Chapter 39 Poisonings
EPIDEMIOLOGY
1 How many poisonings occur in the united states each year? How many exposures involve children < 6 years?
2 How often can poisoning be managed at home with the assistance of a regional poison control center?
3 When was the first poison control center established and why?
Press E, Mellins RB: A poisoning control program. Am J Public Health 44:1515–1525, 1954.
8 Who is more likely to ingest a poison: A 15-year-old boy or a 15-year-old girl?
The girl is more likely to ingest a poison and usually does so intentionally.
11 What are the most dangerous substances, according to reports to the American Association of Poison Control Centers?
| Substance | Hazard Factor |
|---|---|
| Rattlesnake envenomation | 245 |
| Methadone | 75 |
| Chloral hydrate | 66 |
| Cyclic antidepressant | 57 |
| Strychnine | 50 |
| Selenious acid (gun bluing) | 48 |
| Acid drain cleaner (toilet bowel cleaner) | 47 |
| Carbamazepine | 33 |
| Chloroquine (antimalarial) | 32 |
| Carbon monoxide | 31 |
| Paraquat | 24 |
12 Which medicinals are potentially life-threatening or fatal to a 10-kg toddler following ingestion of a single dose?
INITIAL MANAGEMENT
13 Which three antidotal drugs should be immediately considered in the resuscitation of the comatose child?
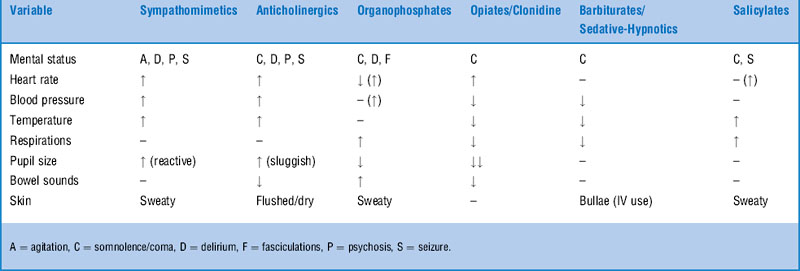
14 What is a “toxidrome”?
Osterhoudt KC: No sympathy for a boy with obtundation. Pediatr Emerg Care 20:403–406, 2004.
18 What other toxicants are associated with characteristic odors?
| Odor | Agent |
|---|---|
| Acetone | Acetone, isopropyl alcohol, phenol |
| Almonds | Cyanide |
| Garlic | Arsenic, thallium, organophosphates, selenious acid |
| Pears | Chloral hydrate, paraldehyde |
| Rotten eggs | Hydrogen sulfide |
| Wintergreen | Methyl salicylate |
19 List the most commonly considered methods of gastrointestinal decontamination of the poisoned patient
29 How often do poisoned patients require special therapy, such as antidote administration, elimination enhancement, or extracorporeal elimination?
30 What are the characteristics of the ideal toxic agent that would be amenable to multiple-dose activated charcoal?
PHARMACEUTICALS
40 What are the three stages of acetaminophen overdose poisoning?
 Stage I (1/2–24 hours after ingestion): Often asymptomatic; occasionally nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, and pallor are seen.
Stage I (1/2–24 hours after ingestion): Often asymptomatic; occasionally nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, and pallor are seen.
 Stage II (24–48 hours after ingestion): Nausea, vomiting, right-upper-quadrant abdominal pain, elevation of hepatic aminotransferase levels.
Stage II (24–48 hours after ingestion): Nausea, vomiting, right-upper-quadrant abdominal pain, elevation of hepatic aminotransferase levels.
 Stage III (72–96 hours after ingestion): Fulminant hepatic failure with jaundice, thrombocytopenia, prolonged prothrombin time, and hepatic encephalopathy. Renal failure and cardiomyopathy may occur. If the patient survives, complete resolution of liver abnormalities is possible.
Stage III (72–96 hours after ingestion): Fulminant hepatic failure with jaundice, thrombocytopenia, prolonged prothrombin time, and hepatic encephalopathy. Renal failure and cardiomyopathy may occur. If the patient survives, complete resolution of liver abnormalities is possible.
