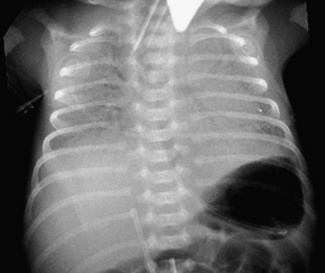
Diaphragmatic hernia
This is usually diagnosed antenatally. It is much commoner on the left. Confirmation of the diagnosis is with a chest X-ray. The presence of gut in the chest causes pulmonary hypoplasia and at birth these babies often require significant resuscitation, including ventilation. It is imperative to avoid bag-mask-valve ventilation until a nasogastric tube is sited to decompress the stomach (which is in the chest!). Repair of the defect proceeds when the baby’s condition allows. Associated severe congenital abnormalities such as Edward’s syndrome (see Chapter 18, p. 277) may make surgery inappropriate.
Neural tube defects
The incidence of neural tube defects has declined over the last 40 years. Antenatal screening (elevated alpha-fetoprotein and/or ultrasound) detects most cases during the early stages of pregnancy, allowing termination. Periconceptual folic acid reduces the risk of recurrence in subsequent pregnancies. The defects are described depending on the site in which the neural tube fails to close (see Table 17.7).
| Diagnosis | Pathology |
|---|---|
| Anencephaly | Absence of the cerebral cortex and much of the skull |
| Encephalocele | The brain protrudes through a midline skull defect |
| Meningocele | Dural and arachnoid tissue herniate through a defect created by an incomplete vertebral arch. The spinal cord remains normally sited |
| Myelomeningocele | Neural tissue from the spinal cord protrudes through the defect |
| Spina bifida occulta | Skin covers the defect. This skin may be abnormal – usually an incidental finding in an asymptomatic individual |