Chapter 29 POSTMENOPAUSAL VAGINAL BLEEDING
Postmenopausal bleeding may be defined as vaginal bleeding starting 12 months or more after the cessation of menses or unscheduled bleeding in a postmenopausal woman who has been taking hormone replacement therapy for 12 months or more. All women with postmenopausal bleeding should be evaluated for potential malignancy, including endometrial cancer, premalignant atypical endometrial hyperplasia, and cervical cancer.
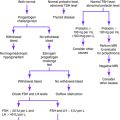
Hysteroscopy is the “gold standard” for the evaluation of postmenopausal bleeding because of the ability to perform directed biopsy. The limitations of hysteroscopy are the invasive nature of the procedure, the requirement for expensive equipment, and the risks associated with general anesthesia.
Causes of Postmenopausal Vaginal Bleeding
Suggested Work-Up
Transvaginal ultrasonography (with biopsy if the endometrial thickness is greater than 5 mm)
No universal algorithm exists for proceeding with an evaluation of a woman with postmenopausal bleeding. Tissue sampling is the most definitive diagnostic procedure, but the techniques have variable sensitivity and specificity. Further research is necessary to determine the best method for evaluating the endometrium in patients with abnormal uterine bleeding.
Additional Work-Up
| Cultures for Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia organisms | If infection is suspected or if the patient is at risk for sexually transmitted disease |
| Complete blood cell count (CBC) | If anemia is suspected |
| Liver function tests and prothrombin time measurement | If liver disease is suspected |
| CBC with platelet count, prothrombin time measurement, and partial thromboplastin time measurement | If coagulopathy is suspected |
| von Willebrand factor assay | If von Willebrand disease is suspected |
Albers JR, Hull SH, Wesley RM. Abnormal uterine bleeding. Am Fam Physician. 2004;69:1915-1926.
Chen BH, Giudice LC. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding. West J Med. 1998;169:280-284.
Davidson KG, Dubinsky TJ. Ultrasonographic evaluation of the endometrium in postmenopausal vaginal bleeding. Radiol Clin North Am. 2003;41:769-780.
Goldstein SR. Abnormal uterine bleeding: the role of ultrasound. Radiol Clin North Am. 2005;44:901-910.
Kilbourn C, Richards C. Abnormal uterine bleeding. Postgrad Med. 2001;109(1):137-140.
Lethaby A, Farquhar C, Sarkis A, et al. Hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women: endometrial hyperplasia and irregular bleeding. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (4):2003. CD000402
Schrager S. Abnormal uterine bleeding associated with hormonal contraception. Am Fam Physician. 2002;65:2073-2080.
Smith-Bindman R, Kerlikowske K, Feldstein VA. Endovaginal ultrasound to exclude endometrial cancer and other endometrial abnormalities. JAMA. 1998;280:1510-1517.
Tabor A, Watt HC, Wald NJ. Endometrial thickness as a test for endometrial cancer in women with postmenopausal vaginal bleeding. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;99:663-670.