51 How much iron is toxic?
Expected toxicity can be estimated by the amount of elemental iron ingested (Table 39-2).
| Dose Ingested (mg/kg Elemental Iron) | Toxicity |
|---|---|
| 20–60 | Mild gastrointestinal symptoms |
| 60–100 | Moderate toxicity |
| 100–200 | Serious toxicity |
| >200 | Possibly lethal |
52 How much elemental iron is present in commonly available preparations?
| Product | Elemental Iron |
|---|---|
| Ferrous sulfate, 325 mg | 65 mg (20% of tablet strength) |
| Ferrous gluconate, 325 mg | 40 mg (12% of tablet strength) |
| Ferrous fumarate, 325 mg | 105 mg (32% of tablet strength) |
| Feosol elixir (sulfate) | 44 mg/5 mL |
| Children’s chewable vitamins | 4–18 mg |
| Infant liquid vitamins | 10 mg/mL |
55 What laboratory studies are helpful in the management of iron poisoning?
| Serum Iron Level (μg/dL) | Toxicity |
|---|---|
| <350 | Minimal |
| 350–500 | Mild |
| >500 | Serious |
56 What special decontamination issues arise with iron poisoning?
Tenenbein M: Whole bowel irrigation in iron poisoning. J Pediatr 111:142–145, 1987.
59 What electrocardiographic findings correlate with potential toxicity from cyclic antidepressants?
60 Why is sodium bicarbonate helpful for drug-induced ventricular dysrhythmias associated with a prolonged QRS interval?
62 Name antidotes that may be useful for specific causes of drug-induced bradydysrhythmias
| Overdose | Antidote |
|---|---|
| β-blocker | Glucagon |
| Calcium-channel blocker | Calcium, insulin/glucose |
| Digoxin | Digoxin-specific Fab fragments (Digibind, Digifab) |
Kenny J: Treating overdose with calcium channel blockers. BMJ 308:992–993, 1994.
65 List problems associated with flumazenil administration after drug overdose
66 How are poison-induced seizures treated?
Wills B, Erickson T: Drug- and toxin-associated seizures. Med Clin North Am 89:1297–1321, 2005.
1 Dangerous acetaminophen poisoning may be asymptomatic initially but can be predicted with serum levels.
2 Prevention of acidemia, maintenance of intravascular volume, and urinary alkalinization are key goals in the treatment of moderate aspirin poisoning.
3 Prevention strategies are important in reducing the pediatric mortality of iron products.
4 Sodium bicarbonate therapy may be beneficial for toxic cardiac syndromes manifested by wide QRS tachycardia.
DRUGS OF ABUSE
68 What is the mnemonic for the opiate toxidrome?
FAME: Flaccid coma, Apnea, Miosis, and Extraocular paralysis.
70 What common pediatric drug toxicity closely mimics opiate intoxication but does not reliably respond to naloxone?
Wiley JF: Clonidine poisoning: Is there any effective therapy? Clin Ped Emerg Med 1:207–212, 2000.
74 Why should neuroleptics, such as haloperidol, be used cautiously in the treatment of drug-induced psychoses?
76 What is the treatment for the tachycardia, hypertension, and hyperpyrexia associated with cocaine overdose?
78 Describe the serotonin syndrome
Boyer EW, Shannon M: The serotonin syndrome. N Engl J Med 352:1112–1120, 2005.
81 What modification to advanced cardiac life support protocol might be beneficial in the treatment of tachydysrhythmia after inhalant abuse?
82 γ hydroxybutyrate and γ butyrolactone are drugs that have received considerable attention recently. What are they?
1 Naloxone dosing in patients overdosed on heroin requires careful consideration of habituation to avoid precipitation of withdrawal.
2 Overdoses with long-acting or synthetic opioids often require increased doses of naloxone to achieve adequate reversal of respiratory depression.
3 Benzodiazepines are the most appropriate initial treatment for agitation caused by sympathomimetic and hallucinogenic drugs of abuse.
4 Malignant hyperthermia from overdoses of cocaine, amphetamines, or serotonergic drugs requires rapid treatment, including cooling measures, benzodiazepine administration, and mechanical ventilation with paralysis and bicarbonate infusion in the setting of rhabdomyolysis.
5 γ hydroxybutyrate and γ butyrolactone (GBL) are popular club drugs that are easily manufactured at home and are widely promoted on the Internet.
ENVIRONMENTAL POISONS AND VENOMS
83 What is the differential diagnosis for an increased anion gap metabolic acidosis?
One can make mountains out of the mnemonic MUDPILES:
 D = Diabetic, alcoholic, or starvation ketoacidosis
D = Diabetic, alcoholic, or starvation ketoacidosis
 P = Paraldehyde (and other aldehydes)
P = Paraldehyde (and other aldehydes)
Louie JP, Peterson J: Pick your poison: Not a basic case. Pediatr Emerg Care 22:461–463, 2006.
