Chapter 5 Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Definition. The definition of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) was revised in 2003 (Rotterdam Consensus criteria). The diagnosis is based on two out of three of the following criteria:
Pathophysiology
Ovaries
Hypothalamus–pituitary
Consequences of PCOS
Metabolic consequences
Assessment
Assessment is based on clinical presentation and investigations to validate the diagnostic criteria, and exclude other endocrinopathies and sequelae.
Investigations
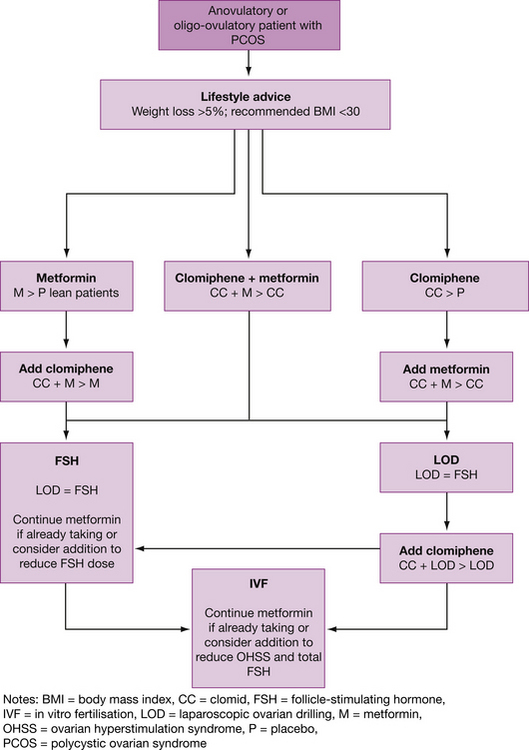
Management
Supportive
Not wanting to conceive
Insulin-sensitising drugs
Wanting to conceive
Other medical treatment
Table 5.1 Comparison of laparoscopic ovarian drilling and FSH stimulation in fertility management in patients with PCOS
| Laparoscopy | FSH | |
|---|---|---|
| Benefits | Comparable success rates One treatment affects multiple cycles Usually produces mono-ovulation No increased risk of OHSS May lower miscarriage rate No medications required No intensive monitoring required Lower cost |
Comparable success rate Non-operative |
| Problems | Surgical risks Adhesion Ovarian atrophy Long-term effect on ovarian function uncertain |
Multiple cycles required Intensive monitoring required Increased risk of multiple pregnancy Increased risk of OHSS Increased cost |
Further reading and references
Ehrmann D.A. Polycystic ovary syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine. 2005;352:1223.
Legro R.S. Type 2 diabetes and polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertility and Sterility. 2006;86(Suppl1):S16-S17.
Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-sponsored PCOS consensus workshop group. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Human Reproduction. 2004;19(1):41-47.