87 List the potential causes of a large osmolar gap
 Acetone Acetone |
 Mannitol Mannitol |
 Ethanol Ethanol |
 Methanol Methanol |
 Glycols Glycols |
 Renal failure Renal failure |
 Isopropanol Isopropanol |
 Severe ketoacidemia Severe ketoacidemia |
 Magnesium Magnesium |
 Severe lactic acidemia Severe lactic acidemia |
89 How can the osmolar gap be used to estimate the levels of toxic alcohols?
This calculation is based upon the molecular weight of the alcohols:
95 What agents can be used to inhibit alcohol dehydrogenase in the setting of methanol or ethylene glycol poisoning?
96 Do any vitamins or nutritional supplements have a role in the treatment of methanol or ethylene glycol poisoning?
101 Which patients should be examined endoscopically after caustic ingestion?
 Ingestion involving a concentrated, strong acid or base
Ingestion involving a concentrated, strong acid or base
 Patients with vomiting, or two or more signs or symptoms of injury
Patients with vomiting, or two or more signs or symptoms of injury
Note: The absence of oral burns is not a sensitive sign for excluding esophageal injury.
102 Give the advantages and disadvantages for using corticosteroids to palliate caustic esophageal burns
109 Which features in the evaluation of an encephalopathic child suggest acute lead encephalopathy?
110 List the clinical manifestations of organophosphate or carbamate insecticide poisoning
112 What is the appropriate response to an exploratory anticoagulant rodenticide ingestion by a toddler?
115 Which member of the family is most likely to suffer the most from equivalent carbon monoxide (CO) exposure?
116 Describe the pathophysiology of toxicity from CO exposure
1 CO displaces oxygen from the hemoglobin molecule, leading to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity. CO has an affinity for hemoglobin approximately 250 times that for O2.
2 Allosteric inhibition of oxygen release to tissues occurs (displacement of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the left).
3 Cellular oxidative metabolism is reduced through inhibition of cytochrome oxidase enzyme systems.
4 Oxidative injury to the brain endothelium begins a cascade of leukocyte activation, lipid peroxidation, and impaired cerebral metabolism.
117 How long does it take the body to eliminate carboxyhemoglobin?
Carboxyhemoglobin elimination depends on inspired oxygen concentration.
119 Describe the characteristic brain abnormalities after significant CO poisoning on magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
120 Cyanosis, unreponsive to supplemental oxygen therapy and in the face of a normal partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood, is characteristic of what physiologic abnormality?
124 What are some of the more common toxicants associated with the production of excessive methemoglobin?
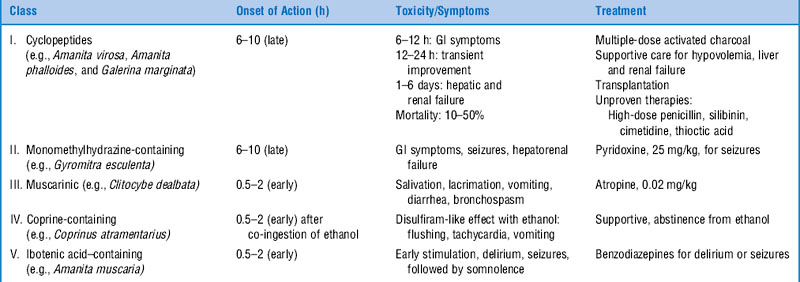
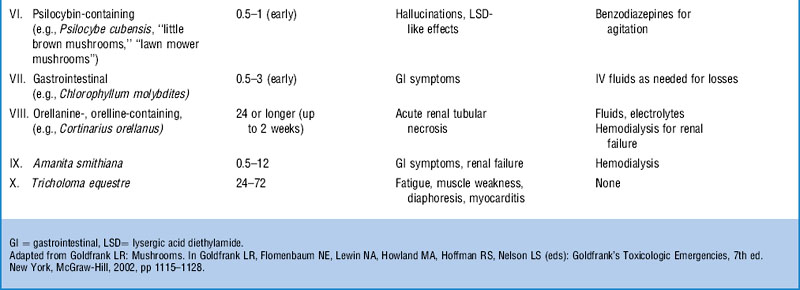
126 What are the clinical classifications syndromes for toxic mushrooms syndromes, typical clinical findings, and poisoning treatment syndromes?
127 What are the most common toxic plant poisonings?
Of the 20 most common plant exposures, the most commonly encountered toxic plants are:
 The Arum family (Dieffenbachia, Philodendron), which may cause severe pharyngeal edema and possible airway obstruction through the elaboration of calcium oxalate crystals and proteolytic enzymes and direct mucosal irritation
The Arum family (Dieffenbachia, Philodendron), which may cause severe pharyngeal edema and possible airway obstruction through the elaboration of calcium oxalate crystals and proteolytic enzymes and direct mucosal irritation
 The Taxus species (yew), which cause gastrointestinal irritation, cardiac dysrhythmias, coma, and seizures if large amounts of leaves or seeds are ingested
The Taxus species (yew), which cause gastrointestinal irritation, cardiac dysrhythmias, coma, and seizures if large amounts of leaves or seeds are ingested
 Solanum family (Jerusalem cherry, black nightshade, climbing nightshade), which cause gastrointestinal effects, lethargy, or delirium
Solanum family (Jerusalem cherry, black nightshade, climbing nightshade), which cause gastrointestinal effects, lethargy, or delirium
 Rhododendron and Azalea spp., which cause gastrointestinal effects, bradycardia, lethargy, and paresthesias through elaboration of grayanotoxins
Rhododendron and Azalea spp., which cause gastrointestinal effects, bradycardia, lethargy, and paresthesias through elaboration of grayanotoxins
128 What other plants have potential for severe toxicity? Describe the treatment
| Symptom Class | Plants | Potential Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| GI irritants | Pokeweed Horse chestnut English ivy |
Supportive care |
| Toxalbumin | Castor bean Rosary pea Autumn crocus (colchicine-containing) |
Multisystem organ failure Supportive care |
| Digitalis-like toxin | Foxglove Oleander Lily of the valley |
Digoxin Fab fragments |
| Other cardiac effects | Mistletoe Monkshood False hellebore Mountain laurel |
Supportive care, standard treatment for dysrhythmias |
| Nicotinic effects | Wild tobacco Tobacco Poison hemlock |
Atropine, supportive care for weakness, paralysis |
| Anticholinergic effects | Jimsonweed Angel’s trumpet Matrimony vine Henbane Belladonna |
Physostigmine for seizures, malignant hyperthermia Benzodiazepines for delirium |
| Seizures | Water hemlock | Anticonvulsants |
| Hallucinations | Morning glory Nutmeg Peyote |
Sedation |
| Cyanogenic | Chokecherry Cherry (pit) Plum (pit) Peach (pit) Apple (seeds) Pear (seeds) Cassava Elderberry (leaves and shoots) Black locust |
Cyanide antidote (rarely needed) |
133 What are the indications for administration of antivenin to a patient following Crotaline envenomation?
134 Name the two antivenin products available for treatment of North American pit viper envenomation
136 Compare the toxic manifestations of bites from black widow spiders (Latrodectus) to those of brown recluse spiders (Loxosceles).
KEY POINTS: ENVIRONMENTAL POISONS AND VENOMS
1 Fomepizole is an antidote that inhibits alcohol dehydrogenase to provide protection in methanol and ethylene glycol poisoning.
2 After carbon monoxide poisoning, hyperbaric oxygen is most beneficial in its ability to halt an inflammatory cascade in the brain.
3 The low surface tension and viscosity of hydrocarbons create great risk for pulmonary injury after ingestion.
4 Snake antivenin purified to Fab fragments poses less risk of anaphylaxis and serum sickness than whole immunoglobulin products.
1 Flomenbaum NE, Goldfrank LR, Hoffman RS, et al, editors. Goldfrank’s Toxicologic Emergencies, 8th ed, New York: McGraw-Hill, 2006.
2 Osterhoudt KC, Burns Ewald M, Shannon M, Henretig FM. Toxicologic emergencies. In: Fleisher G, Ludwig S, Henretig F, editors. Textbook of Pediatric Emergency Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006:951-1031.
3 Osterhoudt KC, Perrone J, De Roos F, et al, editors. Toxicology Pearls. Philadelphia: Elsevier Mosby, 2004.
4 Shannon MW. Ingestion of toxic substances by children. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:186-191.